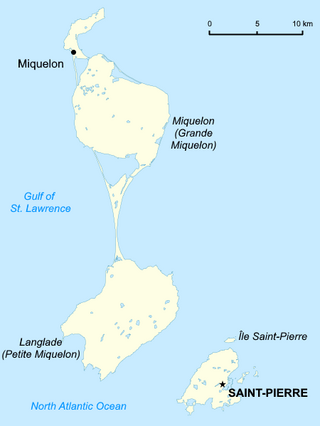
Major Islands’ Areas Mixed With Population
The largest island in area is Miquelon, which has an area of 106km². However, it has a surprisingly low population around 580.
Langlade is the second largest island in terms of area, with 95km². Even though its size is pretty big compared to other islands around the Caribbean, the population is just around 10.
Saint Pierre comes in third by area, being 25km², and it is the largest island by population standards, with 6,000 people. The island houses the capital of the territory, Saint-Pierre, which comprises most of the population.

Saint Pierre and Miquelon, officially the Overseas Collectivity of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, located near the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. An archipelago of eight islands, St. Pierre and Miquelon is a vestige of the once-vast territory of New France. Its residents are French citizens. The collectivity elects its own deputy to the National Assembly and participates in senatorial and presidential elections. It covers 242 km2 (93 sq mi) of land and had a population of 6,008 as of the March 2016 census.
Saint Pierre and Miquelon is a French overseas collectivity in the Western Hemisphere and the Northern Hemisphere. It consists of an island archipelago, off the coast of Newfoundland, near North America. The collectivity shares a maritime boundary with Canada.
The politics of Saint Pierre and Miquelon take place in the framework of a parliamentary representative democratic French overseas collectivity, whereby the President of the Territorial Council is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government.

France is divided into eighteen administrative regions, of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France, while the other five are overseas regions.

Miquelon-Langlade is the larger but less populated of the two communes (municipalities) making up the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, located 22 km (14 mi) to the south of Newfoundland in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. It consists of three geological islands: Miquelon, Langlade and Le Cap, connected with tombolos. The communal seat is the settlement of Miquelon, on the northern tip, where the entire island's permanent population of 580 is located. Miquelon Airport provides flights to Montreal and to nearby Saint-Pierre Airport.
The overseas departments and regions of France are departments of the French Republic which are outside the continental Europe situated portion of France, known as "metropolitan France". The distant parts have exactly the same status as mainland France's regions and departments. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations apply to French overseas regions the same as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas regions cannot themselves pass new laws. On occasion referendums are undertaken to re-assess the sentiment in local status.

The administrative divisions of France are concerned with the institutional and territorial organization of French territory. These territories are located in many parts of the world. There are many administrative divisions, which may have political, electoral (districts), or administrative objectives. All the inhabited territories are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council and their citizens have French citizenship and elect the President of France.
A territorial collectivity, or territorial authority, in many francophone countries, is a legal entity governed by public law that exercises within its territory certain powers devolved to it by the State as part of a decentralization process. In France, it also refers to a chartered administrative division of France with recognized governing authority. It is the generic name for any territory with an elective form of local government and local regulatory authority. The nature of a French territorial collectivity is set forth in Article 72 of the Constitution of France (1958), which provides for local autonomy within limits prescribed by law.

Saint-Pierre is the capital of the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, off the coast of the Canadian island of Newfoundland. Saint-Pierre is the more populous of the two communes (municipalities) making up Saint Pierre and Miquelon.

Langlade Island, also referred to by foreigners as "Little Miquelon", is an island of the French overseas collectivity of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon and forms the southern part of the commune of Miquelon-Langlade.
The galleries below show flags attributed to the eighteen regions, five overseas collectivities, one sui generis collectivity and one overseas territory of France. Most of them are both non-official and traditional as regions often use their logos as a flag though some regions used the banner ol flags.

The flag of Saint Pierre and Miquelon is officially the flag of France, as Saint Pierre and Miquelon is a self-governing overseas collectivity of France.

For elections in the European Union, Overseas Territories was a European Parliament constituency in France until the 2019 European Parliament election. It consisted of all the inhabited French overseas departments and collectivities, even if their territory is not part of the European Union. Constitutionally, all French citizens are also granted the same European citizenship, consequently all of them elected representatives in the European Parliament, independently of their area of residence.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Saint Pierre and Miquelon:

Saint Pierre Island, also spelt as Saint-Pierre Island, is one of the three main islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon. It contains the town of Saint-Pierre, which lies on the island's east coast and is the main population centre of the island group. It is part of an overseas collectivity of France, and is located near the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the French territorial collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
Law enforcement in Saint Pierre and Miquelon is the responsibility of a branch of the French Gendarmerie Nationale. There are two gendarmerie stations in the archipegalo.

Overseas France consists of 13 French territories outside Europe, mostly the remnants of the French colonial empire that remained a part of the French state under various statuses after decolonisation. Most, but not all are part of the European Union.

The Belle River is the largest river in the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon. The river flows through the archipelago's largest island of Miquelon-Langlade, which is formed by a thin strip of land called a tombolo that connects the two northern and southern "islands" of Miquelon and Langlade, respectively. The river is fed by several streams and ponds on Langlade, and flows northwest for the majority of its length. The river's course turns northeast shortly before emptying into the sea on the eastern side of the island in the community of Anse du Gouverneur.













