Related Research Articles

The New Zealand Qualifications Authority is the New Zealand government Crown entity tasked with administering educational assessment and qualifications. It was established by the Education Act 1989.
David Vernon Williams is a professor, and former deputy dean of the University of Auckland's Faculty of Law. He comes from the Hawke's Bay region of New Zealand, and was educated at Wanganui Collegiate School.

The Royal Society Te Apārangi is an independent, statutory not-for-profit body in New Zealand providing funding and policy advice in the fields of sciences and the humanities.

Linda Tuhiwai Te Rina Smith was a professor of indigenous education at the University of Waikato in Hamilton, New Zealand and is now Distinguished Professor at Te Whare Wānanga o Awanuiārangi. The daughter of Sidney Moko Mead, she affiliates to the Ngāti Awa and Ngāti Porou iwi.
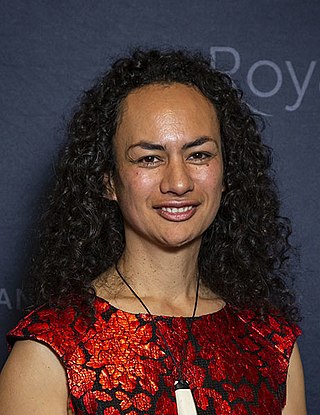
Ocean Ripeka Mercier is a New Zealand academic specialising in physics and Māori science.

Graham Hingangaroa Smith is a New Zealand Māori academic and educationalist of Ngāti Porou, Ngāi Tahu, Ngāti Apa and Ngāti Kahungunu descent. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society Te Apārangi.

Siouxsie Wiles is a British microbiologist and science communicator. Her specialist areas are infectious diseases and bioluminescence. She is based in New Zealand.
Elizabeth Mary Rata is a New Zealand academic who is a sociologist of education and a professor in the School of Critical Studies in Education at the University of Auckland. Her views and research on Māori education and the place of indigenous knowledge in the New Zealand education system have received criticism from other academics.
Jacqueline Rae Beggs, is a New Zealand entomologist and ecologist specialising in biodiversity and biosecurity.

Rangiānehu Mātāmua is a New Zealand indigenous studies and Māori cultural astronomy academic and is Professor of Mātauranga Māori at Massey University. He is Māori, of Tūhoe descent. He is the first Māori to win a Prime Minister's Science Prize, is a Fellow of the Royal Society Te Apārangi, and is the chief advisor to the New Zealand Government on the public holiday Matariki.

Shaun Cameron Hendy is a New Zealand physicist. He is currently a professor at the University of Auckland and was the first director of Te Pūnaha Matatini, a centre of research excellence in complex systems and data analytics. During the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand, he led a team of scientists developing mathematical models of the spread of the virus across the country that influenced the government's response to the outbreak.
Mātauranga is a modern term for the traditional knowledge of the Māori people of New Zealand. Māori traditional knowledge is multi-disciplinary and holistic, and there is considerable overlap between concepts. It includes environmental stewardship and economic development, with the purpose of preserving Māori culture and improving the quality of life of the Māori people over time.
Garth James Smith Cooper is a New Zealand academic biochemist, and as of 2021 is a full professor at the University of Auckland.
Douglas Mark Elliffe is a New Zealand psychology academic, and as of 2021 is a full professor at the University of Auckland.
Robert Nola was a New Zealand philosophy academic, and was an Emeritus Professor in the Department of Philosophy at the University of Auckland. His work focussed on the philosophy and history of science, on epistemology and on metaphysics.

