Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and biological devices, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology such as biological machines. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials.
A radiation oncologist is a specialist physician who uses ionizing radiation in the treatment of cancer. Radiation oncology is one of the three primary specialties, the other two being surgical and medical oncology, involved in the treatment of cancer. Radiation can be given as a curative modality, either alone or in combination with surgery and/or chemotherapy. It may also be used palliatively, to relieve symptoms in patients with incurable cancers. A radiation oncologist may also use radiation to treat some benign diseases, including benign tumors. In some countries, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are controlled by a single oncologist who is a "clinical oncologist". Radiation oncologists work closely with other physicians such as surgical oncologists, interventional radiologists, internal medicine subspecialists, and medical oncologists, as well as medical physicists and technicians as part of the multi-disciplinary cancer team. Radiation oncologists undergo four years of oncology-specific training whereas oncologists who deliver chemotherapy have two years of additional training in cancer care during fellowship after internal medicine residency in the United States.

A soft-tissue sarcoma (STS) is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer, that develops in soft tissue. A soft-tissue sarcoma is often a painless mass that grows slowly over months or years. They may be superficial or deep-seated. Any such unexplained mass must be diagnosed by biopsy. Treatment may include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. Bone sarcomas are the other class of sarcomas.

A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, vascular, or other structural tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates.

In medicine, proton therapy, or proton radiotherapy, is a type of particle therapy that uses a beam of protons to irradiate diseased tissue, most often to treat cancer. The chief advantage of proton therapy over other types of external beam radiotherapy is that the dose of protons is deposited over a narrow range of depth; hence in minimal entry, exit, or scattered radiation dose to healthy nearby tissues.
Elekta is a global Swedish company that develops and produces radiation therapy and radiosurgery-related equipment and clinical management for the treatment of cancer and brain disorders. Elekta has a global presence in more than 120 countries, with over 40 offices around the world and about 4,700 employees.
Magnetofection is a transfection method that uses magnetic fields to concentrate particles containing vectors to target cells in the body. Magnetofection has been adapted to a variety of vectors, including nucleic acids, non-viral transfection systems, and viruses. This method offers advantages such as high transfection efficiency and biocompatibility which are balanced with limitations.

Chad Alexander Mirkin is an American chemist. He is the George B. Rathmann professor of chemistry, professor of medicine, professor of materials science and engineering, professor of biomedical engineering, and professor of chemical and biological engineering, and director of the International Institute for Nanotechnology and Center for Nanofabrication and Molecular Self-Assembly at Northwestern University.

Hyperthermia therapy(or hyperthermia, or thermotherapy) is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to temperatures above body temperature, in the region of 40–45 °C (104–113 °F). Hyperthermia is usually applied as an adjuvant to radiotherapy or chemotherapy, to which it works as a sensitizer, in an effort to treat cancer.
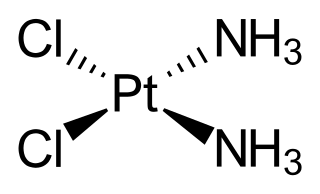
A radiosensitizer is an agent that makes tumor cells more sensitive to radiation therapy. It is sometimes also known as a radiation sensitizer or radio-enhancer.
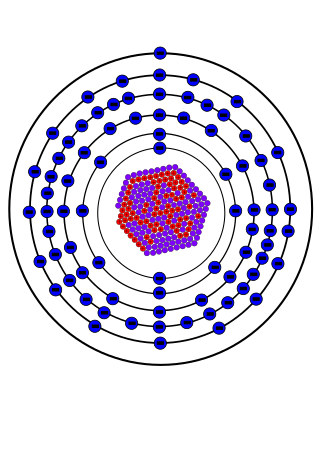
Gold-198 (198Au) is a radioactive isotope of gold. It undergoes beta decay to stable 198Hg with a half-life of 2.69464 days.

Iron oxide nanoparticles are iron oxide particles with diameters between about 1 and 100 nanometers. The two main forms are composed of magnetite and its oxidized form maghemite. They have attracted extensive interest due to their superparamagnetic properties and their potential applications in many fields including molecular imaging.

Nanobiotix is a biotechnology company that uses nanomedicine to develop new radiotherapy techniques for cancer patients. The company is headquartered in Paris, with additional corporate offices in New York and Massachusetts.

Cheon Jinwoo is the H.G. Underwood Professor at Yonsei University and the Director of the Center for Nanomedicine, Institute for Basic Science (IBS). As a leading chemist in inorganic materials chemistry and nanomedicine Cheon and his group research chemical principles for the preparation of complex inorganic materials. He has been a Clarivate Analytics Highly Cited Researcher both in the field of chemistry in 2014, 2015, 2016 and cross-field in 2018. He is a fellow of the American Chemical Society, Royal Society of Chemistry, and Korean Academy of Science and Technology, a senior editor of Accounts of Chemical Research and an editorial advisory board member of Journal of Materials Chemistry, Nano Letters and Materials Horizons.
Combinatorial ablation and immunotherapy is an oncological treatment that combines various tumor-ablation techniques with immunotherapy treatment. Combining ablation therapy of tumors with immunotherapy enhances the immunostimulating response and has synergistic effects for curative metastatic cancer treatment. Various ablative techniques are utilized including cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation, laser ablation, photodynamic ablation, stereotactic radiation therapy, alpha-emitting radiation therapy, hyperthermia therapy, HIFU. Thus, combinatorial ablation of tumors and immunotherapy is a way of achieving an autologous, in-vivo tumor lysate vaccine and treating metastatic disease.
A radioactive nanoparticle is a nanoparticle that contains radioactive materials. Radioactive nanoparticles have applications in medical diagnostics, medical imaging, toxicokinetics, and environmental health, and are being investigated for applications in nuclear nanomedicine. Radioactive nanoparticles present special challenges in operational health physics and internal dosimetry that are not present for other substances, although existing radiation protection measures and hazard controls for nanoparticles generally apply.

The characterization of nanoparticles is a branch of nanometrology that deals with the characterization, or measurement, of the physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles.,. Nanoparticles measure less than 100 nanometers in at least one of their external dimensions, and are often engineered for their unique properties. Nanoparticles are unlike conventional chemicals in that their chemical composition and concentration are not sufficient metrics for a complete description, because they vary in other physical properties such as size, shape, surface properties, crystallinity, and dispersion state.

MagForce AG is a publicly traded German company based in Berlin, Germany that develops medical devices that generate magnetic hyperthermia to treat cancer. The company was founded in 1997 as a spin-off from Charité.
Omid Farokhzad is an Iranian-American physician, scientist, and entrepreneur in the development of nanomedicines. Farokhzad is a Professor of Anesthesiology at Harvard Medical School. Omid Farokhzad is the Chair, Chief Executive Officer and co-founder for Seer, a company focused on deep, unbiased proteomics analysis at scale. The Boston Globe selected him among the top innovators in Massachusetts and the Boston Business Journal selected him among the Health Care Champions for his innovations.
Theranostics, also known as theragnostics, is a technique commonly used in personalised medicine. For example in nuclear medicine, one radioactive drug is used to identify (diagnose) and a second radioactive drug is used to treat (therapy) cancerous tumors. In other words, theranostics combines radionuclide imaging and radiation therapy which targets specific biological pathways.












