
The African forest elephant is one of the two living species of African elephant. It is native to humid tropical forests in West Africa and the Congo Basin. It is the smallest of the three living elephant species, reaching a shoulder height of 2.4 m. As with other African elephants, both sexes have straight, down-pointing tusks, which begin to grow once the animals reach 1–3 years old. The forest elephant lives in highly sociable family groups of up to 20 individuals. Since they forage primarily on leaves, seeds, fruit, and tree bark, they have often been referred to as the 'megagardener of the forest'; the species is one of many that contributes significantly to maintaining the composition, diversity and structure of the Guinean Forests of West Africa and the Congolese rainforests. Seeds of various plants will go through the elephant’s digestive tract and eventually pass through in the animal’s droppings, thus helping to maintain the spread and biodiversity of the forests.
J. Michael Fay is an American ecologist and conservationist notable for, among other things, the MegaTransect, in which he spent 455 days walking 2,000 miles across Africa and the MegaFlyover in which he and pilot Peter Ragg spent months flying 70,000 miles in a small plane at low altitude, taking photographs every twenty seconds. Both projects were sponsored by the National Geographic Society, which produced articles and documentaries about the projects.

The bay duiker, also known as the black-striped duiker and the black-backed duiker, is a forest-dwelling duiker native to western and southern Africa. It was first described by British zoologist John Edward Gray in 1846. Two subspecies are identified. The bay duiker is reddish-brown and has a moderate size. Both sexes reach 44–49 cm (17–19 in) at the shoulder. The sexes do not vary considerably in their weights, either; the typical weight range for this duiker is 18–23 kg (40–51 lb). Both sexes have a pair of spiky horns, measuring 5–8 cm (2.0–3.1 in). A notable feature of this duiker is the well-pronounced solid stripe of black extending from the back of the head to the tail.

The blue duiker is a small antelope found in central, southern and eastern Africa. It is the smallest species of duiker. The species was first described by Swedish naturalist Carl Peter Thunberg in 1789. 12 subspecies are identified. The blue duiker reaches 32–41 centimetres (13–16 in) at the shoulder and weighs 3.5–9 kilograms (7.7–19.8 lb). Sexually dimorphic, the females are slightly larger than the males. The dark tail measures slightly above 10 centimetres (3.9 in). It has short, spiky horns, around 5 centimetres (2.0 in) long and hidden in hair tufts. The subspecies show a great degree of variation in their colouration. The blue duiker bears a significant resemblance to Maxwell's duiker.

The Dja River is a stream in west-central Africa. It forms part of Cameroon–Republic of Congo border and has a course of roughly 720 kilometres (450 mi).

The wildlife of Cameroon is composed of its flora and fauna. Bordering Nigeria, it is considered one of the wettest parts of Africa and records Africa's second highest concentration of biodiversity. To preserve its wildlife, Cameroon has more than 20 protected reserves comprising national parks, zoos, forest reserves and sanctuaries. The protected areas were first created in the northern region under the colonial administration in 1932; the first two reserves established were Mozogo Gokoro Reserve and the Bénoué Reserve, which was followed by the Waza Reserve on 24 March 1934. The coverage of reserves was initially about 4 percent of the country's area, rising to 12 percent; the administration proposes to cover 30 percent of the land area.
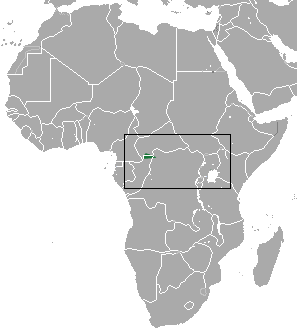
The Ugandan musk shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in Uganda, the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Central African Republic. Its range, population size and habits are poorly known.
The Central African Republic has seen a decrease in tourism due to its recent history of conflict, unrest, instability as well as the insecurity in certain areas of the country, particularly the north and northwest.

Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park is a national park in the Republic of the Congo. Established in 1993, in the northern provinces of Congo, it is home to forest elephants, great apes, including western lowland gorillas and the eastern sub-species of chimpanzees and bongo. It is 3,921.61 km2 (1,514.14 sq mi) of pristine tropical rainforest with no human habitation within it and with human population densities in its periphery that are comparatively low for the sub-region. The forests have a rich biodiversity of 300 bird species, plus 1,000 plant and tree species which include endangered mahoganies.

