The Amur River or Heilong River is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China. The Amur proper is 2,824 km (1,755 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 1,855,000 km2 (716,000 sq mi). If including its main stem tributary, the Argun, the Amur is 4,444 km (2,761 mi) long, making it the world's tenth longest river.

Vembanad is the longest lake in India, as well as the largest in the state of Kerala. The lake has an area of 230 square kilometers and a maximum length of 96.5 km.

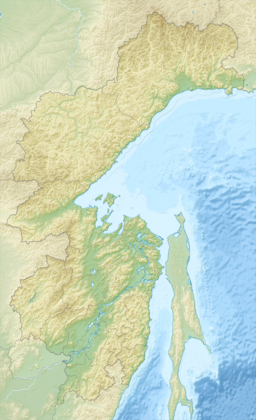
Lake Khanka or Lake Xingkai, is a freshwater lake on the border between Primorsky Krai, Russia and Heilongjiang province, Northeast China.

Hulun Lake or Dalai Lake is a large lake in the Inner Mongolia region of northern China.

The Madu Ganga is a minor watercourse which originates near Uragasmanhandiya in the Galle District of Sri Lanka, before widening into the Madu Ganga Lake at Balapitiya. The river then flows for a further a 4.4 km (2.7 mi) before draining into the Indian Ocean. It is located 88 km (55 mi) south of Colombo and 35 km (22 mi) north of Galle.

Achit Lake is the largest freshwater lake in Uvs Province, Mongolia, in the west of the country. At an elevation of 1,435 m above sea level it covers an area of 290 km2. It is 28 km long, 16 km wide, and 10 m deep. The coast is covered with steppes, mostly hilly but swampy on the northwest and northeast. Several rivers flow into the lake.

Lake Udyl is a large freshwater lake in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It has an area of 330 square kilometres (130 sq mi). It is 50 miles (80 km) long and 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) wide. Maximum depth is about 5 metres (16 ft). It lies near the left bank of the Amur River.

Sasthamcotta Lake or Sasthamkotta Lake, also categorized as a wetland, is the largest fresh water lake in Kerala, a state of India on the south of the West Coast. The lake is named after the ancient Sastha temple located on its bank. It meets the drinking water needs of half million people of the Quilon district and also provides fishing resources. The purity of the lake water for drinking use is attributed to the presence of large population of larva called cavaborus that consumes bacteria in the lake water. The lake is a designated wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention since November 2002.

Song-Köl is an alpine lake in northern Naryn Region, Kyrgyzstan. It lies at an altitude of 3016 m, and has an area of about 270 km2 and volume of 2.64 km3. The lake's maximum length is 29 km, breadth about 18 km at its widest, and the deepest point is 13.2 m. It is the second largest lake in Kyrgyzstan after Issyk-Kul, and the largest fresh water lake in the country.

The Malagarasi River is a river in western Tanzania, flowing through Kigoma Region, although one of its tributaries comes from southeastern Burundi. The river also forms the western border of Tabora Region, the southern border of Kagera Region and the southwestern border of Geita Region. It is the second-longest river in Tanzania behind the Rufiji—Great Ruaha, and has the largest watershed of any river flowing into Lake Tanganyika. The Malagarasi-Muyovozi Wetlands are a designated a Ramsar site. Local tribes have nicknamed the Malagarasi as "the river of bad spirits".

Bao BolongWetland Reserve is a protected area in The Gambia. Established in 1996, it covers 296.5 square kilometres.

The Coongie Lakes is a freshwater wetland system located in the Far North region of South Australia. The 21,790-square-kilometre (8,410 sq mi) lakes system is located approximately 1,046 kilometres north of the Adelaide city centre. The wetlands includes lakes, channels, billabongs, shallow floodplains, deltas, and interdune swamps. It lies on the floodplain of Cooper Creek, an ephemeral river flowing through a desert landscape in the Lake Eyre Basin which rarely, after occasional large floods, empties into Lake Eyre. The wetland system has been recognised both as being of international importance by designation under the Ramsar Convention with a listing on 15 June 1987 and being nationally important within Australia with a listing in A Directory of Important Wetlands in Australia (DIWA). Its extent includes the regional town of Innamincka, the Malkumba-Coongie Lakes National Park, the Innamincka Regional Reserve, the Strzelecki Regional Reserve and the Coongie Lakes Important Bird Area.
The New South Wales Central Murray Forests lie on the floodplain of the Murray River in the Riverina region of south-central New South Wales, Australia. On 20 May 2003 the forests were recognised as a wetland site of international importance (RS1291) by designation under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.

Meshchyorsky National Park covers extensive wetlands and pine/birch woodlands in the Meshchera Lowlands on the East European Plain in the northern section of Ryazan Oblast, Russia, about 120 km east of Moscow. The wetland habitat provides for extremely rich biodiversity among the plants and animals. "Meshchersky" (Мещёрский) National Park is not to be confused with "Meshchyora" (Мещёра) National Park, which is just to the north, over the border in Vladimir Oblast. The park protects a section of the Pra River, Lake Beloye, and associated wetlands and forests. About 54% of the park territory is used and managed for agricultural purposes by local communities.

Khingan Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik', located in the extreme south-east of the Amur River region of the Russian Far East. The reserve covers two types of habitat: the flat Arkharinskaya lowlands with abundant wetlands, and forested spurs of the Lesser Khingan mountains. In particular, Khingan Reserve was created to protect steppe and forest-steppe landscapes, and nesting sites of the endangered Red-crowned crane and the vulnerable White-naped crane. The reserve is situated in the Arkharinsky District of Amur Oblast.

Bolon Nature Reserve is the oldest Russian 'zapovednik' in the Russian Far East. It is located on the Middle Amur River lowlands adjacent to the south-west of Lake Bolon. The reserve covers the wetlands of international importance. Large numbers of migratory waterfowl use the area for nesting and stopovers on long flights. The reserve is situated halfway between the city of Khabarovsk and Komsomolsk-on-Amur, in the Amursky District of Khabarovsk Krai. The reserve was created in 1997, and covers an area of 100,000 ha (390 sq mi).

The Ussuri broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion covers a mountainous areas above the lower Amur River and Ussuri River in Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsk Krai in the Russian Far East. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, with a Humid Continental climate. It covers 187,357 km2 (72,339 sq mi).

The Suiphun–Khanka meadows and forest meadows ecoregion is a relatively small ecoregion centered on Lake Khanka, a fresh water lake in the Russian Far East, with a portion in China. The terrain is unforested, flat, and marshy. The area is an important stopover spot for migratory birds, including many vulnerable species. It has an area of 33,929 square kilometres (13,100 sq mi), and is in the Flooded grasslands and savannas biome.

The Amur meadow steppe ecoregion is spread over two sections of the middle Amur River valley in the Russian Far East. The terrain is one of flat floodplains on alluvial soil. Due to high water table and frequent flooding, the area has remained relatively forest-free, and is today characterized by extensive wetlands of bogs and grasslands. The area remained ice-free during the Pleistocene glaciation, creating a refuge for many plant and animal species. It has an area of 123,283 square kilometres (47,600 sq mi).