
Propafenone, sold under the brand name Rythmol among others, is a class 1c anti-arrhythmic medication, which is used to treat illnesses associated with rapid heart beat such as atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.

Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia.

Dofetilide is a class III antiarrhythmic agent. It is marketed under the trade name Tikosyn by Pfizer, and is available in the United States in capsules containing 125, 250, and 500 µg of dofetilide. It is not available in Europe or Australia. In the United States it is only available by mail order or through specially trained local pharmacies.

Quinidine is a class IA antiarrhythmic agent used to treat heart rhythm disturbances. It is a stereoisomer of antimalarial agent quinine, originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tree. The drug causes increased action potential duration, as well as a prolonged QT interval. As of 2019, its IV formulation is no longer being manufactured for use in the United States.

Pittosporum is a genus of about 200 species of flowering plants in the family Pittosporaceae. The genus is probably Gondwanan in origin; its present range extends from Australasia, Oceania, eastern Asia and some parts of Africa. Citriobatus can be included here, but might be a distinct genus. They are commonly known as pittosporums or, more ambiguously, cheesewoods.

Ibutilide is a Class III antiarrhythmic agent that is indicated for acute cardioconversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter of a recent onset to sinus rhythm. It exerts its antiarrhythmic effect by induction of slow inward sodium current, which prolongs action potential and refractory period (physiology) of myocardial cells. Because of its Class III antiarrhythmic activity, there should not be concomitant administration of Class Ia and Class III agents.

Lorajmine (17-monochloroacetylajmaline) is a drug that is a potent sodium channel blocker that was used for treating arrhythmia. It is derived from ajmaline, an alkaloid from the roots of Rauvolfia serpentina, by synthetically adding a chloroacetate residue.

Prajmaline (Neo-gilurythmal) is a class Ia antiarrhythmic agent which has been available since the 1970s. Class Ia drugs increase the time one action potential lasts in the heart. Prajmaline is a semi-synthetic propyl derivative of ajmaline, with a higher bioavailability than its predecessor. It acts to stop arrhythmias of the heart through a frequency-dependent block of cardiac sodium channels.

Pittosporum undulatum is a fast-growing tree in the family Pittosporaceae. It is sometimes also known as sweet pittosporum, native daphne, Australian cheesewood, Victorian box or mock orange.

Pilsicainide (INN) is an antiarrhythmic agent. It is marketed in Japan as サンリズム (Sunrythm). It was developed by Suntory Holdings Limited and first released in 1991. The JAN applies to the hydrochloride salt, pilsicainide hydrochloride.
Sodium channel blockers are drugs which impair the conduction of sodium ions (Na+) through sodium channels.
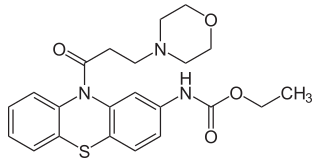
Moracizine or moricizine, sold under the trade name Ethmozine, is an antiarrhythmic of class IC. It was used for the prophylaxis and treatment of serious and life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, but was withdrawn in 2007 for commercial reasons.
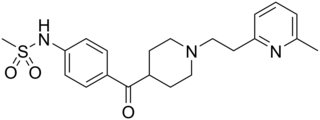
E-4031 is an experimental class III antiarrhythmic drug that blocks potassium channels of the hERG-type.

Pittosporum tobira is a species of sweet-smelling flowering plant in the pittosporum family Pittosporaceae known by several common names, including Australian laurel, Japanese pittosporum, mock orange and Japanese cheesewood. It is native to Japan, China, Taiwan, and Korea, but it is used throughout the world as an ornamental plant in landscaping and as cut foliage.

BRL-32872 is an experimental drug candidate that provides a novel approach to the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia. Being a derivative of verapamil, it possesses the ability to inhibit Ca+2 membrane channels. Specific modifications in hydrogen bonding activity, nitrogen lone pair availability, and molecular flexibility allow BRL-32872 to inhibit K+ channels as well. As such, BRL-32872 is classified as both a class III (K+ blocking) and class IV (Ca+2 blocking) antiarrhythmic agent.
Almokalant is a drug used to treat arrhythmia. It is a potassium channel blocker. It has been found to have teratogenic effects in rats.
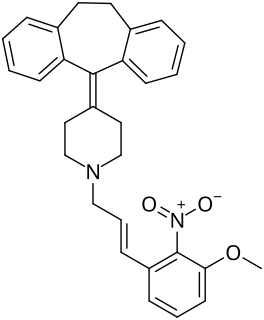
AH-1058 is a lipophilic antiarrhythmic calcium channel blocker synthesized by the Pharmaceutical Research Laboratories of Ajinomoto Co., Inc in Kawasaki, Japan. It is derived from cyproheptadine, a compound with known antiserotonic, antihistaminic and calcium channel blocking properties. The IUPAC name of AH-1058 is: 4-(5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-1-[E-3-(3-methoxy-2-nitro) phenyl-2-propenyl]piperidine hydrochloride.

Budiodarone (ATI-2042) is an antiarrhythmic agent and chemical analog of amiodarone that is currently being studied in clinical trials. Amiodarone is considered the most effective antiarrhythmic drug available, but its adverse side effects, including hepatic, pulmonary and thyroid toxicity as well as multiple drug interactions, are discouraging its use. Budiodarone only differs in structure from amiodarone through the presence of a sec-butyl acetate side chain at position 2 of the benzofuran moiety. This side chain allows for budiodarone to have a shorter half-life in the body than amiodarone which allows it to have a faster onset of action and metabolism while still maintaining similar electrophysiological activity. The faster metabolism of budiodarone allows for fewer adverse side effects than amiodarone principally due to decreased levels of toxicity in the body.
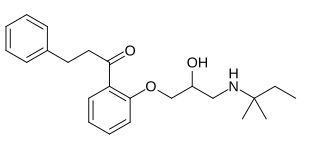
Diprafenone is an antiarrhythmic beta adrenergic antagonist.

















