Natural rubber, also called by other names of India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, caucho or caoutchouc, as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds, plus water. Thailand and Indonesia are two of the leading rubber producers. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers.

Leopold II was King of the Belgians from 1865 to 1909. Born in Brussels as the second but eldest surviving son of Leopold I and Louise of Orléans, he succeeded his father to the Belgian throne in 1865 and reigned for 44 years until his death – the longest reign of any Belgian monarch. He died without surviving sons. The current Belgian king descends from his nephew and successor, Albert I.

The Congo Free State, also known as the Independent State of the Congo, was a large state in Central Africa from 1885 to 1908. It was ruled personally by Leopold II and not by the government of Belgium, of which he was the constitutional monarch. Leopold II was able to procure the region by convincing other Eurasian states at the Berlin Conference that he was involved in humanitarian and philanthropic work and would not tax trade. Via the International Association of the Congo, he was able to lay claim to most of the Congo basin. On 29 May 1885, after the closure of the Berlin Conference, the king announced that he planned to name his possessions "the Congo Free State", an appellation which was not yet used at the Berlin Conference and which officially replaced "International Association of the Congo" on 1 August 1885. The Congo Free State operated as a corporate state privately controlled by Leopold II, although he never personally visited the state.

The French Congo or Middle Congo was a French colony which at one time comprised the present-day area of the Republic of the Congo and parts of Gabon, and the Central African Republic. In 1910, it was made part of the larger French Equatorial Africa.

King Leopold's Ghost: A Story of Greed, Terror and Heroism in Colonial Africa (1998) is a best-selling popular history book by Adam Hochschild that explores the exploitation of the Congo Free State by King Leopold II of Belgium between 1885 and 1908, as well as the large-scale atrocities committed during that period. The book succeeded in increasing public awareness of these Belgian colonial crimes.

Belgium controlled two colonies during its history, the Belgian Congo from 1908 to 1960, and Ruanda-Urundi from 1922 to 1962. It also had a concession in China, and was a co-administrator of the Tangier International Zone in Morocco.
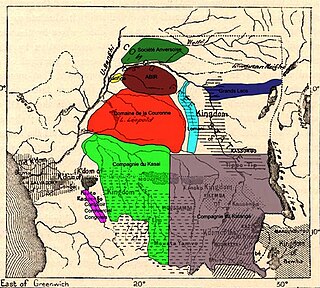
The Société Anversoise was a concession company of the Congo Free State, headquartered in Antwerp. It was, with the Lulonga Company and the Abir Congo Company, one of the main producers of rubber in the Free State. Alongside Abir and the Lulonga Company the Société Anversoise handed back control of the concession to the Congo Free State in 1906. The Société Anversoise merged with Abir in 1911 to form the Compagnie du Congo Belge with a focus of the management of rubber plantations instead of the harvesting of naturally occurring rubber. The Société Anversoise was quoted on the Antwerp Stock Exchange from 27 July 1898.

The Lomani Company was a concession company of the Congo Free State. In the colonial era, the Lomami Company forced the people of the Lomami River region from Opala and Lokilo down to Ilambi to collect large amounts of rubber. The Mbole people of the region vividly described their view of the effect of this work with the phrase wando wo limolo, meaning "tax-caused loss of weight".

The Lulonga Company was a concession company of the Congo Free State. It was, with the Société Anversoise and the Abir Congo Company, one of the main producers of rubber in the Free State. The company's rubber production declined in the early 20th century as a result of over harvesting of the natural rubber vine and the entire concession produced just seven tons of rubber in 1905. Like Abir and the Société Anversoise, the Lulonga Company handed back control of the concession to the Congo Free State in 1906.

The Abir Congo Company was a company that exploited natural rubber in the Congo Free State, the private property of King Leopold II of Belgium. The company was founded with British and Belgian capital and was based in Belgium. By 1898 there were no longer any British shareholders and the Anglo-Belgian India Rubber Company changed its name to the Abir Congo Company and changed its residence for tax purposes to the Free State. The company was granted a large concession in the north of the country and the rights to tax the inhabitants. This tax was taken in the form of rubber obtained from a relatively rare rubber vine. The collection system revolved around a series of trade posts along the two main rivers in the concession. Each post was commanded by a European agent and manned with armed sentries to enforce taxation and punish any rebels.

Congo Maisie is a 1940 comedy-drama film directed by H. C. Potter and starring Ann Sothern for the second time in the ten film Maisie series as showgirl Maisie Ravier.

The Congo Free State propaganda war was a worldwide media propaganda campaign waged by both King Leopold II of Belgium and the critics of the Congo Free State. Leopold was very astute in using the media to support his virtual private control of the Congo. Edmund Dene Morel successfully campaigned against Leopold and focused public attention on the violence of Leopold's rule. Morel used newspaper accounts, pamphlets, and books to publish evidence from reports, eye-witness testimony, and pictures from missionaries and others involved directly in the Congo. As Morel gained high-profile supporters, the publicity generated by his campaign eventually forced Leopold to relinquish control of the Congo to the Belgian government.
The Mbole people are an ethnic group of about 150,000 people living in the Orientale Province, southwest of Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Mbole were previously referred to as Bambole.

Opala is a territory in the Tshopo Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Ilambi is a community in the Tshopo Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the Lomami River. It is 20 kilometres (12 mi) to the south of the point where the Lomani enters the Congo River. Most of the inhabitants are Topoke people.

Alice Seeley Harris (1870–1970) was an English missionary and an early documentary photographer. Her photography helped to expose the human rights abuses in the Congo Free State under the regime of Leopold II, King of the Belgians.

Liberia did not become militarily involved in World War II until January 1944, with the election of William Tubman, at which time the country declared war on Germany and Japan. However, even before the start of Liberia's official military involvement, the nation participated in the war for two years under the terms of a Defense Agreement with the United States. Apart from Ceylon and the Belgian Congo, Liberia possessed one of the few remaining sources of rubber for the Allies. To guarantee a steady supply of rubber from the world's largest rubber plantation, operated at Harbel by the Firestone Company since 1926, the US government built roads throughout the country, created an international airport, and transformed the capital, Monrovia, by building a deep water port.

Landolphia owariensis is a species of liana from the family Apocynaceae found in tropical Africa. Latex can be extracted from this plant for the manufacture of natural rubber. Other names for this vine are eta, the white rubber vine and the Congo rubber plant. Congo rubber was a commercial rubber exported from the Congo starting in 1890, most notable for its forced harvesting under conditions of great human suffering, in the Congo Free State, detailed in the 1904 Casement Report. From 1885 to 1908, millions died as a result of murder, deprivation, and disease, with population falling by millions in this period; some writers estimate this loss to be as high as 10 million people.

In the period from 1885 to 1908, many well-documented atrocities were perpetrated in the Congo Free State which, at the time, was a colony under the personal rule of King Leopold II of the Belgians. These atrocities were particularly associated with the labour policies used to collect natural rubber for export. Together with epidemic disease, famine, and a falling birth rate caused by these disruptions, the atrocities contributed to a sharp decline in the Congolese population. The magnitude of the population fall over the period is disputed, but it is thought to be between one and fifteen million.
Jason Eyenga Lokilo is a Congolese professional footballer who plays as a winger for League One side Doncaster Rovers on loan from Premier League club Crystal Palace.