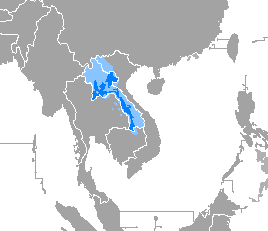
Lao, sometimes referred to as Laotian, is the official language of Laos and a significant language in the Isan region of northeastern Thailand, where it is usually referred to as the Isan language. Spoken by over 3 million people in Laos and 3.2 million in all countries, it serves as a vital link in the cultural and social fabric of these areas. It is written in the Lao script, an abugida that evolved from ancient Tai scripts.

The Lao people are a Tai ethnic group native to Southeast Asia. They primarily speak the Lao language, which belongs to the Kra–Dai language family. Lao people constitute the majority ethnic group of Laos, comprising 53.2% of the country's total population. They are also found in significant numbers in northeastern Thailand, particularly in the Isan region, as well as in smaller communities in Cambodia, Vietnam, and Myanmar.

The Shan people, also known as the Tai Long or Tai Yai, are a Tai ethnic group of Southeast Asia. The Shan are the biggest minority of Burma (Myanmar) and primarily live in the Shan State of this country, but also inhabit parts of Mandalay Region, Kachin State, Kayah State, Sagaing Region and Kayin State, and in adjacent regions of China, Laos, Assam and Meghalaya, Cambodia, Vietnam and Thailand. Though no reliable census has been taken in Burma since 1935, the Shan are estimated to number 4–6 million, with CIA Factbook giving an estimate of five million spread throughout Myanmar which is about 10% of the overall Burmese population.
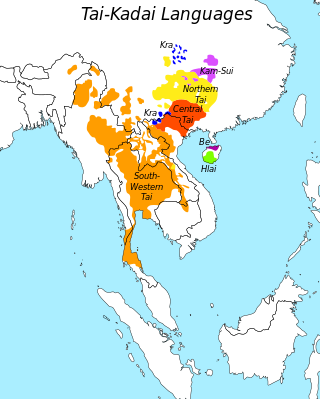
The term Kra–Dai peoples or Kra–Dai-speaking peoples refers collectively to the ethnic groups of southern China and Southeast Asia, stretching from Hainan to Northeast India and from southern Sichuan to Laos, Thailand and parts of Vietnam, who not only speak languages belonging to the Kra–Dai language family, but also share similar traditions, culture and ancestry.

The Northern Thai people or Tai Yuan, self-designation khon mu(e)ang, are a Tai ethnic group, native to nine provinces in Northern Thailand, principally in the area of the former kingdom of Lan Na. As a Tai group, they are closely related to Tai Lü and Tai Khün with regards to common culture, language and history as well as to Thailand's dominant Thai ethnic group. There are approximately 6 million Tai Yuan. Most of them live in Northern Thailand, with a small minority 29,442 living across the border in Bokeo Province of Laos. Their language is called Northern Thai, Lanna or Kham Mueang.

Xishuangbanna, sometimes shortened to Banna, is one of the eight autonomous prefectures of Yunnan Province. The autonomous prefecture for Dai people in the extreme south of Yunnan province, China, borders both Myanmar and Laos. Xishuangbanna lies at latitude 21°10′-22°40′ and longitude 99°55′-101°50′ east, on the northern edge of the tropics south of the Tropic of Cancer. It has an area of 19,124.5 square kilometers, bordering Pu'er City to the northeast and northwest, Laos to the southeast and Myanmar to the southwest. The border is 966.3 kilometers long, one river connects six countries, and there are four national ports. The prefectural seat is Jinghong, the largest settlement in the area and one that straddles the Mekong, called the "Lancang River" in Chinese.

The Dai people are several Tai-speaking ethnic groups living in the Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture and the Dehong Dai and Jingpo Autonomous Prefecture of China's Yunnan Province. The Dai people form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. By extension, the term can apply to groups in Laos, Vietnam, Thailand and Myanmar when Dai is used to mean specifically Tai Yai, Lue, Chinese Shan, Tai Dam, Tai Khao or even Tai in general. For other names, see the table below.

