List
| Rank | Species | Binomial name | Image | Maximum weight (kg) | Weight range (kg) | Maximum length (m) [a] | Length range (m) | Shoulder height (cm) | Native range by continent(s) | Range map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wolf | Canis lupus |  | 79 [1] 86 [2] (verified) 103 [3] (unverified) | 14–65 [4] | 2.13 [5] -2.5 [6] [7] | 1.4-1.90 [8] | 97 | North America and Eurasia | |
| 2 | Red wolf | Canis rufus |  | 40 [9] | 23-39 | 1.7 [10] | 1.2-1.65 [11] | 80 | North America |  |
| 3 | Eastern wolf | Canis lycaon |  | 36.7 [12] | 23-30 | 1.8 [13] | 0.91-1.65[ citation needed ] | 70 | North America |  |
| 4 | Maned wolf | Chrysocyon brachyurus |  | 36 [14] | 20-30 | 1.9 [15] | 1.5-1.8 [16] [17] | 107 | South America |  |
| 5 | African wild dog | Lycaon pictus |  | 36 [18] | 20-30 [19] | 1.5 [20] | 1.10-1.40 [21] | 75 | Africa |  |
| 6 | Coyote | Canis latrans |  | 33.91 [22] | 8-20 | 1.5 [23] | 1.0-1.3 [24] | 70 | North America | 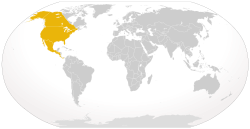 |
| 7 | Dhole | Cuon alpinus |  | 25 | 10-21 | 1.45 [25] | 0.9-1.3 [26] | 56 | Asia | 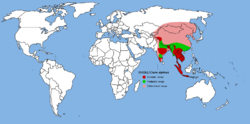 |
| 8 | Ethiopian wolf | Canis simensis |  | 20 [27] | 11-19 | 1.45 [28] [29] | 1.1-1.4 [30] | 62 | Africa |  |
| 9 | Red fox | Vulpes vulpes |  | 17.2 [31] | 2-14 | 1.5 [32] | 0.76-1.4 [33] | 50 | North America, Eurasia, Africa | 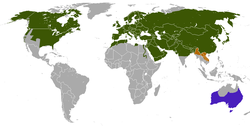 |
| 10 | African wolf | Canis lupaster |  | 15 | 7-14 | 1.50 [34] | 1.2-1.4 [35] [36] | 40 | Africa |  |
| 11 | Side-striped jackal | Lupulella adusta |  | 15 | 6.5-14 | 0.95 | 69-81 | 50 [37] | Africa |  |
| 12 | Golden jackal | Canis aureus |  | 14.9 | 6-14 | 1.25 | 69-85 [38] | 45-50 | Eurasia |  |
| 13 | Culpeo fox | Lycalopex culpaeus |  | 14 | 5-13.5 | 1.52 | 94-1.33 | 45-65 | South America |  |
| 14 | Common raccoon dog | Nyctereutes procyonoides |  | 9-10 [39] | 3-7 | 0.89 | 45-71 | 20 cm | Europe and Asia |  |