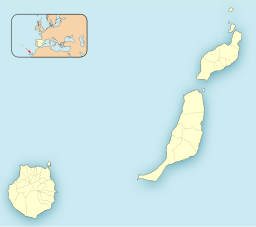
The Canary Islands, also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish region, autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are 100 kilometres west of Morocco and the Western Sahara. They are the southernmost of the autonomous communities of Spain. The islands have a population of 2.2 million people and are the most populous special territory of the European Union.

Fuerteventura is one of the Canary Islands, in the Atlantic Ocean, geographically part of Macaronesia, and politically part of Spain. It is located 97 km (60 mi) away from the coast of North Africa. The island was declared a biosphere reserve by UNESCO in 2009.

Cook Strait is a strait that separates North Island from the South Island of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is 22 kilometres (14 mi) wide at its narrowest point, and is considered one of the most dangerous and unpredictable waters in the world. Regular ferry services run across the strait between Picton in the Marlborough Sounds and Wellington.

The Northumberland Strait is a strait in the southern part of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in eastern Canada. The strait is formed by Prince Edward Island and the gulf's eastern, southern, and western shores.

Lanzarote is a Spanish island, the easternmost of the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, 125 kilometres off the north coast of Africa and 1,000 kilometres from the Iberian Peninsula. Covering 845.94 square kilometres, Lanzarote is the fourth-largest of the islands in the archipelago. With 152,289 inhabitants at the start of 2019, it is the third most populous Canary Island, after Tenerife and Gran Canaria. Located in the centre-west of the island is Timanfaya National Park, one of its main attractions. The island was declared a biosphere reserve by UNESCO in 1993. The island's capital is Arrecife, which lies on the eastern coastline. It is the smaller main island of the Province of Las Palmas.

Arrecife is the capital city and a municipality of Lanzarote in the Canary Islands. It was made the island's capital in 1852. The city owes its name to the rock reef which covers its local beach. It also gives its name to the nearby Arrecife Airport. The population of the municipality was 64,645 in 2020. Its area is 22.72 square kilometres (8.77 sq mi).

Graciosa Island or commonly La Graciosa is a volcanic island in the Canary Islands of Spain, located two kilometres north of Lanzarote across the Strait of El Río. As the rest of the Canary Islands, it was formed by the Canary hotspot. The island is part of the Chinijo Archipelago and the Chinijo Archipelago Natural Park. It is administered by the municipality of Teguise in the neighboring island of Lanzarote. In 2018 La Graciosa was officially declared the eighth Canary Island by the Spanish Senate, with few real effects. Before then, the island had the status of an islet. It's administratively dependent on the island of Lanzarote.
Lobos is a small island of the Canary Islands (Spain) located just 2 kilometres north of the island of Fuerteventura. It belongs to the municipality of La Oliva on the island of Fuerteventura. It has an area of 4.68 square kilometres (1.8 sq mi). It has been a nature reserve since 1982.
Fred. Olsen Express is an inter-island ferry service based in the Canary Islands, Spain. It operates a fleet of six modern fast ferries on five routes. Its fleet includes a trimaran fast ferry, the Benchijigua Express, which was the first such vehicle in the world when it entered service in 2005. The company is owned by the Olsen family-controlled Bonheur and Ganger Rolf, which among other things also owns the shipping companies Fred. Olsen Cruise Lines and First Olsen Tankers.
Corralejo is a town and resort located on the northern tip of Fuerteventura, one of the Canary Islands, facing the smaller islet of Lobos. It is in the municipality of La Oliva.

LZ-2 is one of the main roads on the island of Lanzarote in the Canary Islands. It leads south from the island's capital, Arrecife, ending at the island's southernmost town of Playa Blanca. From here, ferries are available to cross the strait of La Bocayna, effectively connecting the LZ-2 to the FV-1 on the island of Fuerteventura. Lanzarote Airport is also accessed by the LZ-2.

Playa Blanca is the southernmost town of the Spanish island of Lanzarote. It is the newest resort on the island, and is part of the municipality of Yaiza.

Naviera Armas is a Spanish company, founded in the 1940s, which operates a number of ferry services in Spain. The company mainly operates in the Canary Islands, with additional routes connecting the Canary Islands and the north African coast to the Spanish mainland. As of August 2019, the company operates a fleet of 11 ferries and 5 fast ferries.

The Pechiguera or Punta Pechiguera Lighthouse is an active lighthouse on the Canary island of Lanzarote. It is the second lighthouse to be built at Punta Pechiguera, which is at the south-western end of the island.

The Punta Martiño Lighthouse is an active lighthouse on the Canary island of Lobos, near Fuerteventura in the municipality of La Oliva.

The Port of Funchal is the port and harbour of Funchal and is frequently used as a stop-over by transatlantic ships, en route from Europe to the Caribbean, as it is the northernmost Atlantic island that lies in the path of the Westerlies.

Bocayna Express is a catamaran fast ferry operated by the Spanish-Norwegian shipping company Fred. Olsen Express between the Canary Islands of Fuerteventura and Lanzarote in the Atlantic Ocean. It was delivered to Fred. Olsen in September 2003 and has been operating the route between the towns of Corralejo (Fuerteventura) and Playa Blanca (Lanzarote) since then. The ship is named after the Bocayna strait which separates the two islands it serves.

El Río is the name given to the sea strait that separates La Graciosa from Lanzarote in the Canary Islands. Río, in Spanish, means 'river'. At its narrowest point, the strait is just over 1.1 kilometres wide.

Volcán de Tindaya is a roll-on/roll-off passenger ferry operated by the Spanish shipping company Naviera Armas between the Canary Islands of Fuerteventura and Lanzarote in the Atlantic Ocean. It was built and delivered to Armas in 2003 and has been operating the route between the towns of Corralejo (Fuerteventura) and Playa Blanca (Lanzarote) since then. The ship is named after the Tindaya mountain on Fuerteventura.

The geology of the Canary Islands is dominated by volcanoes and volcanic rock. The Canary Islands are a group of volcanic islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, near the coast of Northwest Africa. The main islands are Lanzarote, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Tenerife, La Gomera, La Palma, and El Hierro. There are also some minor islands and islets. The Canary Islands are on the African tectonic plate but they are far from the plate's edges; this controls the type of volcanic activity, known as intraplate volcanism, that has formed the islands.