
Vadodara, formerly also known as Baroda, is the third largest city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of Vadodara District and is located on the banks of the Vishwamitri river, 141 kilometres (88 mi) from the state capital Gandhinagar. The railway line and NH 8 that connect Delhi and Mumbai pass through Vadodara. The city got its name because of the copious amount of Banyan(Vad) Trees present here. The city is also famous as Sanskari Nagari and Kala Nagari of India.

The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda (MSU), formerly Baroda College is a public university in the city of Vadodara, in Gujarat state, India. Originally established as a college in 1881, it became a university in 1949 after the independence of the country. It was later renamed after its benefactor Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III, the former ruler of Baroda State.

The Imperial Order of the Crown of India is an order in the British honours system. The Order was established by Queen Victoria in 1878, when she became Empress of India. The Order is open only to women and no additional appointments have been made since the Partition of India in 1947. The Order was limited to British princesses, wives or female relatives of Indian princes and the wife or female relatives of any person who held the office of:

Maharani Gayatri Devi, was the third Maharani consort of Jaipur from 1940 to 1949, through her marriage to Maharaja Sawai Man Singh II. Following her husband's signature for the Jaipur State to become part of the Union of India and her step-son's assumption of the title in 1970, she was known as Maharani Gayatri Devi, Rajmata of Jaipur.

The Gaekwads of Baroda are Hindu Marathas who trace their origins to Dawadi village near Poona to a Maratha clan by the name of Matre, which means Mantri meaning Minister. A dynasty belonging to this clan ruled the princely state of Baroda in western India from the early 18th century until 1947. The ruling prince was known as the Maharaja Gaekwad of Baroda. With the city of Baroda (Vadodara) as its capital, during the British Raj its relations with the British were managed by the Baroda Residency. It was one of the largest and wealthiest princely states existing alongside British India, with wealth coming from the lucrative cotton business as well as rice, wheat and sugar production.

Maharaja Chamarajendra Wadiyar X was the twenty-third maharaja of the Kingdom of Mysore, between 1868 and 1894.

The Lakshmi Vilas Palace in Vadodara, Gujarat, India, was constructed by the Gaekwad family, a prominent Maratha family, who ruled the Baroda State. Major Charles Mant was credited to be the main architect of the palace.
![Sayajirao Gaekwad III Farzand-i-Khas-i-Daulat-i-Inglishia, Shrimant Maharaja Sir , Sena Khas Khel Shamsher Bahadur Maharaja Gaekwad of Baroda, GCSI, GCIE, KIH[[Category:Articles with links needing disambiguation from April 2020]]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/Sayajirao_Gaekwad_III%2C_Maharaja_of_Baroda%2C_1919.jpg/232px-Sayajirao_Gaekwad_III%2C_Maharaja_of_Baroda%2C_1919.jpg)
Sayajirao Gaekwad III was the Maharaja of Baroda State from 1875 to 1939, and is remembered for reforming much of his state during his rule. He belonged to the royal Gaekwad dynasty of the Marathas which ruled parts of present-day Gujarat.
Shrimant Maharaja Sir Pratap Singh Rao Gaekwad, belonging to the Gaekwad dynasty of the Marathas, was the last ruling Maharaja of Baroda. He succeeded to the throne upon the death of his grandfather Sayajirao Gaekwad III in 1939. In 1947, British India was partitioned into two independent dominions, and Pratapsinh acceded his state to the Dominion of India. By 1949, Baroda had been merged into India.

Colonel Maharaja Raol Sir Shri Krishna Kumarsinhji Bhavsinhji KCSI was an Indian monarch and politician, the last Maharaja of the Gohil dynasty, who ruled Bhavnagar State from 1919 to 1948 and also served as the first Indian Governor of Madras from 1948 to 1952,After handover Rule of Bhavnagar State to Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel as part of Indian Union, and Bhavnagar is first state which joined Indian Union.
Ranjitsinhrao Gaekwad was an Indian politician and the titular Maharaja of Baroda from 1988 until his death in 2012.
Behari Lal Gupta was a member of the Indian Civil Service and a politician.
Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway (GBSR) was a narrow gauge railway line owned by the Princely State of Baroda, which was ruled by the Gaekwar dynasty.
William Goldring was a landscape architect, and naturalist. Goldring arrived in Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew (1875) where he was in charge of the Herbaceous Department at the world-famous botanical garden. He served as the Assistant Editor of The Garden (1879), and the Editor of Woods and Forests (1883-1886). He was also President of the Kew Guild, The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London, England (1913). Goldring's work included many private houses, hospitals, asylums and public parks in England, Wales, India, and the United States of America. He is responsible for work on nearly 700 different garden landscape projects in England alone.
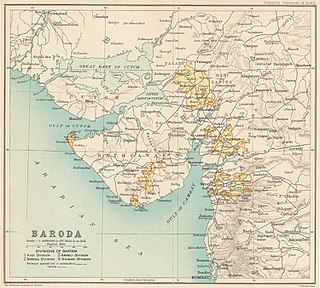
Baroda State was a state in present-day Gujarat, ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty of the Maratha Confederacy from its formation in 1721 until its accession to the newly-formed Dominion of India in 1949. With the city of Baroda (Vadodara) as its capital, during the British Raj its relations with the British were managed by the Baroda Residency. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs. 13,661,000. Baroda formally acceded to the Union of India, on 1 May 1949, prior to which an interim government was formed in the state.
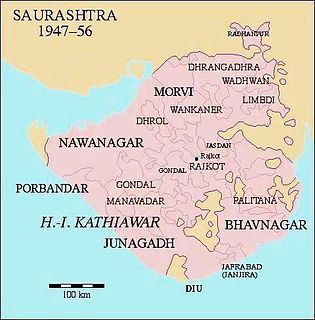
Palitana was a princely state in India during the British Raj until 1948. The center was the city of Palitana. The last ruler of the state received a privy purse of 180,000 Rupees at the state's accession to independent India on 15 February 1948.
The following list includes a brief about the titles of nobility or orders of chivalry used by the Marathas of India and by the Marathis/Konkanis in general.

Indore State, also known as Holkar State, was a royal state in India. Its rulers belonged to the Holkar dynasty. Indore was a 19-gun salute Maratha princely state during the British rule in India.
Shrimant Maharaja Sir Khanderao II Gaekwad, Sena Khas Khel Shamsher Bahadur, GCSI (1828–1870) was the Maharaja of Baroda State from 1856 to 1870.
Maharajkumar Shivajirao Gaekwad was an Indian first-class cricketer.







![Sayajirao Gaekwad III Farzand-i-Khas-i-Daulat-i-Inglishia, Shrimant Maharaja Sir , Sena Khas Khel Shamsher Bahadur Maharaja Gaekwad of Baroda, GCSI, GCIE, KIH[[Category:Articles with links needing disambiguation from April 2020]]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/Sayajirao_Gaekwad_III%2C_Maharaja_of_Baroda%2C_1919.jpg/232px-Sayajirao_Gaekwad_III%2C_Maharaja_of_Baroda%2C_1919.jpg)



