
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in the mesosomes of cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words χλωρός, khloros and φύλλον, phyllon ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light.

Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC.
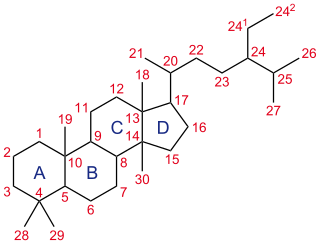
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes which alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene.
Synthesis or synthesize may also refer to:

Lobelia is a genus of flowering plants comprising 415 species, with a subcosmopolitan distribution primarily in tropical to warm temperate regions of the world, a few species extending into cooler temperate regions. They are known generally as lobelias.
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or better bioactivity.
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.

Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin by humans, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).

Isopentenyl pyrophosphate is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway and in the non-mevalonate MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids.

Stilbenoids are hydroxylated derivatives of stilbene. They have a C6–C2–C6 structure. In biochemical terms, they belong to the family of phenylpropanoids and share most of their biosynthesis pathway with chalcones. Most stilbenoids are produced by plants, and the only known exception is the antihelminthic and antimicrobial stilbenoid, 2-isopropyl-5-[(E)-2-phenylvinyl]benzene-1,3-diol, biosynthesized by the Gram-negative bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens.
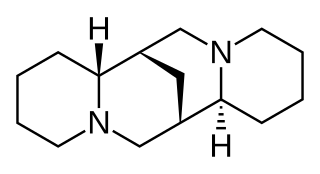
Sparteine is a class 1a antiarrhythmic agent; a sodium channel blocker. It is an alkaloid and can be extracted from scotch broom. It is the predominant alkaloid in Lupinus mutabilis, and is thought to chelate the bivalent cations calcium and magnesium. It is not FDA approved for human use as an antiarrhythmic agent, and it is not included in the Vaughan Williams classification of antiarrhythmic drugs.
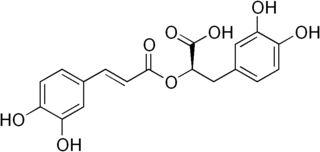
Rosmarinic acid, named after rosemary, is a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, including rosemary, perilla, sage, mint, and basil.
Pyrimidine biosynthesis occurs both in the body and through organic synthesis.

Lobeline is a pyridine alkaloid found in a variety of plants, particularly those in the genus Lobelia, including Indian tobacco, Devil's tobacco, great lobelia, Lobelia chinensis, and Hippobroma longiflora. In its pure form, it is a white amorphous powder which is freely soluble in water.

Sir Alan Rushton Battersby was an English organic chemist best known for his work to define the chemical intermediates in the biosynthetic pathway to vitamin B12 and the reaction mechanisms of the enzymes involved. His research group was also notable for its synthesis of radiolabelled precursors to study alkaloid biosynthesis and the stereochemistry of enzymic reactions. He won numerous awards including the Royal Medal in 1984 and the Copley Medal in 2000. He was knighted in the 1992 New Year Honours. Battersby died in February 2018 at the age of 92.

In enzymology, a homocitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Hippobroma longiflora, also called Star of Bethlehem or madamfate, is a flowering plant in the family Campanulaceae. It is the only species in the genus Hippobroma. It is endemic to the West Indies, but has become naturalized across the American tropics and Oceania.
In enzymology, a beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Piperidine alkaloids are naturally occurring chemical compounds from the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from piperidine.














