
Asteraceae is a large family of flowering plants that consists of over 32,000 known species in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. The number of species in Asteraceae is rivaled only by the Orchidaceae, and which is the larger family is unclear as the quantity of extant species in each family is unknown. The Asteraceae were first described in the year 1740 and given the original name Compositae. The family is commonly known as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family.

The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol, the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless.

Chronobiology is a field of biology that examines timing processes, including periodic (cyclic) phenomena in living organisms, such as their adaptation to solar- and lunar-related rhythms. These cycles are known as biological rhythms. Chronobiology comes from the ancient Greek χρόνος, and biology, which pertains to the study, or science, of life. The related terms chronomics and chronome have been used in some cases to describe either the molecular mechanisms involved in chronobiological phenomena or the more quantitative aspects of chronobiology, particularly where comparison of cycles between organisms is required.

The gymnosperms are a group of woody, perennial seed-producing plants, typically lacking the protective outer covering which surrounds the seeds in flowering plants, that include conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae The term gymnosperm comes from the composite word in Greek: γυμνόσπερμος, and literally means 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds. The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or on their own as in yew, Torreya, and Ginkgo.

Crassulacean acid metabolism, also known as CAM photosynthesis, is a carbon fixation pathway that evolved in some plants as an adaptation to arid conditions that allows a plant to photosynthesize during the day, but only exchange gases at night. In a plant using full CAM, the stomata in the leaves remain shut during the day to reduce evapotranspiration, but they open at night to collect carbon dioxide and allow it to diffuse into the mesophyll cells. The CO2 is stored as four-carbon malic acid in vacuoles at night, and then in the daytime, the malate is transported to chloroplasts where it is converted back to CO2, which is then used during photosynthesis. The pre-collected CO2 is concentrated around the enzyme RuBisCO, increasing photosynthetic efficiency. This mechanism of acid metabolism was first discovered in plants of the family Crassulaceae.

Alexander Sergeyevich Yakovlev was a Soviet aeronautical engineer. He designed the Yakovlev military aircraft and founded the Yakovlev Design Bureau. Yakovlev joined the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1938.

Alexander Georg von Bunge was a Russian botanist. He is best remembered for scientific expeditions into Asia and especially Siberia.

Gentianaceae is a family of flowering plants of 105 genera and about 1600 species.
Rhizoids are protuberances that extend from the lower epidermal cells of bryophytes and algae. They are similar in structure and function to the root hairs of vascular land plants. Similar structures are formed by some fungi. Rhizoids may be unicellular or multicellular.

Nepenthes danseri is a species of tropical pitcher plant. It is known only from the northern coast of Waigeo Island; plants from Halmahera, the largest of the Maluku Islands, are now recognised as belonging to a separate species, N. halmahera.
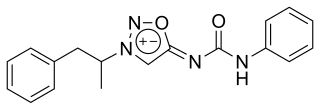
Mesocarb, sold under the brand name Sidnocarb or Sydnocarb and known by the developmental code name MLR-1017, is a psychostimulant medication which has been used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders and for a number of other indications in the Soviet Union and Russia. It is currently under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and sleep disorders. It is taken by mouth.

Lagochilus is a genus of the mint family that contains Turkistan mint . It is native to central, south-central, and eastern Asia.

The vault or vault cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein is a eukaryotic organelle whose function is not yet fully understood. Discovered and isolated by Nancy Kedersha and Leonard Rome in 1986, vaults are cytoplasmic structures which, when negative-stained and viewed under an electron microscope, resemble the arches of a cathedral's vaulted ceiling, with 39-fold symmetry. They are present in many types of eukaryotic cells and appear to be highly conserved among eukaryotes.
Imperatoxin I (IpTx) is a peptide toxin derived from the venom of the African scorpion Pandinus imperator.

Tutin is a poisonous plant derivative found in New Zealand tutu plants. It acts as a potent antagonist of the glycine receptor, and has powerful convulsant effects. It is used in scientific research into the glycine receptor. It is sometimes associated with outbreaks of toxic honey poisoning when bees feed on honeydew exudate from the sap-sucking passion vine hopper insect, when the vine hoppers have been feeding on the sap of tutu bushes. Toxic honey is a rare event and is more likely to occur when comb honey is eaten directly from a hive that has been harvesting honeydew from passionvine hoppers feeding on tutu plants.

Bromantane, sold under the brand name Ladasten, is an atypical central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and anxiolytic drug of the adamantane family that is related to amantadine and memantine. Medically, it is approved in Russia for the treatment of neurasthenia. Although the effects of bromantane have been determined to be dependent on the dopaminergic and possibly serotonergic neurotransmitter systems, its exact mechanism of action is unknown, and is distinct in its properties relative to typical stimulants such as amphetamine. Bromantane has sometimes been described as an actoprotector.

Nooglutyl is a nootropic agent that was studied at the Research Institute of Pharmacology, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences as a potential treatment for amnesia.

Ctenis is a genus of fossil foliage attributable to the Cycadales, being one of the most common genera of cycad fossil leaves in the Mesozoic.
Signal Transition Graphs (STGs) are typically used in electronic engineering and computer engineering to describe dynamic behaviour of asynchronous circuits, for the purposes of their analysis or synthesis.
















