
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy including solar water heating, and solar architecture.

A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. A mountain differs from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is larger than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges.

Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential energy of water, pumped from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is typically used to run the pumps. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Although the losses of the pumping process make the plant a net consumer of energy overall, the system increases revenue by selling more electricity during periods of peak demand, when electricity prices are highest. If the upper lake collects significant rainfall or is fed by a river then the plant may be a net energy producer in the manner of a traditional hydroelectric plant.

Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors.

Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially utilized for electricity generation and as photosensors.

A heliostat is a device that includes a mirror, usually a plane mirror, which turns so as to keep reflecting sunlight toward a predetermined target, compensating for the sun's apparent motions in the sky. The target may be a physical object, distant from the heliostat, or a direction in space. To do this, the reflective surface of the mirror is kept perpendicular to the bisector of the angle between the directions of the sun and the target as seen from the mirror. In almost every case, the target is stationary relative to the heliostat, so the light is reflected in a fixed direction. According to contemporary sources the heliostata, as it was called at first, was invented by Willem 's Gravesande (1688–1742). Other contenders are Giovanni Alfonso Borelli (1608–1679) and Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686–1736).

A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module or just solar panel is an assembly of photo-voltaic cells mounted in a framework for installation. Solar panels use sunlight as a source of energy to generate direct current electricity. A collection of PV modules is called a PV panel, and a system of PV panels is called an array. Arrays of a photovoltaic system supply solar electricity to electrical equipment.

There are several solar power plants in the Mojave Desert which supply power to the electricity grid. Insolation in the Mojave Desert is among the best available in the United States, and some significant population centers are located in the area. These plants can generally be built in a few years because solar plants are built almost entirely with modular, readily available materials. Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) is the name given to nine solar power plants in the Mojave Desert which were built in the 1980s, the first commercial solar plant. These plants have a combined capacity of 354 megawatts (MW) which made them the largest solar power installation in the world, until Ivanpah Solar Power Facility was finished in 2014.

Solar power represented a very small part of electricity production in the United Kingdom (UK) until the 2010s when it increased rapidly, thanks to feed-in tariff (FIT) subsidies and the falling cost of photovoltaic (PV) panels.

Solar power is the conversion of renewable energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV), indirectly using concentrated solar power, or a combination. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic effect.

A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system's overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
The nominal power is the nameplate capacity of photovoltaic (PV) devices, such as solar cells, modules and systems, and is determined by measuring the electric current and voltage in a circuit, while varying the resistance under precisely defined conditions. The nominal power is important for designing an installation in order to correctly dimension its cabling and converters.

A solar power tower, also known as 'central tower' power plant or 'heliostat' power plant, is a type of solar furnace using a tower to receive focused sunlight. It uses an array of flat, movable mirrors to focus the sun's rays upon a collector tower. Concentrated solar thermal is seen as one viable solution for renewable, pollution-free energy.

Cadmium telluride (CdTe) photovoltaics describes a photovoltaic (PV) technology that is based on the use of cadmium telluride in a thin semiconductor layer designed to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity. Cadmium telluride PV is the only thin film technology with lower costs than conventional solar cells made of crystalline silicon in multi-kilowatt systems.

Solar architecture is an architectural approach that takes in account the Sun to harness clean and renewable solar power. It is related to the fields of optics, thermics, electronics and materials science. Both active and passive solar housing skills are involved in solar architecture.

Concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) is a photovoltaic technology that generates electricity from sunlight. Unlike conventional photovoltaic systems, it uses lenses or curved mirrors to focus sunlight onto small, highly efficient, multi-junction (MJ) solar cells. In addition, CPV systems often use solar trackers and sometimes a cooling system to further increase their efficiency.
Amonix, Inc. is a solar power system developer based in Seal Beach, California. The company manufactures concentrator photovoltaic (CPV) products designed for installation in sunny and dry climates. CPV products convert sunlight into electrical energy in the same way that conventional solar photovoltaic technology does, except that they use optics to focus the solar radiation before the light is absorbed by solar cells. According to a comparative study of energy production of solar technologies, CPV systems require no water for energy production and produce more energy per megawatt (MW) installed than traditional PV systems. Amonix has nearly 70 megawatts of CPV solar power systems deployed globally, including Southwestern U.S. and Spain. In May 2012, the Alamosa Solar Generating project, owned and operated by Cogentrix Energy, began commercial operation. This is the largest CPV power plant in the world and is expected to produce enough clean renewable energy per year to power more than 6,500 homes and will avoid the emissions of over 43,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. The Alamosa Solar Generating Project is supported by a power purchase agreement (PPA), which is a long-term agreement to sell the power it will generate. Under the project's PPA, the Public Service Company of Colorado will buy the power generated by the solar facility for the next 20 years. In July 2012, Amonix set the world record for photovoltaic module efficiency at 33.5% under nominal operating conditions, verified by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. In April 2013, Amonix broke the record set in July 2012, demonstrating photovoltaic module efficiency at 34.9% under normal concentrator standard operating conditions, also verified by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. In August 2013, Amonix announced it had achieved a 35.9% photovoltaic module efficiency rating under concentrator standard test conditions (CSTC) as calculated by NREL. In June, 2014, the assets of Amonix were acquired by Arzon Solar, LLC for the purpose of continued development of CPV technology and products.
Solar energy – radiant light and heat from the sun. It has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar energy technologies include solar heating, solar photovoltaics, solar thermal electricity and solar architecture, which can make considerable contributions to solving some of the most urgent problems that the world now faces.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE is an institute of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft. Located in Freiburg, Germany, The Institute performs applied scientific and engineering research and development for all areas of solar energy. Fraunhofer ISE has three external branches in Germany which carry out work on solar cell and semiconductor material development: the Laboratory and Service Center (LSC) in Gelsenkirchen, the Technology Center of Semiconductor Materials (THM) in Freiberg, and the Fraunhofer Center for Silicon Photovoltaics (CSP) in Halle. Since 2006, Prof. Dr. Eicke R. Weber is the director of Fraunhofer ISE. With over 1,100 employees, Fraunhofer ISE is the largest institute for applied solar energy research in Europe. The 2012 Operational Budget including investments is 74.3 million euro.
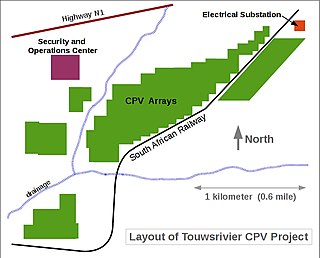
Touwsrivier CPV Solar Project is a 44 MWp (36 MWAC) concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) power station located 13 km outside the town of Touwsrivier in the Western Cape of South Africa. The installation reached full capacity in December 2014 and is the second largest operating CPV facility in the world. Electricity produced by the plant is fed into the national grid operated by Eskom under a 20-year power purchase agreement (PPA).




















