
The politics of Turkmenistan takes place in the framework of a presidential republic, whereby the President of Turkmenistan is both head of state and head of government. However, no true opposition parties are allowed; every registered political party supports the second and current President Gurbanguly Berdimuhamedow. The country is frequently described as a totalitarian state.

Turkmenistan, also known as Turkmenia, is a landlocked country in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ashgabat is the capital and largest city of the country. The population of the country is about 6 million, the lowest of the Central Asian republics. Turkmenistan is one of the most sparsely populated nations in Asia. Citizens of Turkmenistan are known as Turkmenistanis, Turkmenians or Turkmens.

Turkmen, sporadically referred to as "Turkmen Turkic" or "Turkmen Turkish", is a Turkic language spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia, mainly of Turkmenistan, Iran and Afghanistan. It has an estimated five million native speakers in Turkmenistan, a further 719,000 speakers in Northeastern Iran and 1.5 million people in Northwestern Afghanistan. Turkmen has official status in Turkmenistan, but it does not have official status in Iran or Afghanistan, where big communities of ethnic Turkmens live. Turkmen is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Turkmen communities of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and by diaspora communities, primarily in Turkey and Russia.

The unicameral Assembly of the Union of the Comoros is the country's legislative body. It was established in 2004.

The Chamber of Deputies is the lower house of the Parliament of Equatorial Guinea.

The Chamber of Deputies is the lower house of Haiti's bicameral legislature, the Haitian Parliament. The upper house of the Haitian Parliament is the Senate of Haiti. The Chamber has 119 members who are elected by popular vote to four-year terms. There are no term limits for Deputies; they may be re-elected indefinitely.
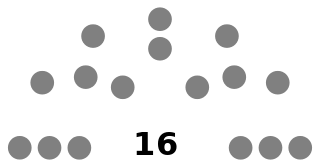
The House of Delegates of Palau is the lower house of the Palau National Congress, Palau's bicameral legislature. The Senate of Palau is the upper house. The House of Delegates has 16 members, each serving four-year terms in single-seat constituencies. Each state represents one constituency. No political parties exist. The last election was held on 3 November 2020.

The Assembly is since March 2021 the lower house of the National Council of Turkmenistan. It has 125 members, elected for five-year terms in single-seat constituencies.

The State Security Council of Turkmenistan is an important decision-making body in the field of the defence of Turkmenistan. It is the highest decision-making body in the armed forces next to the Ministry of Defense and the General Staff, with its members directly advising the President of Turkmenistan on matters of national security.

The Constitution of Turkmenistan adopted on 18 May 1992 is the supreme law of Turkmenistan. In its preamble, the Constitution emphasizes self-determination for the Turkmen people, as well as the rule of law and rights for citizens..

Raşit Öwezgeldiýewiç Meredow, is a Turkmen politician and diplomat who has served as Vice President of Turkmenistan since 2007.

The Central Bank of Turkmenistan is the national bank of Turkmenistan. It is located in the centre of Ashgabat. It was established in 1991 and regulates the country's banking system and supervises the national financial policy.
The Military ranks of Turkmenistan are the military insignia used by the Armed Forces of Turkmenistan. Being a former Soviet state, Turkmenistan shares a rank structure similar to that of Russia.

The Supreme Court of Turkmenistan is a constitutional institution in Turkmenistan. It is one of three Turkmen institutions to exercise governmental power and is the highest ranking court in the country. Established in 1992 after the adoption of the Constitution of Turkmenistan, the Supreme Court currently consists of 22 judges who are appointed by the President of Turkmenistan for a 5-year term. It is the successor to the Supreme Court of the Turkmen SSR. The associate judges are divided into three different chambers, each specifically focusing on civil, criminal, and military law. The Supreme Court is affiliated to different regional munincipal, provincial courts, district and city courts, as well as the Supreme Economic Court.
The Parliament of the Kingdom of Laos was the bicameral legislature of the Kingdom of Laos from 1947 to 1975. It consisted of the National Assembly, whose members were popularly elected, and the Royal Council, whose members were appointed by the King or elected by the National Assembly. The last elections to the National Assembly took place in 1972.