John Scott Werry is a New Zealand psychiatry academic and as of 2021 is an emeritus professor at the University of Auckland.
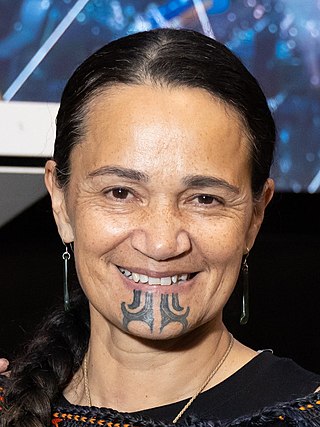
Waikaremoana Waitoki, also known as Moana Waitoki, is a New Zealand clinical psychologist, academic, and former president of the New Zealand Psychological Society from 2020 until 2022. She is a senior lecturer at the University of Waikato, and focuses her research on indigenous psychology, Mātauranga Māori and cultural competency.
The New Zealand Free Speech Union (FSU) is an organisation that advocates for freedom of speech. It was formed as the Free Speech Coalition in 2018 and relaunched as the Free Speech Union in 2021.
Tara G McAllister is a New Zealand freshwater ecology academic and is associated with Te Pūnaha Matatini at the University of Auckland. She is a Māori of Te Aitanga ā Māhaki and Ngāti Porou descent.
Ngā Pae o te Māramatanga (NPM) is New Zealand's Māori Centre of Research Excellence (CoRE). It was established in 2002 and is hosted by the University of Auckland with 21 research partners and is funded, like other CoRE's, by the Tertiary Education Commission. The mission was to conduct research for, with and by Māori communities which leads to transformation and positive change.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Kendall Clements, Garth Cooper, Michael Corballis, Doug Elliffe, Robert Nola, Elizabeth Rata, and John Werry. “In Defence of Science.” New Zealand Listener , 31 July 2021. p.4. The text of their letter was republished online at 'In Defence of Science Article', with a claim of permission
- ↑ "Seven planned changes to strengthen NCEA". NCEA Education. Ministry of Education. Archived from the original on 16 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ "Change 2 – Equal status for mātauranga Māori in NCEA". NCEA Education. Ministry of Education. Archived from the original on 20 May 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 Sachdeva, Sam (18 November 2021). "Royal Society investigation into mātauranga Māori letter sparks academic debate". Newsroom . Archived from the original on 17 November 2021. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ↑ "Statement in relation to complaints about a letter to the New Zealand Listener". www.royalsociety.org.nz. 11 March 2022. Retrieved 13 March 2022.
- ↑ Dunlop, Māni (28 July 2021). "University academics' claim mātauranga Māori 'not science' sparks controversy". Radio New Zealand . Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ↑ "Vice-Chancellor comments – The University of Auckland". University of Auckland. 26 July 2021. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ↑ "University academics' claim that mātauranga Māori is 'not science' sparks controversy". Stuff . 24 July 2021. Archived from the original on 29 December 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ↑ "Joint statement from President and Chair of Academy Executive Committee". Royal Society Te Apārangi. 27 July 2021. Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ↑ "Mātauranga and Science" (PDF). New Zealand Association of Scientists. 27 July 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 October 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- 1 2 Henry, Dubby (28 July 2021). "Professors slammed for letter claiming Māori knowledge is not science". Newstalk ZB . Archived from the original on 28 October 2021.
- ↑ Ngata, Tina (25 July 2021). "Defence of colonial racism". www.tinangata.com. Archived from the original on 21 November 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ↑ Wiggins, Amy (29 July 2021). "Experts Shaun Hendy and Siouxsie Wiles among those rejecting claim Māori knowledge isn't science as 'scientific racism'". The New Zealand Herald . Archived from the original on 7 November 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ Sowmand-Lund, Stewart (30 July 2021). "Live updates, July 30: 2,000 sign open letter response on mātauranga Māori and science". The Spinoff . Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ "Paul Goldsmith: Mātauranga Māori shouldn't be taught at the expense of science". Newstalk ZB . 30 July 2021. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ↑ Coyne, Jerry (3 December 2021). ""Ways of knowing": New Zealand pushes to have "indigenous knowledge" (mythology) taught on parity with modern science in science class". Why Evolution is True. Archived from the original on 26 December 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ Dawkins, Richard (4 December 2021). "Myths Do Not Belong in Science Classes: Letter to the Royal Society of New Zealand". Richard Dawkins Foundation for Reason & Science. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ Young, Toby (4 December 2021). "Why punish a scientist for defending science?". The Spectator . Archived from the original on 24 December 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ New Zealand Free Speech Union (17 November 2021). "Exclusive: Royal Society Is Investigating Academics For Defending Science". Scoop. Archived from the original on 23 November 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ Johnston, Michael; Kierstead, James; Lillis, David; Schwerdtfeger, Peter; White, Lindsey; Boyd, Brian (23 December 2021). "Academics: Don't stifle healthy debate". Newsroom . Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ Freshwater, Dawn (14 December 2021). "Statement from the Vice-Chancellor on mātauranga Māori and science". University of Auckland. Archived from the original on 14 December 2021. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- 1 2 "University of Auckland to host mātauranga Māori symposium". The New Zealand Herald . 14 December 2021. Archived from the original on 8 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ↑ Mayron, Sapeer (13 March 2022). "Controversial 'Listener letter' deemed not worthy of Royal Society investigation". Stuff . Retrieved 13 March 2022.