Lobéké National Park is a national park of southeastern Cameroon within the Moloundou Arrondissement of East Province. Located in the Congo Basin, it is bounded on the east by the Sangha River which serves as Cameroon's international border with Central African Republic and the Republic of the Congo. It is adjacent to two other reserves in the CAR and Congo. To the northwest is Boumba Bek National Park, another national park in Cameroon's East Province.

The Dzanga-Sangha Special Reserve is a protected reserve of southwestern Central African Republic. It was established in 1990 and covers 6,865.54 km2 (2,650.80 sq mi). It is one of several areas within the Dzanga-Sangha Complex of Protected Areas (DSCPA), each within its own protective status and along with Lobéké National Park in Cameroon and Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park in Republic of Congo, it is part of the Sangha Trinational Landscape. Other areas within the DSCPA include the Dzanga Ndoki National Park which has two sectors, the 495 km2 (191 sq mi) Dzanga park and the 725 km2 (280 sq mi) Ndoki park. A conference of the Ministers of Forests of Central African Forest Commission (COMIFAC) had resolved to establish within the Congo basin, the Sangha River Tri-national Protected area (STN) encompassing these three parks. The forest special reserve is operated by the Central African Forest Commission (COMIFAC).
The Dzanga-Ndoki National Park is located in the southwestern extremity of the Central African Republic. Established in 1990, the national park is 1,143.26 square kilometres (441.42 sq mi). The national park is split into two non-continuous sectors, the northern Dzanga sector 49,500 ha and the southern Ndoki sector 72,500 ha. Notable in the Dzanga sector is a gorilla density of 1.6/km2 (4.1/sq mi), one of the highest densities ever reported for the western lowland gorilla.

The Dzanga-Sangha Complex of Protected Areas (DSPAC) is a protected area in the extreme southwestern Central African Republic. The dense forest block, created in 1990, measures 4,589 km2 (1,772 sq mi). It consists of the Dzanga-Sangha Special Reserve and the Dzanga Ndoki National Park which has two sectors, the 495 km (308 mi) Dzanga Park and the 725 km (450 mi) Ndoki Park. Since their gazetting, management of the park and the reserve has been under the Dzanga-Sangha project, a collaborative effort of the country's government, the GTZ/LUSO, a German technical agency, and the World Wildlife Fund. Financial and technical assistance have been provided by the German and United States governments, the World Bank, and several private organizations and donors.

The wildlife of the Central African Republic is in the vast natural habitat in the Central African Republic (CAR) located between the Congo Basin's rain forests and large savannas, where the human density was smaller than 0.5 per km2 prior to 1850. The forest area of 22.755 million, considered one of the richest storehouses of wildlife spread over national parks, hunting reserves and community hunting areas, experienced an alarming loss of wildlife because of greed for ivory and bushmeat exploitation by hunters – mostly Arab slavers from across the borders of the Central African Republic with Chad and Sudan.
The Central African Forest Commission is an intergovernmental organisation in Central Africa. Its goal is to manage the forests of Central Africa in a sustainable manner and is supported by the wildlife trade monitoring network TRAFFIC. The secretariat is based in Yaoundé, Cameroon. Raymond Mbitikon serves as its Executive Secretary.

Sangha Trinational is a forest divided between the nations of Central African Republic, Cameroon and Congo-Brazzaville. It was added as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2012 because of its outstanding biodiversity and unique biological communities. The site includes 3 contiguous national parks within the humid tropical forests of Central Africa: Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park in Congo, Lobéké National Park in Cameroon, and Dzanga-Ndoki National Park in Central African Republic. The large size of the site and the relatively limited amount of deforestation within the three parks has allowed populations of vulnerable species such as African forest elephants, gorillas, sitatunga, and chimpanzees to thrive. In addition, populations of critically endangered plant species such as Mukulungu are protected within the site's borders.

The Northwestern Congolian lowland forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion that spans Cameroon, Gabon, the Republic of Congo, the Central African Republic and a minuscule part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It forms part of the larger Congolian rainforests region in Central Africa. The region is noteworthy for very high levels of species richness and endemism. It is home to a core population of the critically endangered Western lowland gorilla. There are also large populations of forest elephants.

Bayanga is a town and sub-prefecture of Sangha-Mbaéré in the Central African Republic. It is one of the few tourist destinations in the country.
Mossapoula, also spelled Moussapola or Mossapola, is a village situated near Bayanga town in Sangha-Mbaéré Prefecture, Central African Republic.