An autonomous building is a building designed to be operated independently from infrastructural support services such as the electric power grid, gas grid, municipal water systems, sewage treatment systems, storm drains, communication services, and in some cases, public roads.

Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to as distributed energy resources (DER).

An Earthship is a style of architecture developed in the late 20th century to early 21st century by architect Michael Reynolds. Earthships are designed to behave as passive solar earth shelters made of both natural and upcycled materials such as earth-packed tires. Earthships may feature a variety of amenities and aesthetics, and are designed to withstand the extreme temperatures of a desert, managing to stay close to 70 °F (21 °C) regardless of outside weather conditions. Earthship communities were originally built in the desert of northern New Mexico, near the Rio Grande, and the style has spread to small pockets of communities around the globe, in some cases in spite of legal opposition to its construction and adoption.
Energy demand management, also known as demand-side management (DSM) or demand-side response (DSR), is the modification of consumer demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and behavioral change through education.

Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand.
A microgrid is a local electrical grid with defined electrical boundaries, acting as a single and controllable entity. It is able to operate in grid-connected and in island mode. A 'stand-alone microgrid' or 'isolated microgrid' only operates off-the-grid and cannot be connected to a wider electric power system. Very small microgrids are called nanogrids.

Off-the-grid or off-grid is a characteristic of buildings and a lifestyle designed in an independent manner without reliance on one or more public utilities. The term "off-the-grid" traditionally refers to not being connected to the electrical grid, but can also include other utilities like water, gas, and sewer systems, and can scale from residential homes to small communities. Off-the-grid living allows for buildings and people to be self-sufficient, which is advantageous in isolated locations where normal utilities cannot reach and is attractive to those who want to reduce environmental impact and cost of living. Generally, an off-grid building must be able to supply energy and potable water for itself, as well as manage food, waste and wastewater.

Microgeneration is the small-scale production of heat or electric power from a "low carbon source," as an alternative or supplement to traditional centralized grid-connected power.
Kommune Niederkaufungen is one of the largest intentional communities in Germany. Founded in 1986, it is an egalitarian, left-wing, income-sharing commune with consensus decision-making. It is situated in a complex of former farm buildings in the historic centre of the village of Niederkaufungen (Kaufungen), seven kilometres from the city of Kassel (Hessen). It has grown from 15 founder members to 62 adults and nearly 20 children and teenagers (2009). It is a member of "Kommuja", the German network of political communes and egalitarian communities.

An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power over long distances, and finally electric power distribution to customers. In that last step, voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage. Power stations are typically built close to energy sources and far from densely populated areas. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the power grid.

A solar-powered refrigerator is a refrigerator which runs on energy directly provided by sun, and may include photovoltaic or solar thermal energy.

Husk Power Systems, founded in 2008, is a company based in Fort Collins, Colorado, US, that provides clean energy services to off-grid or weak grid rural communities in East Africa, West Africa and South Asia, primarily by building renewable energy mini-grids/micro-grids. Its original technology generated electricity using a biomass gasifier that created fuel from rice husks, a waste product of rice hullers that separate the husks as chaff from the rice, a staple food in both Asia and Africa. In the mid-2010s, with the rapid decline in the price of solar PV and batteries, Husk pivoted its business model to focus more on solar-plus-storage mini-grids, while continuing to use biomass in combination with solar to serve communities with larger electricity demand. In 2021, Husk Power was recognized in the REN21 Renewables Global Status Report as the first mini-grid company to achieve significant scale, by surpassing 100 solar hybrid community mini-grids, and 5,000 small business customers. In 2022, Husk signed an Energy Compact with the United Nations, in which it set a target of building 5,000 mini-grids and connecting at least 1 million customers by 2030.
Zero-carbon housing is housing that does not emit greenhouse gasses (GHGs) into the atmosphere, either directly, or indirectly due to consumption electricity produced using fossil fuels. Most commonly zero-carbon housing is taken to mean zero emissions of carbon dioxide, which is the main climate pollutant from homes, although fugitive methane may also be emitted from natural gas pipes and appliances.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to solar energy:
Passive survivability refers to a building's ability to maintain critical life-support conditions in the event of extended loss of power, heating fuel, or water. This idea proposes that designers should incorporate ways for a building to continue sheltering inhabitants for an extended period of time during and after a disaster situation, whether it be a storm that causes a power outage, a drought which limits water supply, or any other possible event.
A captive power plant, also called autoproducer or embedded generation, is an electricity generation facility used and managed by an industrial or commercial energy user for their own energy consumption. Captive power plants can operate off-grid or they can be connected to the electric grid to exchange excess generation.
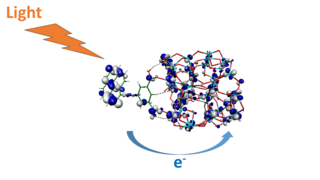
Solar energy conversion describes technologies devoted to the transformation of solar energy to other (useful) forms of energy, including electricity, fuel, and heat. It covers light-harvesting technologies including traditional semiconductor photovoltaic devices (PVs), emerging photovoltaics, solar fuel generation via electrolysis, artificial photosynthesis, and related forms of photocatalysis directed at the generation of energy rich molecules.

Home energy upgrades from public utilities are added home energy efficiency and renewable energy features planned or installed by public utilities. Help from a public utility can make it easier for a homeowner to select, install or operate climate-friendly components. The utility might assist with coordinated use of utility-supplied energy, building features, financing, operating options and neighborhood supplied energy.

A mini-grid is an aggregation of electrical loads and one or more energy sources operating as a single system providing electricity and possibly heat, isolated from a main power grid. A modern mini-grid may include renewable- and fossil fuel-based power generation, energy storage, and load control. A mini grid can be fully isolated from the main grid or interconnected to it. If it is interconnected to the main grid, it must also be able to isolate (“island”) from the main grid and continue to serve its customers while operating in an island or autonomous mode. Mini-grids are used as a cost-effective solution for electrifying rural communities where a grid connection is challenging in terms of transmission and cost for the end user population density, with mini-grids often used to electrify rural communities of a hundred or more households that are 10 km or more from the main grid.













