The Senegal River is a 1086-kilometre-long (675 mi) river in West Africa; much of its length marks part of the border between Senegal and Mauritania. It has a drainage basin of 270000 km2, a mean flow of 680 m3/s (24,000 cu ft/s), and an annual discharge of 21.5 km3 (5.2 cu mi). Important tributaries are the Falémé River, Karakoro River, and the Gorgol River. The river divides into two branches once it passes Kaédi The left branch, called the Doué, runs parallel to the main river to the north. After 200 km (120 mi) the two branches rejoin a few kilometers downstream of Podor.

Biffeche or Bifeche is an area of Senegal centred on the town of Savoigne, around 30 kilometres north-east of the major coastal city of Saint-Louis.
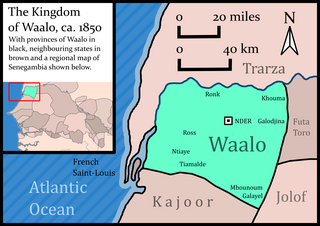
Waalo was a kingdom on the lower Senegal River in West Africa, in what is now Senegal and Mauritania. It included parts of the valley proper and areas north and south, extending to the Atlantic Ocean. To the north were Moorish emirates; to the south was the kingdom of Cayor; to the east was Jolof.

The Eurasian spoonbill, or common spoonbill, is a wading bird of the ibis and spoonbill family Threskiornithidae, native to Europe, Africa and Asia. The species is partially migratory with the more northerly breeding populations mostly migrating south for the winter.

The African spoonbill is a long-legged wading bird of the ibis and spoonbill family Threskiornithidae. The species is widespread across Africa and Madagascar, including Botswana, Kenya, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, and Zimbabwe.

Saint-Louis or Saint Louis, is the capital of Senegal's Saint-Louis Region. Located in the northwest of Senegal, near the mouth of the Senegal River, and 320 kilometres (200 mi) north of Senegal's capital city Dakar. It had a population of 254,171 in 2023. Saint-Louis was the capital of the French colony of Senegal from 1673 until 1902 and French West Africa from 1895 until 1902, when the capital was moved to Dakar. From 1920 to 1957, it also served as the capital of the neighboring colony of Mauritania.

The roseate spoonbill is a gregarious wading bird of the ibis and spoonbill family, Threskiornithidae. It is a resident breeder in both South and North America. The roseate spoonbill's pink color is diet-derived, consisting of the carotenoid pigment canthaxanthin, like the American flamingo.
The Diawling National Park lies in south west Mauritania around the Senegal River delta. During the rainy season, much of the park consists of large lakes. It is known for having over 220 species of identified birds, including pelicans, black storks, and flamingos, and also for its fish.

The Banc d'Arguin National Park of Bay of Arguin lies in Western Africa on the west coast of Mauritania between Nouakchott and Nouadhibou and is the former mouth of the Tamanrasset River. The World Heritage Site is a major site for migratory birds and breeding birds, including flamingos, pelicans and terns. Much of the breeding is on sand banks including the islands of Tidra, Niroumi, Nair, Kijji and Arguim. The surrounding waters are some of the richest fishing waters in western Africa and serve as nesting grounds for the entire western region.

The black-faced spoonbill is a species of wading bird in the ibis and spoonbill family Threskiornithidae, found in eastern Asia. This species has the most restricted distribution of the six spoonbill species, and it is the only one regarded as endangered. Spoonbills are large water birds with dorso-ventrally flattened, spatulate bills. These birds use a tactile method of feeding, wading in the water and sweeping their beaks from side-to-side to detect prey. Confined to the coastal areas of eastern Asia, it seems that it was once common throughout its area of distribution. It currently breeds only on a few small rocky islands off the west coast of North Korea, with four wintering sites at Macau, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Vietnam, as well as other places where they have been observed in migration. Wintering also occurs in Jeju, South Korea, Kyushu and Okinawa, Japan, and the Red River delta in Vietnam. More recently, sightings of black-faced spoonbill birds were noted in Thailand, the Philippines, and additional sites in China.
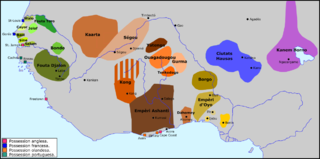
Futa Toro, often simply the Futa, is a semidesert region around the middle run of the Senegal River. This region, along the border of Senegal and Mauritania, is historically significant as the center of several Fulani states, and a source of jihad armies and migrants to the Fouta Djallon.

The royal spoonbill also known as the black-billed spoonbill, occurs in intertidal flats and shallows of fresh and saltwater wetlands in Australia, New Zealand, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands. It has also been recorded as a vagrant in New Caledonia. The royal spoonbill lives in wetlands and feeds on crustaceans, fish and small insects by sweeping its bill from side to side. It always flies with its head extended. Widespread throughout its large range, the royal spoonbill is evaluated as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.

The yellow-billed spoonbill is a gregarious wading bird of the ibis and spoonbill family, Threskiornithidae. It is native to Australia, and is a vagrant to New Zealand, Lord Howe Island and Norfolk Island.

The Godavari–Krishna mangroves are a mangrove ecoregion of India's eastern coast.
Brak was the title of the kings of the kingdoms of Waalo and Biffeche on the Senegal River in Senegal and Mauritania in West Africa until the 19th century.

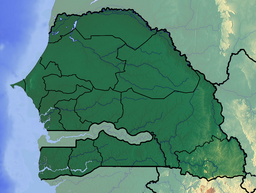
The wildlife of Senegal consists of the flora and fauna of this nation in West Africa. Senegal has a long Atlantic coastline and a range of habitat types, with a corresponding diversity of plants and animals. Senegal has 188 species of mammals and 674 species of bird.
The French conquest of Senegal started in 1659 with the establishment of Saint-Louis, Senegal, followed by the French capture of the island of Gorée from the Dutch in 1677, but would only become a full-scale campaign in the 19th century.
The Diep River Fynbos Corridor is a nature reserve located in the Blaauwberg region of Cape Town, South Africa. It forms part of the larger Table Bay Nature Reserve, which was established in June 2012.
The Rivière aux eaux mortes flows entirely in forest areas in two territories Quebec, in Canada:

Chibougamau Lake is a freshwater body of the municipality of Chibougamau, in the administrative region of Nord-du-Québec, in province of Quebec, in Canada.