
Design by contract (DbC), also known as contract programming, programming by contract and design-by-contract programming, is an approach for designing software.
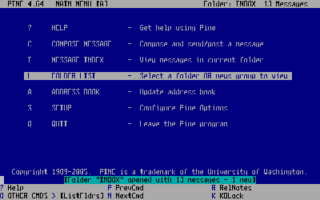
Pine is a freeware, text-based email client which was developed at the University of Washington. The first version was written in 1989, and announced to the public in March 1992. Source code was available for only the Unix version under a license written by the University of Washington. Pine is no longer under development, and has been replaced by the Alpine client, which is available under the Apache License.
Trade dress is the characteristics of the visual appearance of a product or its packaging that signify the source of the product to consumers. Trade dress is an aspect of trademark law, which is a form of intellectual property protection law.

The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark registration authority for the United States. The USPTO's headquarters are in Alexandria, Virginia, after a 2005 move from the Crystal City area of neighboring Arlington, Virginia.
A trademark is a word, phrase, or logo that identifies the source of goods or services. Trademark law protects a business' commercial identity or brand by discouraging other businesses from adopting a name or logo that is "confusingly similar" to an existing trademark. The goal is to allow consumers to easily identify the producers of goods and services and avoid confusion.

GPE is a graphical user interface environment for handheld computers, such as palmtops and personal digital assistants (PDAs), running some Linux kernel-based operating system. GPE is a complete environment of software components and applications which makes it possible to use a Linux handheld for tasks such as personal information management (PIM), audio playback, email, and web browsing.
DWG is a proprietary binary file format used for storing two- and three- dimensional design data and metadata. It is the native format for several CAD packages including DraftSight, AutoCAD, BricsCAD, IntelliCAD, Caddie and Open Design Alliance compliant applications. In addition, DWG is supported non-natively by many other CAD applications. The .bak, .dws, .dwt and .sv$ files are also DWG files.

Joseph Enterprises, Inc is a gadget company which is owned by Joseph Pedott and based in San Francisco, California, United States, North America. Two of their most popular products are The Clapper and the Chia Pet.

In the United States, a design patent is a form of legal protection granted to the ornamental design of an article of manufacture. Design patents are a type of industrial design right. Ornamental designs of jewelry, furniture, beverage containers and computer icons are examples of objects that are covered by design patents.

Canadian trademark law provides protection to marks by statute under the Trademarks Act and also at common law. Trademark law provides protection for distinctive marks, certification marks, distinguishing guises, and proposed marks against those who appropriate the goodwill of the mark or create confusion between different vendors' goods or services. A mark can be protected either as a registered trademark under the Act or can alternately be protected by a common law action in passing off.

The United States Air Force Symbol is the symbol of the United States Air Force. It was introduced in January 2000. Guidelines that outlined appropriate uses for the new Air Force symbol were released March 23. The symbol was first tested on gates and water towers in August.
"I've fallen, and I can't get up!" is a catchphrase of the late 1980s and early 1990s popular culture based upon a line from a United States-based television commercial.
Trademark distinctiveness is an important concept in the law governing trademarks and service marks. A trademark may be eligible for registration, or registrable, if it performs the essential trademark function, and has distinctive character. Registrability can be understood as a continuum, with "inherently distinctive" marks at one end, "generic" and "descriptive" marks with no distinctive character at the other end, and "suggestive" and "arbitrary" marks lying between these two points. "Descriptive" marks must acquire distinctiveness through secondary meaning—consumers have come to recognize the mark as a source indicator—to be protectable. "Generic" terms are used to refer to the product or service itself and cannot be used as trademarks.
Proprietary software, also known as non-free software or closed-source software, is computer software for which the software's publisher or another person reserves some licensing rights to use, modify, share modifications, or share the software, restricting user freedom with the software they lease. It is the opposite of open-source or free software. Non-free software sometimes includes patent rights.

A trademark is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression that identifies products or services from a particular source and distinguishes them from others. The trademark owner can be an individual, business organization, or any legal entity. A trademark may be located on a package, a label, a voucher, or on the product itself. Trademarks used to identify services are sometimes called service marks.

The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.
Iran is a member of the WIPO since 2001 and has acceded to several WIPO intellectual property treaties. Iran joined the Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property in 1959. In December 2003 Iran became a party to the Madrid Agreement and the Madrid Protocol for the International Registration of Marks. In 2005 Iran joined the Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration, which ensures the protection of geographical names associated with products. As at February 2008 Iran had yet to accede to The Hague Agreement for the Protection of Industrial Designs.
Typefaces, fonts, and their glyphs raise intellectual property considerations in copyright, trademark, design patent, and related laws. The copyright status of a typeface—and any font file that describes it digitally—varies between jurisdictions. In the United States, the shapes of typefaces are not eligible for copyright, though the shapes may be protected by design patent. Typefaces can be protected in other countries, including the UK, Germany, and France, by industrial design protections that are similar to copyright or design patent in that they protect the abstract shapes. Additionally, in the US and in some other countries, computer fonts—the digital instantiation of the shapes as vector outlines—may be protected by copyright on the computer code that produces them. The name of a typeface may also be protected as a trademark.
The Madrid system, or Madrid Protocol is the primary international system for facilitating the registration of trademarks in multiple jurisdictions around the world. Its legal basis is the multilateral treaty Madrid Agreement Concerning the International Registration of Marks of 1891, as well as the Protocol Relating to the Madrid Agreement (1989).
An unregistered trademark or common law trademark is an enforceable mark created by a business or individual to signify or distinguish a product or service. It is legally different from a registered trademark granted by statute.









