
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the process of recording and processing information about economic entities, such as businesses and corporations. Accounting measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators. Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms "accounting" and "financial reporting" are often used interchangeably.

Bookkeeping is the recording of financial transactions, and is part of the process of accounting in business and other organizations. It involves preparing source documents for all transactions, operations, and other events of a business. Transactions include purchases, sales, receipts and payments by an individual person, organization or corporation. There are several standard methods of bookkeeping, including the single-entry and double-entry bookkeeping systems. While these may be viewed as "real" bookkeeping, any process for recording financial transactions is a bookkeeping process.

GnuCash is an accounting program that implements a double-entry bookkeeping system. It was initially aimed at developing capabilities similar to Intuit, Inc.'s Quicken application, but also has features for small business accounting. Recent development has been focused on adapting to modern desktop support-library requirements.

Factoring is a financial transaction and a type of debtor finance in which a business sells its accounts receivable to a third party at a discount. A business will sometimes factor its receivable assets to meet its present and immediate cash needs. Forfaiting is a factoring arrangement used in international trade finance by exporters who wish to sell their receivables to a forfaiter. Factoring is commonly referred to as accounts receivable factoring, invoice factoring, and sometimes accounts receivable financing. Accounts receivable financing is a term more accurately used to describe a form of asset based lending against accounts receivable. The Commercial Finance Association is the leading trade association of the asset-based lending and factoring industries.

Accounts payable (AP) is money owed by a business to its suppliers shown as a liability on a company's balance sheet. It is distinct from notes payable liabilities, which are debts created by formal legal instrument documents. An accounts payable department's main responsibility is to process and review transactions between the company and its suppliers and to make sure that all outstanding invoices from their suppliers are approved, processed, and paid. The accounts payable process starts with collecting supply requirements from within the organization and seeking quotes from vendors for the items required. Once the deal is negotiated, purchase orders are prepared and sent. The goods delivered are inspected upon arrival and the invoice received is routed for approvals. Processing an invoice includes recording important data from the invoice and inputting it into the company's financial, or bookkeeping, system. After this is accomplished, the invoices must go through the company's respective business process in order to be paid.
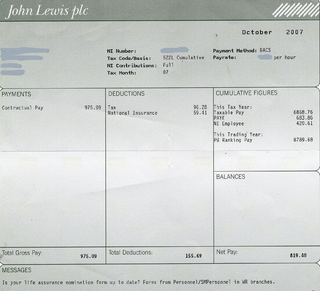
A payroll is a list of employees of a company who are entitled to receive compensation as well as other work benefits, as well as the amounts that each should obtain. Along with the amounts that each employee should receive for time worked or tasks performed, payroll can also refer to a company's records of payments that were previously made to employees, including salaries and wages, bonuses, and withheld taxes, or the company's department that deals with compensation. A company may handle all aspects of the payroll process in-house or can outsource aspects to a payroll processing company.
Electronic data processing (EDP) or business information processing can refer to the use of automated methods to process commercial data. Typically, this uses relatively simple, repetitive activities to process large volumes of similar information. For example: stock updates applied to an inventory, banking transactions applied to account and customer master files, booking and ticketing transactions to an airline's reservation system, billing for utility services. The modifier "electronic" or "automatic" was used with "data processing" (DP), especially c. 1960, to distinguish human clerical data processing from that done by computer.

An accounting information system (AIS) is a system of collecting, storing and processing financial and accounting data that are used by decision makers. An accounting information system is generally a computer-based method for tracking accounting activity in conjunction with information technology resources. The resulting financial reports can be used internally by management or externally by other interested parties including investors, creditors and tax authorities. Accounting information systems are designed to support all accounting functions and activities including auditing, financial accounting porting, -managerial/ management accounting and tax. The most widely adopted accounting information systems are auditing and financial reporting modules.
QuickBooks is an accounting software package developed and marketed by Intuit. First introduced in 1992, QuickBooks products are geared mainly toward small and medium-sized businesses and offer on-premises accounting applications as well as cloud-based versions that accept business payments, manage and pay bills, and payroll functions.
Time-tracking software are computer programs that allows users to record time spent on tasks or projects.
A financial bureau is an accounting business whose main focus is the preparation of finance for other businesses. In the United States such firms are often run by Certified Public Accountants, though a typical financial processing company will refer to itself as a bureau rather than a CPA firm, to distinguish its finance from the general tax and accounting that are generally not offered by a financial bureau. The typical client of a bureau is a small business - one just large enough for finance to be complicated to the point of a hassle, but one still small enough to not merit its own full-time finance department.
An umbrella company is a company that employs agency contractors who work on temporary contract assignments, usually through a recruitment agency in the United Kingdom. Recruitment agencies prefer to issue contracts to a limited company to reduce their own liability. It issues invoices to the recruitment agency and, when payment of the invoice is made, will typically pay the contractor through PAYE with the added benefit of offsetting some of the income through claiming expenses such as travel, meals, and accommodation.

LedgerSMB is a libre software double entry accounting and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, focussed on functionality required by small (self-employment) and medium size businesses. However, companies with millions of journal lines should also feel supported. Accounting data is stored in a free to use database server (PostgreSQL) and a standard web browser can be used as its user interface. The software is suited for hosting locally as well as on various public cloud providers. Commercial support can be obtained from several providers.
Sales Tax Management Service (STMS) is a type of accounting software that helps companies comply with United States sales tax requirements. STMS systems automatically calculate taxes for individual sales transactions and are delivered on-demand as a web-based “software as a service” (SaaS). They are designed to be compatible with a business's accounting software.

Accounting software is a computer program that maintains account books on computers, including recording transactions and account balances. It may depend on virtual thinking. Depending on the purpose, the software can manage budgets, perform accounting tasks for multiple currencies, perform payroll and customer relationship management, and prepare financial reporting. Work to have accounting functions be implemented on computers goes back to the earliest days of electronic data processing. Over time, accounting software has revolutionized from supporting basic accounting operations to performing real-time accounting and supporting financial processing and reporting. Cloud accounting software was first introduced in 2011, and it allowed the performance of all accounting functions through the internet.
The XBRL Global Ledger Taxonomy Framework is a holistic and generic XML and XBRL-based representation of the detailed data that can be found in accounting and operational systems, and is meant to be the bridge from transactional standards to reporting standards, integrating the Business Reporting Supply Chain.
WorkingPoint is a web-based application providing a suite of small business management tools. It is designed to offer a single point-of-access for all business management needs while offering a user-friendly interface. WorkingPoint’s functionalities include double-entry bookkeeping, contact management, inventory management, invoicing and bill & expense management.

Wave is a Canadian company that provides financial services and software for small businesses. Wave is headquartered in the East Bayfront neighborhood in Toronto, Canada.
A human resources management system (HRMS), also human resources information system (HRIS) or human capital management (HCM) system, is a form of human resources (HR) software that combines a number of systems and processes to ensure the easy management of human resources, business processes and data. Human resources software is used by businesses to combine a number of necessary HR functions, such as storing employee data, managing payroll, recruitment, benefits administration, time and attendance, employee performance management, and tracking competency and training records.
Making Tax Digital (MTD) is a UK government initiative that sets out a vision for the 'end of the tax return' and a 'transformed tax system', announced in 2015 and originally intended to be in place by 2020. HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) states that the main goal of MTD is to make tax administration more effective, more efficient and simpler for taxpayers.






