The foreign policy of Lebanon reflects its geographic location, the composition of its population, and its reliance on commerce and trade. Until 2005, Lebanon's foreign policy had been heavily influenced by Syria. The framework for relations was first codified in May 1991, when Lebanon and Syria signed a treaty of mutual cooperation. This treaty came out of the Taif Agreement, which stipulated that "Lebanon is linked to Syria by distinctive ties deriving strength from kinship, history, and common interests." The Lebanese-Syria treaty calls for "coordination and cooperation between the two countries" that would serve the "interests of the two countries within the framework of sovereignty and independence of each." Numerous agreements on political, economic, and security. After Syria's military withdrawal in 2005, Lebanon's foreign policy charted a more independent course.

This article deals with the diplomatic affairs, foreign policy and international relations of Uruguay. At the political level, these matters are officially handled by the Ministry of Foreign Relations, also known as Cancillería, which answers to the President.

Foreign relations exist between Armenia and Uruguay. Uruguay, as a small South American nations hosts a large Armenian community for its size. The Armenian community in Uruguay totals approximately 16,000 people.

Canada–Uruguay relations are foreign relations between Canada and the Republic of Uruguay. Both countries are members of the Cairns Group, the Organization of American States and the United Nations.

Japan–Uruguay relations are foreign relations between Japan and Uruguay. Both countries are members of the United Nations and the World Trade Organization.
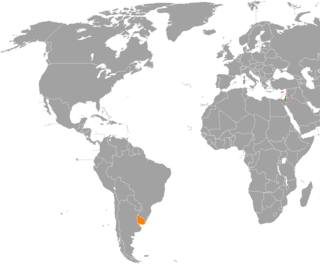
Israel–Uruguay relations are foreign relations between Israel and Uruguay. Uruguay was the first South American country to recognize Israel.

Mexico–Uruguay relations are foreign relations between Mexico and Uruguay. Both nations are members of the Latin American Integration Association, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.

Paraguay and Uruguay established diplomatic relations on April 6, 1845. Paraguay has an embassy and a consulate-general in Montevideo. Uruguay has an embassy and a consulate-general in Asunción. Paraguay also has an honorary consulate in Punta del Este. Both countries were founding members of the Mercosur, and both are full members of the Rio Group, the Latin Union, the Association of Spanish Language Academies, the Organization of American States, the Organization of Ibero-American States, the Union of South American Nations, the URUPABOL, the Cairns Group and the Group of 77.

There are about 53,000 to 75,000 Lebanese Uruguayans, or Uruguayans of Lebanese origin. The Lebanese are one of the larger non-European communities, though still not as large a group as most European groups. Relations between Uruguay and Lebanon have always been close.

Greece–Uruguay relations are diplomatic relations between Greece and Uruguay. Both nations are members of the World Trade Organization.

Cuba–Uruguay relations refers to the diplomatic relations between the Republic of Cuba and the Oriental Republic of Uruguay. Both nations are members of the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, Group of 77, Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.

Portugal–Uruguay relations refers to the current and historical relations between Portugal and Uruguay. Both nations are members of the Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.

Diplomatic relations between Iran and Uruguay were established in 1983. Iran has an embassy in Montevideo. Uruguay has an embassy in Tehran.
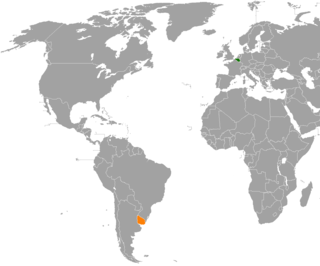
Belgium–Uruguay relations refer to the bilateral relations between Belgium and Uruguay. Belgium has an honorary consulate in Montevideo, under the jurisdiction of the Belgian embassy in Buenos Aires. Uruguay has an embassy in Brussels.

India is represented in Uruguay through its embassy in Buenos Aires in Argentina; it also has a consulate general in Montevideo. Uruguay has an embassy in New Delhi and a consulate in Mumbai. Diplomatic relations were established in 1948. The Uruguayan embassy in New Delhi was first opened in 1960 and operated until 1975. It was re-opened in 1998. In May 2010, Uruguayan ambassador to India Cesar Ferrer requested India to open an embassy in Montevideo.

Indonesia–Lebanon relations were officially established in 1950. Indonesia has an embassy in Beirut and a consulate general in Tripoli, while Lebanon has an embassy in Jakarta.

Lebanon–Mexico relations are the diplomatic relations between Lebanon and Mexico. Both nations enjoy friendly relations, the importance of which centers on the history of Lebanese immigration to Mexico. Both nations are members of the Group of 24 and the United Nations.

Nicaragua–Uruguay relations refers to the diplomatic relations between the Republic of Nicaragua and the Oriental Republic of Uruguay. Both nations are members of the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, Group of 77, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.

Lebanon–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Lebanon has an embassy in Madrid, and Spain has an embassy in Beirut.























