
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD) or the Chinese Nationalist Party, is a major political party in the Republic of China throughout its historical periods in both the Chinese mainland as well as Taiwan. It was the dominant ruling party of the Republic of China on the mainland from 1928 to 1949. The party was then forced to exile from the mainland due to its defeat in the Chinese Civil War, but retained its authoritarian rule over Taiwan under the Dang Guo system until democratic reforms were enacted in the 1990s. In Taiwanese politics, the KMT is the dominant party in the Pan-Blue Coalition and primarily competes with the rival Democratic Progressive Party (DPP). It is currently the largest opposition party in the Legislative Yuan. The current chairman is Eric Chu.

Kaohsiung City is a special municipality in southern Taiwan. It ranges from the coastal urban centre to the rural Yushan Range with an area of 2,952 km2 (1,140 sq mi). Kaohsiung City has a population of approximately 2.77 million people and is Taiwan's third most populous city and largest city in southern Taiwan.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of 36,193 square kilometres (13,974 sq mi). The main island of Taiwan, formerly known as Formosa, has an area of 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi), with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Kaohsiung, Taichung, Tainan, and Taoyuan. With 23.45 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country located in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, formerly known in Western literature as Formosa, makes up 99% of the land area of the country. The main island measures 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi) and lies some 180 kilometres (112 mi) across the Taiwan Strait from the southeastern coast of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The East China Sea lies to the north of the island, the Philippine Sea to its east, the Luzon Strait directly to its south and the South China Sea to its southwest. The ROC also controls a number of smaller islands, including the Penghu archipelago in the Taiwan Strait, the Kinmen and Matsu Islands near the PRC's coast, and some of the South China Sea Islands.

The economy of Taiwan is a highly developed free-market economy. It is the 8th largest in Asia and 18th-largest in the world by purchasing power parity, allowing Taiwan to be included in the advanced economies group by the International Monetary Fund. It is gauged in the high-income economies group by the World Bank. Taiwan is the most technologically advanced computer microchip maker in the world.
The Taiwan independence movement is a political movement which advocates the formal declaration of an independent and sovereign Taiwanese state, as opposed to the status quo of "Two Chinas" or Chinese unification.

Taiwanese indigenous peoples, Formosan people, Austronesian Taiwanese, Yuanzhumin or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, who number about 569,000 or 2.38% of the island's population. This total is increased to more than 800,000 people if the indigenous peoples of the plains in Taiwan are included, pending future official recognition. Recent research suggests their ancestors have been living on Taiwan for approximately 6,500 years. A wide body of evidence suggests Taiwan's indigenous peoples maintained regular trade networks with regional cultures before the Han Chinese began settling on the island from the 17th century.

The term "mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China excluding dependent territories of the PRC and other territories within Greater China. By convention, the territories that fall outside of the Chinese mainland include:

Taipei, officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of Taiwan. Located in Northern Taiwan, Taipei City is an enclave of the municipality of New Taipei City that sits about 25 km (16 mi) southwest of the northern port city of Keelung. Most of the city rests on the Taipei Basin, an ancient lakebed. The basin is bounded by the relatively narrow valleys of the Keelung and Xindian rivers, which join to form the Tamsui River along the city's western border.
Taiwanese, also known as Taigi/Taigu, Taiwanese Hokkien, Taiwanese Minnan, Hoklo and Holo, is a variety of the Hokkien language spoken natively by about 70%+ of the population of Taiwan. It is spoken by the Taiwanese people, who descended from immigrants from southern Fujian during the Qing dynasty. The POJ romanization is a orthography for Taiwanwe.
The controversy surrounding the political status of Taiwan is a result of the Chinese Civil War and the subsequent split of China into the two present-day self-governing entities of the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China.
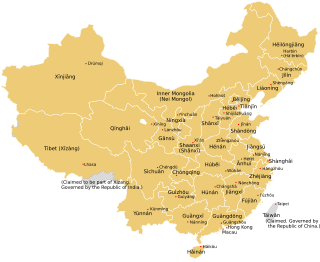
The provincial level administrative divisions are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan".

"Chinese Taipei" is the term used in various international organizations and tournaments for groups representing the Republic of China (ROC), a state commonly known as Taiwan.

The Chinese people or simply Chinese, are people or ethnic groups identified with China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation.

The Republic of China Navy, also called the ROC Navy and colloquially the Taiwan Navy, is the maritime branch of the Republic of China Armed Forces (ROCAF).

Tsai Ing-wen is a Taiwanese politician and academic serving as the President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) since 2016. A member of the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), Tsai is the first female president of Taiwan. She has served as chair of the DPP since 2020, and previously from 2008 to 2012 and 2014 to 2018.
Taiwanese people may be generally considered the people of Taiwan who share a common culture, ancestry and speak Taiwanese Mandarin, Hokkien, Hakka or indigenous Taiwanese languages as a mother tongue. Taiwanese people may also refer to the indigenous peoples of the areas under the control of the Government of the Republic of China since 1945, including Penghu, Kinmen and Matsu Islands.

The island of Taiwan, together with the Penghu Islands, became a dependency of Japan in 1895, when the Qing dynasty ceded Taiwan Prefecture in the Treaty of Shimonoseki after the Japanese victory in the First Sino-Japanese War. The short-lived Republic of Formosa resistance movement was suppressed by Japanese troops and quickly defeated in the Capitulation of Tainan, ending organized resistance to Japanese occupation and inaugurating five decades of Japanese rule over Taiwan. Its administrative capital was in Taihoku (Taipei) led by the Governor-General of Taiwan.

Hokkien is a Southern Min language originating from the Minnan region in the south-eastern part of Fujian Province in Southeastern Mainland China and spoken widely there. It is also spoken widely in Taiwan ; by the Chinese diaspora in Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, the Philippines and other parts of Southeast Asia; and by other overseas Chinese beyond Asia and all over the world. The Hokkien 'dialects' are not all mutually intelligible, but they are held together by ethnolinguistic identity. Taiwanese Hokkien is, however, mutually intelligible with the 2 to 3 million speakers of the Amoy (Xiamen) and Singaporean dialects, save for a few loanwords.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Taiwan is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. As of 30 April 2022, 14,758,774 tests had been conducted in Taiwan, of which 115,883 are confirmed cases, including 865 deaths.



















