Breton is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language group spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of the insular branch instead of the continental grouping.

Brittany is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period of Roman occupation. It became an independent kingdom and then a duchy before being united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province governed as a separate nation under the crown.

Rennes is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the rivers Ille and Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department. In 2017, the urban area had a population of 357,327 inhabitants, and the larger metropolitan area had 739,974 inhabitants. The inhabitants of Rennes are called Rennais (masculine) or Rennaises (feminine) in French.

Brittany is the westernmost region of Metropolitan France. It covers about four fifths of the territory of the historic province of Brittany. It is one of two regions in Metropolitan France that do not contain any landlocked departments, the other being Corsica.

Ille-et-Vilaine is a department of France, located in the region of Brittany in the northwest of the country. It is named after the two rivers of the Ille and the Vilaine. It had a population of 1,079,498 in 2019.

Loire-Atlantique is a department in Pays de la Loire on the west coast of France, named after the river Loire and the Atlantic Ocean. It had a population of 1,429,272 in 2019.

The Côtes-d'Armor, formerly known as Côtes-du-Nord until 1990, is a department in the north of Brittany, in northwestern France. In 2019, it had a population of 600,582.

Châteaubriant is a town in western France, about 350 km (220 mi) southwest of Paris, and one of the three sous-préfectures of the Loire-Atlantique department. Châteaubriant is also situated in the historical and cultural region of Brittany, and it is the capital of the Pays de la Mée.

Gallo is a regional language of eastern Brittany. It is one of the langues d'oïl, a Romance sub-family that includes French. Today it is spoken only by a minority of the population, as the standard form of French now predominates in this area.
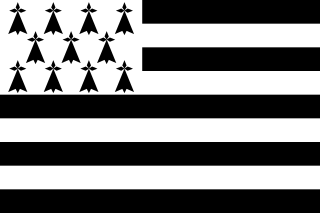
The flag of Brittany, a region in the northwest of France, is called the Gwenn-ha-du, which means white and black, in Breton. The flag was designed in 1923 by Morvan Marchal. It is also unofficially used in the department of Loire-Atlantique, although this now belongs to the Pays de la Loire and not to the region of Brittany, as the territory of Loire-Atlantique is historically part of the province of Brittany. Nantes, its prefecture, was once one of the two capital cities of Brittany.

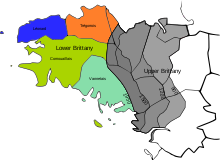
Lower Brittany denotes the parts of Brittany west of Ploërmel, where the Breton language has been traditionally spoken, and where the culture associated with this language is most prolific. The name is in distinction to Upper Brittany, the eastern part of Brittany, which is of a predominantly Romance culture.

The Bretons are a Celtic ethnic group native to Brittany, north-western France. They trace their heritage to groups of Brittonic speakers who emigrated from southwestern Great Britain, particularly Cornwall and Devon, mostly during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. They migrated in waves from the 3rd to 9th century into Armorica, which was subsequently named Brittany after them.

Batz-sur-Mer is a commune in the Loire-Atlantique department in western France.

Rennes 2 University is a public university located in Upper Brittany, France. It is one of the four universities of the Academy of Rennes. The main campus is situated in the northwest of Rennes in the Villejean neighborhood, not far from the other campus, at La Harpe.
The Battle of Jengland took place on 22 August 851, between the Frankish army of Charles the Bald and the Breton army of Erispoe, Duke of Brittany. The Bretons were victorious, leading to the signing of the Treaty of Angers in September 851 which secured Breton independence.

Upper Brittany is the eastern part of Brittany, France, which is predominantly of a Romance culture and is associated with the Gallo language. The name is in counterpoint to Lower Brittany, the western part of the ancient province and present-day region, where the Breton language has traditionally been spoken. However, there is no certainty as to exactly where the line between 'Upper' and 'Lower' Brittany falls.
The French–Breton War lasted from 1487 to 1491. The cause of this war was the approaching death of the Breton Duke Francis II of Brittany, who had no clear successor. If not resolved, this meant a resumption of issues from a previous War of the Breton Succession (1341–1364), which had rival claimants allying with England or France, resulting in an ambiguous peace treaty that failed to prevent future succession disputes.

Vikings were active in Brittany during the Middle Ages, even occupying a portion of it for a time. Throughout the 9th century, the Bretons faced threats from various flanks: they resisted full incorporation into the Frankish Carolingian Empire yet they also had to repel an emerging threat of the new duchy of Normandy on their eastern border by these Scandinavian colonists.