
Polymastia is a genus of sea sponges containing about 30 species. These are small to large encrusting or dome-shaped sponges with a smooth surface having many teat-shaped projections (papillae). In areas of strong wave action, this genus does not grow the teat structures, but instead grows in a corrugated form.

Halichondriidae is a family of sea sponges belonging to the order Suberitida. These sponges have a skeleton consisting of dense bundles of spicules occurring in a more or less random pattern.

Spongia is a genus of marine sponges in the family Spongiidae, originally described by Carl Linnaeus in 1759, containing more than 60 species. Some species, including Spongia officinalis, are used as cleaning tools, but have mostly been replaced in that use by synthetic or plant material.

Ircinia strobilina is a species of sponge in the family Irciniidae. It is grey or shiny black in colour, with spiny structures (conules) dotting the surface. The spiny structures are interconnected by ridges, though not arranged in an orderly lattice. This species is globular and massive in shape, but usually no more than 0.3 metres (1 ft) across. I. strobilina is lobed and spherical and has a tough consistency. The large excurrent pores are located in depressions at the top of the sponge. Many smaller incurrent pores are scattered across the surface, more densely at the sides.

Tethya is a genus of sea sponges belonging to the family Tethyidae. Members of this genus all have a spherical body form and some are known to be able to move at speeds of between 1 and 4 mm per day.

Clathria is a large genus of demosponges in the family Microcionidae.

Haliclona is a genus of demosponges in the family Chalinidae.

Ircinia is a genus of sea sponges in the family Irciniidae.

Spongia officinalis, better known as a variety of bath sponge, is a commercially used sea sponge. Individuals grow in large lobes with small openings and are formed by a mesh of primary and secondary fibers. It is light grey to black in color. It is found throughout the Mediterranean Sea up to 100 meters deep on rocky or sandy surfaces.

Amphimedon compressa, the erect rope sponge, red tree sponge, red tubular sponge, or red sponge is a demosponge found in southern Florida, the Caribbean Sea, and the Bahamas. It can be deep red, orange, brown, or black.
Ptilocaulis is a genus of demosponges. The species within this genus are usually red or orange. They are often called tree sponges, as they grow many branches from a single stem resembling trees. They can grow to large size.
Terpios is a genus of sea sponges belonging to the family Suberitidae.

Agelas is a genus of sea sponge in the class Demospongiae.

Callyspongia is a genus of demosponges in the family Callyspongiidae.
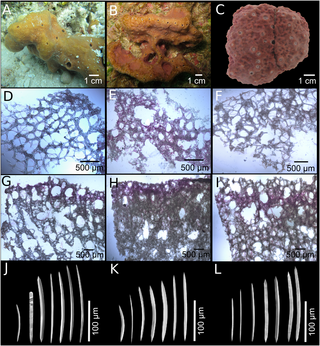
Neopetrosia proxima is a species of marine petrosiid sponge native to the tropical and subtropical waters of the western Atlantic Ocean.
Neopetrosia is a genus of marine petrosiid sponges. It was first established by the American spongiologist Max Walker de Laubenfels in 1932. It contains these 27 species:

Aplysina is a genus of sea sponges in the order Verongiida. It was first authenticated and described by Giovanni Domenico Nardo in 1834.

Mycale is a genus of demosponge with 240 recognised species in 11 subgenera. It has been a large genus with multiple subdivisions since it was first described in 1867.

Phorbas is a genus of demosponges belonging to the family Hymedesmiidae.




















