
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation for the sounds of speech. The IPA is used by lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguists, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators.
A phoneme is any set of similar speech sounds that is perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible phonetic unit—that helps distinguish one word from another. All languages contain phonemes, and all spoken languages include both consonant and vowel phonemes. Phonemes are primarily studied under the branch of linguistics known as phonology.
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All oral languages use pitch to express emotional and other para-linguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast and other such features in what is called intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with phoneme. Tonal languages are common in East and Southeast Asia, Africa, the Americas and the Pacific.
Anusvara, also known as Bindu, is a symbol used in many Indic scripts to mark a type of nasal sound, typically transliterated ⟨ṃ⟩ or ⟨ṁ⟩ in standards like ISO 15919 and IAST. Depending on its location in the word and the language for which it is used, its exact pronunciation can vary. In the context of ancient Sanskrit, anusvara is the name of the particular nasal sound itself, regardless of written representation.
In phonetics, palatalization or palatization is a way of pronouncing a consonant in which part of the tongue is moved close to the hard palate. Consonants pronounced this way are said to be palatalized and are transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet by affixing the letter ⟨ʲ⟩ to the base consonant. Palatalization is not phonemic in English, but it is in Slavic languages such as Russian and Ukrainian, Finnic languages such as Estonian and Võro, Irish, Marshallese, Kashmiri, and Japanese.
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds. Speech sounds can be described as either voiceless or voiced.
In phonetics, vowel roundedness is the amount of rounding in the lips during the articulation of a vowel. It is labialization of a vowel. When a rounded vowel is pronounced, the lips form a circular opening, and unrounded vowels are pronounced with the lips relaxed. In most languages, front vowels tend to be unrounded, and back vowels tend to be rounded. However, some languages, such as French, German and Icelandic, distinguish rounded and unrounded front vowels of the same height, and Vietnamese distinguishes rounded and unrounded back vowels of the same height. Alekano has only unrounded vowels. In the International Phonetic Alphabet vowel chart, rounded vowels are the ones that appear on the right in each pair of vowels. There are also diacritics, U+0339◌̹COMBINING RIGHT HALF RING BELOW and U+031C◌̜COMBINING LEFT HALF RING BELOW, to indicate greater and lesser degrees of rounding, respectively. Thus has less rounding than cardinal, and has more. These diacritics can also be used with unrounded vowels: is more spread than cardinal, and is less spread than cardinal.
In phonetics and phonology, gemination, or consonant lengthening, is an articulation of a consonant for a longer period of time than that of a singleton consonant. It is distinct from stress. Gemination is represented in many writing systems by a doubled letter and is often perceived as a doubling of the consonant. Some phonological theories use 'doubling' as a synonym for gemination, while others describe two distinct phenomena.
The Royal Thai General System of Transcription (RTGS) is the official system for rendering Thai words in the Latin alphabet. It was published by the Royal Institute of Thailand in early 1917, when Thailand was called Siam.
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived length of a vowel sound: the corresponding physical measurement is duration. In some languages vowel length is an important phonemic factor, meaning vowel length can change the meaning of the word, for example in Arabic, Czech, Dravidian languages, some Finno-Ugric languages, Japanese, Kyrgyz, Samoan, and Xhosa. Some languages in the past likely had the distinction even though their descendants do not, with an example being Latin and its descendent Romance languages.
In linguistics, a chroneme is an abstract phonological suprasegmental feature used to signify contrastive differences in the length of speech sounds. Both consonants and vowels can be viewed as displaying this features. The noun chroneme is derived from Ancient Greek χρόνος (khrónos) 'time', and the suffixed -eme, which is analogous to the -eme in phoneme or morpheme. Two words with different meaning that are spoken exactly the same except for length of one segment are considered a minimal pair. The term was coined by the British phonetician Daniel Jones to avoid using the term phoneme to characterize a feature above the segmental level.
In phonetics, clipping is the process of shortening the articulation of a phonetic segment, usually a vowel. A clipped vowel is pronounced more quickly than an unclipped vowel and is often also reduced.
Americanist phonetic notation, also known as the North American Phonetic Alphabet (NAPA), the Americanist Phonetic Alphabet or the American Phonetic Alphabet (APA), is a system of phonetic notation originally developed by European and American anthropologists and language scientists for the phonetic and phonemic transcription of indigenous languages of the Americas and for languages of Europe. It is still commonly used by linguists working on, among others, Slavic, Uralic, Semitic languages and for the languages of the Caucasus, of India, and of much of Africa; however, Uralicists commonly use a variant known as the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet.
Finno-Ugric transcription (FUT) or the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet (UPA) is a phonetic transcription or notational system used predominantly for the transcription and reconstruction of Uralic languages. It was first published in 1901 by Eemil Nestor Setälä, a Finnish linguist; it was somewhat modified in the 1970s.
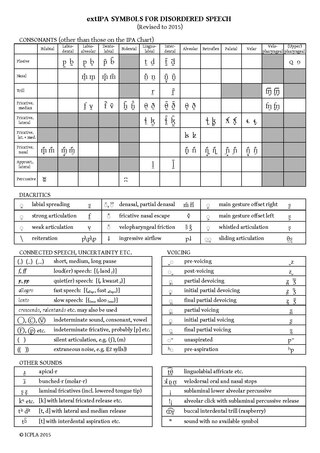
The Extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet for Disordered Speech, commonly abbreviated extIPA, are a set of letters and diacritics devised by the International Clinical Phonetics and Linguistics Association to augment the International Phonetic Alphabet for the phonetic transcription of disordered speech. Some of the symbols are used for transcribing features of normal speech in IPA transcription, and are accepted as such by the International Phonetic Association.
In phonetics and phonology, relative articulation is description of the manner and place of articulation of a speech sound relative to some reference point. Typically, the comparison is made with a default, unmarked articulation of the same phoneme in a neutral sound environment. For example, the English velar consonant is fronted before the vowel compared to articulation of before other vowels. This fronting is called palatalization.
Lithuanian has 11 vowels and 45 consonants, including 22 pairs of consonants distinguished by the presence or absence of palatalization. Most vowels come in pairs which are differentiated through length and degree of centralization.
This article is about the phonology of Latvian. It deals with synchronic phonology as well as phonetics.
Standard Cantonese pronunciation originates from Guangzhou, also known as Canton, the capital of Guangdong Province. Hong Kong Cantonese is closely related to the Guangzhou dialect, with only minor differences. Yue dialects spoken in other parts of Guangdong and Guangxi provinces, such as Taishanese, exhibit more significant divergences.
ISO 11940-2 is an ISO standard for a simplified transcription of the Thai language into Latin characters.

