
Berkshire County is the westernmost county in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. As of the 2020 census, the population was 129,026. Its largest city and traditional county seat is Pittsfield. The county was founded in 1761. The Berkshire Hills are centered on Berkshire County. Residents are known as Berkshirites. It exists today only as a historical geographic region, and has no county government, with the exception of the retirement board for former county workers, and the offices of the sheriff and the registrar of deeds.

Housatonic is a census-designated place (CDP) in the town of Great Barrington in Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. It is part of the Pittsfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 1,109 at the 2010 census. It was named after the Housatonic River.

Pittsfield is the largest city and the county seat of Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the principal city of the Pittsfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses all of Berkshire County. Pittsfield’s population was 43,927 at the 2020 census. Although its population has declined in recent decades, Pittsfield remains the third-largest municipality in Western Massachusetts, behind only Springfield and Chicopee.

Great Barrington is a census-designated place (CDP) located in the town of Great Barrington in Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 2,231 at the 2010 census, out of 7,104 in the entire town of Great Barrington.

Lee is a census-designated place (CDP) located in the town of Lee in Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 2,051 at the 2010 census, out of 5,943 in the entire town of Lee.

Lenox is a town in Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. The town is in Western Massachusetts and part of the Pittsfield Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 5,095 at the 2020 census. Lenox is the site of Shakespeare & Company and Tanglewood, summer home of the Boston Symphony Orchestra. Lenox includes the villages of New Lenox and Lenoxdale, and is a tourist destination during the summer.

The Housatonic River is a river, approximately 149 miles (240 km) long, in western Massachusetts and western Connecticut in the United States. It flows south to southeast, and drains about 1,950 square miles (5,100 km2) of southwestern Connecticut into Long Island Sound.

The Ashuwillticook Rail Trail is a 14.05-mile (22.61 km) rail trail that runs north-south through the towns of Cheshire, Lanesborough and Adams, and into the city of Pittsfield, Massachusetts. It is a multi-use trail for biking, walking, roller-blading, and jogging. The trail is managed by the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation (DCR). It was built on the former Pittsfield and North Adams Railroad.

The Boston and Albany Railroad was a railroad connecting Boston, Massachusetts to Albany, New York, later becoming part of the New York Central Railroad system, Conrail, and CSX Transportation. The mainline is currently used by CSX for freight as the Berkshire Subdivision and Boston Subdivision. Passenger service is provided on the line by Amtrak, as part of their Lake Shore Limited service, and by the MBTA Commuter Rail system, which owns the section east of Worcester and operates it as its Framingham/Worcester Line.
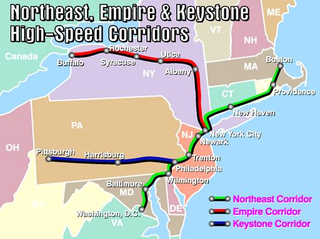
The Empire Corridor is a 461-mile (742 km) passenger rail corridor in New York State running between Penn Station in New York City and Niagara Falls, New York. Major cities on the route include Poughkeepsie, Albany, Schenectady, Amsterdam, Utica, Syracuse, Rochester, and Buffalo. Much of the corridor was once part of the New York Central Railroad's main line.

The Housatonic Railroad is a Class III railroad operating in southwestern New England and eastern New York. It was chartered in 1983 to operate a short section of ex-New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in northwestern Connecticut, and has since expanded north and south, as well as west into New York State.

The Danbury Branch is a diesel branch of the Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line in the U.S. state of Connecticut, running from downtown Norwalk north to Danbury. It opened in 1852 as the Danbury and Norwalk Railroad. Until the early 1970s, passenger service continued north from Danbury to Canaan, Connecticut, and Pittsfield, Massachusetts. Metro-North took over operation of the line from Conrail in 1983, and the modern-day branch is mostly single-tracked.

Route 8 is the portion of the 148 mile multistate New England Route 8 within the state of Massachusetts. The highway runs 66.643 miles (107.252 km) from the Connecticut state line in Sandisfield, where the highway continues as Connecticut Route 8, north to the Vermont state line in Clarksburg, where the highway continues as Vermont Route 8 and VT 100. Route 8 serves several towns in eastern and northern Berkshire County. The highway is the main highway between the cities of Pittsfield and North Adams, where the route intersects Route 9 and Route 2, respectively. Route 8 also intersects U.S. Route 20 in Becket.

The Joseph Scelsi Intermodal Transportation Center is a transit facility located in downtown Pittsfield, Massachusetts, United States. The $11 million facility is named after Joseph Scelsi, a longtime State Representative who represented Pittsfield. Owned by the Berkshire Regional Transit Authority (BRTA), it is serviced by local BRTA bus services, Amtrak intercity rail service, and Peter Pan intercity bus service. The second floor of the building houses two classrooms used by Berkshire Community College and Massachusetts College of Liberal Arts.

The Umpachene River is an 8.3-mile-long (13.4 km) tributary of the Housatonic River in New Marlborough, Massachusetts. Issuing from small ponds and wetlands on the east side of town, it meanders generally westward through mostly wooded areas before emptying into the Konkapot River near the village of Southfield.

The Pittsfield and North Adams Railroad was a railroad based in northwestern Massachusetts. It was chartered in 1842 and was purchased by the Western Railroad of Massachusetts before construction was finished in 1846, then acquired by the Boston and Albany Railroad in 1870, only to face a gradual demise between the 1960s and 1990. It ran 18.539 mi (29.836 km) from North Adams Junction in Pittsfield to North Adams, where it connected to the Troy and Greenfield Railroad, an affiliate of the Fitchburg Railroad.

Great Barrington station is a former railroad station in Great Barrington, Massachusetts along the Housatonic Railroad Berkshire Line.

The Berkshire Flyer is a seasonal Amtrak passenger train service between New York City and the Berkshire Mountains in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, via the Hudson Valley. The weekly train departs Penn Station on Friday and Sunday afternoons during the summer and returns on Sundays. The route's 2023 season began on May 26 and ran through October 9 as the second year of a three-year pilot program.
The Berkshire was a New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad named train running from New York City's Grand Central Terminal to Pittsfield, Massachusetts. It was the longest-running north–south train in Litchfield Hills of western Connecticut and the Berkshires of Massachusetts. From New York City it followed the New Haven Line to South Norwalk, the Danbury Line to Danbury and the Berkshire Division to Pittsfield. It began in the 1940s and ran until 1968. The train was preceded by the Berkshire Express, of c.1938-c.1943. It terminated at Pittsfield Union Station until 1960, when the New Haven moved it to another station in the city.

















