Henrica is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Verrucariaceae. It has four species. The genus was circumscribed by Maurice Bouly de Lesdain in 1921, with Henrica ramulosa assigned as the type species. The generic name Henrica honours Italian clergyman and lichenologist Joseph-Marie Henry (1870–1947).
Parmularia is a genus of fungi in the family Parmulariaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Joseph-Henri Léveillé in 1846.

Punctelia is a genus of foliose lichens belonging to the large family Parmeliaceae. The genus, which contains about 50 species, was segregated from genus Parmelia in 1982. Characteristics that define Punctelia include the presence of hook-like to thread-like conidia, simple rhizines, and point-like pseudocyphellae. It is this last feature that is alluded to in the vernacular names speckled shield lichens or speckleback lichens.

Skyttea is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi in the family Cordieritidaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1981 by lichenologists Martha Allen Sherwood, David L. Hawksworth, and Brian J. Coppins, with Skyttea nitschkei assigned as the type species.

A lichenicolous fungus is a parasitic fungus that only lives on lichen as the host. A lichenicolous fungus is not the same as the fungus that is the component of the lichen, which is known as a lichenized fungus. They are most commonly specific to a given fungus as the host, but they also include a wide range of pathogens, saprotrophs, and commensals. It is estimated there are 3000 species of lichenicolous fungi. More than 1800 species are already described among the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota. More than 95% of lichenicolous fungi described as of 2003 are ascomycetes, in 7 classes and 19 orders. Although basidiomycetes have less than 5% of lichenicolous lichen species, they represent 4 classes and 8 orders. Many lichenicolous species have yet to be assigned a phylogenetic position as of 2003.

Lecanora cenisia is a species of crustose lichen in the family Lecanoraceae. It is a known host of the lichenicolous fungus species Carbonea supersparsa.
Xyleborus is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Stereocaulaceae. It has two species. The genus was circumscribed in 2009 by Richard C. Harris and Douglas Ladd with Xyleborus sporodochifer assigned as the type species. A second species, X. sporodochifer, was added to the genus in 2015.

Lecanora polytropa, commonly known as the granite-speck rim lichen, is a species of saxicolous lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. A small, inconspicuous species that grows in the cracks of rock surfaces, it has a cosmopolitan distribution and has been recorded on all continents, including Antarctica.
Briancoppinsia is a fungal genus in the family Arthoniaceae. It is monotypic, containing the single species Briancoppinsia cytospora, a lichenicolous fungus that parasitises parmelioid lichens, as well as Cladonia, Lepra, and Lecanora conizaeoides, among others. The species was first described scientifically by Léon Vouaux in 1914 as Phyllosticta cytospora. The genus was circumscribed in 2012 by Paul Diederich, Damien Ertz, James Lawrey, and Pieter van den Boom. The genus was named for Brian John Coppins, who is, according to the authors, an "eminent British lichenologist and expert of lichenicolous fungi".
Trichosphaerella buckii is a species of lichenicolous fungus in the family Niessliaceae. It was described as a new species in 2016 by Richard Harris and James Lendemer. The type was found growing immersed in a moribund thallus of the lichen Punctelia rudecta, which itself was on the trunk of a maple tree. This tree was in the Alligator River Game Land, in the Coastal Plain region of eastern North Carolina. Although at the time of publication the fungus was known only from the type locality, it was suspected to have a larger distribution, considering its lichen host has a widespread North American distribution.
Lichenosticta is a genus of fungi of uncertain familial placement in the order Lecanorales. It has five species. All species are lichenicolous, meaning they are parasitic on lichens.

Ochrolechia africana, commonly known as the frosty saucer lichen, is a species of crustose and corticolous (bark-dwelling) lichen in the family Ochrolechiaceae. It is a widely distributed species, found in tropical and subtropical areas of southern Africa, Asia, Australia, North America, and South America. The lichen is characterized by the presence of a white "frosty" or powdery apothecia.
Maurice Léopold Joseph Bouly de Lesdain was a French botanist and lichenologist.

Marchandiomyces corallinus is a lichenicolous fungus that parasitizes lichens, particularly those in the genera Physcia, Parmelia, Flavoparmelia, Lepraria, Pertusaria, Lasallia, and Lecanora. It is commonly found in eastern North America and Europe.
Buelliella lecanorae is a species of lichenicolous (lichen-eating) fungus in the class Dothideomycetes. It is found in a few locations in Estonia and in Crimea, where it grows parasitically on members of the Lecanora subfusca species group.
Heteroacanthella ellipsospora is a species of fungus of uncertain familial placement in the order Auriculariales. The fungus is lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling), and it parasitises the apothecia and thallus of the crustose lichen Lecanora carpinea. Heteroacanthella ellipsospora was formally described as a new species in 2014 by Juan Carlos Zamora, Sergio Pérez-Ortega and Víctor Rico. It was first described from specimens collected in the Spanish provinces of Jaén and Madrid, and later reported from Sweden.
Carbonea aggregantula is a species of lichen belonging to the family Lecanoraceae.

Verseghya is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Pertusariaceae. It has two species. The genus was circumscribed in 2016 by lichenologists Sergey Kondratyuk, Laszlo Lőkös, and Jae-Seoun Hur, with Verseghya klarae assigned as the type species. This crustose species is found in South Korea, where it grows on the bark of a wide variety of both deciduous and coniferous trees. Molecular phylogenetic analysis showed that Verseghya klarae occupied a separate phylogenetic branch in the Pertusariaceae, situated between the genera Ochrolechia and Pertusaria and the Lecanora subcarnea species complex. Verseghya thysanophora was transferred to the genus in 2019. It is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere.
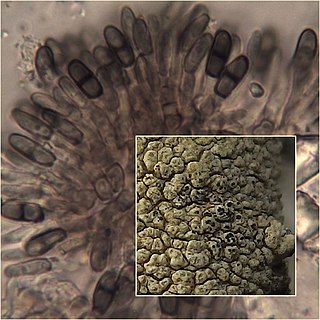
Minutoexcipula is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi of uncertain familial placement in the order Chaetothyriales. It has eight species. The genus was circumscribed in 1994 by M. Violeta Atienza Tamarit and David Leslie Hawksworth, with Minutoexcipula tuckerae assigned as the type species. The genus is characterized both by its black convex sporodochia-like conidiomata, as well as the well-differentiated exciple on these structures.