Isan or Northeastern Thai refers to the local development of the Lao language in Thailand, after the political split of the Lao-speaking world at the Mekong River at the conclusion of the Franco-Siamese crisis of 1893. The language is still referred to as Lao by native speakers.

Tai Lue or Xishuangbanna Dai is a Tai language of the Lu people, spoken by about 700,000 people in Southeast Asia. This includes 280,000 people in China (Yunnan), 200,000 in Burma, 134,000 in Laos, 83,000 in Thailand and 4,960 in Vietnam. The language is similar to other Tai languages and is closely related to Kham Mueang or Tai Yuan, which is also known as Northern Thai language. In Yunnan, it is spoken in all of Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture, as well as Jiangcheng Hani and Yi Autonomous County in Pu'er City.

Tai Dam, also known as Black Tai, is a Tai language spoken by the Tai Dam in Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and China.

Thai people are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Thailand. In a narrower and ethnic sense, the Thais are also a Tai ethnic group dominant in Central and Southern Thailand. Part of the larger Tai ethno-linguistic group native to Southeast Asia as well as Southern China and Northeast India, Thais speak the Sukhothai languages, which is classified as part of the Kra–Dai family of languages. The majority of Thais are followers of Theravada Buddhism.
Laotian Canadians, are Canadian citizens of Laotian origin or descent. In the 2016 Census, 24,580 people indicated Laotian ancestry. Bilateral relations between Canada and Laos were established in 1954 with the formalization of the independence of the Kingdom of Laos from France. In August 2015, Canada's first resident diplomat opened the Office of the Embassy of Canada in Vientiane, Laos.
Mueang, Muang, Mong, Meng or Mường (Vietnamese) were pre-modern semi-independent city-states or principalities in mainland Southeast Asia, adjacent regions of Northeast India and Southern China, including what is now Thailand, Laos, Burma, Cambodia, parts of northern Vietnam, southern Yunnan, western Guangxi and Assam.
The Tai Bueng are an ethnic group in Thailand. They are also referred to as Lao Bueng.
The Lao Wiang, sometimes also referred to as Lao Wieng, are a Tai sub-ethnic group of the Isan region. Approximately 50,000 self-proclaimed Lao Wiang live in villages throughout Thailand, especially the provinces of Prachinburi, Udon Thani, Nakhon Pathom, Chai Nat, Lopburi, Saraburi, Nakhon Nayok, Suphan Buri, Ratchaburi, Phetchaburi, and Roi Et with a significant number in Bangkok.
The Rau people, also known as Lao, were an ethnic group of ancient China. Their descendants are the Zhuang, Buyei, Tày–Nùng and other Kra–Dai-speaking peoples.

The Tai folk religion, Satsana Phi or Ban Phi is the ancient native ethnic religion of Tai people still practiced by various Tai groups. Tai folk religion was dominant among Tai people in Asia until the arrival of Buddhism and Hinduism. It is primarily based on worshipping deities called Phi, Khwan and Ancestors.
The Lao Khrang are a sub-group of the Lao ethnic group. Also known as the Tai Khrang, they speak a dialect of the Lao language that is not too different from the modern Lao/Isan languages of Laos and Isan. The Lao Khrang should not be confused with the Tai Khang who are a closely related people inhabiting northeastern Laos.

Tai Nüa is one of the Tai ethnicities in South East Asia. They are mostly found in the Yunnan Province of China, Laos, Thailand, Burma and Vietnam and some have emigrated to the United States of America. There are however two different groups of Tai people called Tai Nua, one in China and Burma, the other in Laos.
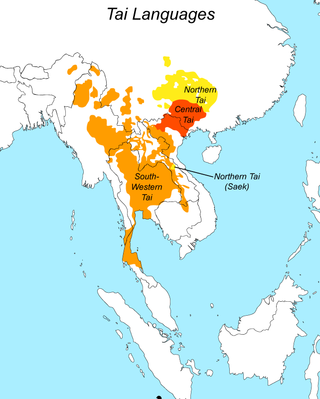
Tai peoples are the populations who speak the Tai languages. There are a total of about 93 million people of Tai ancestry worldwide, with the largest ethnic groups being Dai, Thai, Isan, Tai Yai (Shan), Lao, Tai Ahom, Tai Kassay and some Northern Thai peoples.













