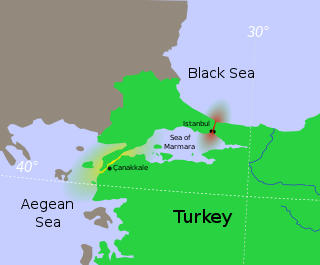
The Bosporus or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul, Turkey. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and forms one of the continental boundaries between Asia and Europe. It also divides Turkey by separating Asia minor from Thrace. It is the world's narrowest strait used for international navigation.

The Dardanelles, also known as the Strait of Gallipoli and in Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont, is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey. Together with the Bosporus, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits.

The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about 2,500,000 km2 (970,000 sq mi), representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only 14 km (9 mi) wide.

The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa. The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles at its narrowest point. Ferries cross between the two continents every day in as little as 35 minutes. The Strait's depth ranges between 300 and 900 metres.

The Anatolian side of Turkey is the largest portion in the country that bridges southeastern Europe and west Asia. East Thrace, the European portion of Turkey comprises 3% of the landmass but over 15% of the population. East Thrace is separated from Asia Minor, the Asian portion of Turkey, by the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles. İskilip, Çorum province, is considered to be the geographical center of Earth. Turkey is very vulnerable to earthquakes.

A monsoon is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains.

The Sea of Azov is an inland shelf sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow Strait of Kerch, and sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea. The sea is bounded by Russia on the east, and by Ukraine on the northwest and southwest. It is an important access route for Central Asia, from the Caspian Sea via the Volga–Don Canal.

The mistral is a strong, cold, northwesterly wind that blows from southern France into the Gulf of Lion in the northern Mediterranean. It produces sustained winds averaging 31 miles an hour, sometimes reaching 60 miles an hour. It can last for several days. Periods of the wind exceeding 30 km/h for more than sixty-five hours have been reported. It is most common in the winter and spring, and strongest in the transition between the two seasons.

A Foehn, or Föhn, is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes. As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes.
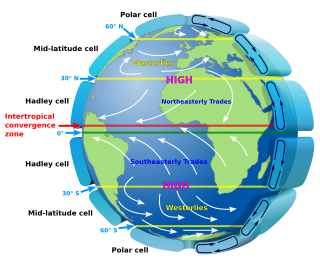
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller-scale weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory.

The stone pine, botanical name Pinus pinea, also known as the Italian stone pine, Mediterranean stone pine, umbrella pine and parasol pine, is a tree from the pine family (Pinaceae). The tree is native to the Mediterranean region, occurring in Southern Europe and the Levant. The species was introduced into North Africa millennia ago, and is also naturalized in the Canary Islands, South Africa and New South Wales.

The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled European colonization of the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.

In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze-land breeze cycle is the most important cause of the prevailing wind. In areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow. Wind direction at any given time is influenced by synoptic-scale and mesoscale weather like pressure systems and fronts. Local wind direction can also be influenced by microscale features like buildings.
The etesians, meltemia, or meltem (Turkish) are the strong, dry north winds of the Aegean Sea, which blow periodically from about mid-May to mid-September. The Etesian winds are a dominant weather influence in the Aegean Basin.

The libeccio is the westerly or south-westerly wind which predominates in northern Corsica all year round; it frequently raises high seas and may give violent westerly squalls. In summer it is most persistent, but in winter it alternates with the Tramontane. The word libeccio is Italian, coming from Greek through Latin, and originally means "Libyan".

The naval Battle of the Dardanelles took place on 22 May 1807 as a part of the Napoleonic Wars during the Russo-Turkish War of 1806–1812. It was fought between the Russian and Ottoman navies near the Dardanelles Strait.

The Turkish Straits are two internationally significant waterways in northwestern Turkey. The Straits create a series of international passages that connect the Aegean and Mediterranean seas to the Black Sea. They consist of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The straits are on opposite ends of the Sea of Marmara. The straits and the Sea of Marmara are part of the sovereign sea territory of Turkey and are treated as Turkish internal waters.

Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology.

The levant is an easterly wind that blows in the western Mediterranean Sea and southern France, an example of mountain-gap wind. In Roussillon it is called "llevant" and in Corsica "levante". In the western Mediterranean, particularly when the wind blows through the Strait of Gibraltar, it is called the Viento de Levante or the Levanter. It is also known as the Solano.














