
The Annex is a neighbourhood in Downtown Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The traditional boundaries of the neighbourhood are north to Dupont Street, south to Bloor Street, west to Bathurst Street and east to Avenue Road. The City of Toronto recognizes a broader neighbourhood definition that includes the adjacent Seaton Village and Yorkville areas.

Gannett Peak is the highest mountain peak in the U.S. state of Wyoming at 13,804 feet (4,207 m). It lies in the Wind River Range within the Bridger Wilderness of the Bridger-Teton National Forest. Straddling the Continental Divide along the boundary between Fremont and Sublette counties, it has the second greatest topographic prominence in the state (7076') after Cloud Peak (7077'), and is the highest ground for 290.36 miles in any direction.

The Selkirk Mountains are a mountain range spanning the northern portion of the Idaho Panhandle, eastern Washington, and southeastern British Columbia which are part of a larger grouping of mountains, the Columbia Mountains. They begin at Mica Peak and Krell Hill near Spokane and extend approximately 320 km north from the border to Kinbasket Lake, at the now-inundated location of the onetime fur company post Boat Encampment. The range is bounded on its west, northeast and at its northern extremity by the Columbia River, or the reservoir lakes now filling most of that river's course. From the Columbia's confluence with the Beaver River, they are bounded on their east by the Purcell Trench, which contains the Beaver River, Duncan River, Duncan Lake, Kootenay Lake and the Kootenay River. The Selkirks are distinct from, and geologically older than, the Rocky Mountains. The neighboring Monashee and Purcell Mountains, and sometimes including the Cariboo Mountains to the northwest, are also part of the larger grouping of mountains known as the Columbia Mountains. A scenic highway loop, the International Selkirk Loop, encircles the southern portions of the mountain range.

Scotland is the most mountainous country in the United Kingdom. Scotland's mountain ranges can be divided in a roughly north to south direction into: the Scottish Highlands, the Central Belt and the Southern Uplands, the latter two primarily belonging to the Scottish Lowlands. The highlands eponymously contains the country's main mountain ranges, but many hills and mountains are to be found south of these as well. The below lists are not exhaustive; there are countless subranges throughout the country.

The mountains and hills of the British Isles are categorised into various lists based on different combinations of elevation, prominence, and other criteria such as isolation. These lists are used for peak bagging, whereby hillwalkers attempt to reach all the summits on a given list, the oldest being the 282 Munros in Scotland, created in 1891.

The Tualatin Mountains are a range on the western border of Multnomah County, Oregon, United States. A spur of the Northern Oregon Coast Range, they separate the Tualatin Basin of Washington County, Oregon, from the Portland Basin of western Multnomah County and Clark County, Washington.

The Lowther Hills, also sometimes known as the Lowthers, are an extensive area of hill country in the Southern Uplands of Scotland, though some sub-ranges of hills in this area also go under their own local names - see "Hillwalking" below. They form a roughly rhomboidal or lozenge shape on the map with the acute angles being to north and south. It has river valleys along its boundaries to north east (Clydesdale) and south west (Nithsdale) which carry the two largest arterial routes northwards into the west side of the Central Belt of Scotland. A string of small towns have long since developed along these routes. Most of the Lowther Hills lie in the Administrative County of Dumfries and Galloway, though part in the administrative county of South Lanarkshire moves into them around the village of Leadhills and the Daer Reservoir.

Croft Head is a hill in the Ettrick Hills range, part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland. It offers unobstructed views to the Solway Firth, the fells and mountains of Cumbria and the Pennines to the south and east. To the north, the major Moffat Hills are close by and to the west, Queensberry, the Lowthers and many of the Galloway Hills can be seen. Its summit is easily reached from Moffat by taking the Southern Upland Way path east from the Moffat water bridge near Craigbeck. A quite dramatic ridge loop is possible by climbing north on the forestry fire road shortly after Craigbeck Hope cottage via Gateshaw Rig to Croft Head's summit and descending via Cat Shoulder to the junction of the SUW and the Selcoth burn pass.
Three Waters Mountain is located in the northern Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Three Waters Mountain straddles the Continental Divide and is in both Bridger-Teton and Shoshone National Forests. The mountain receives its name from being the triple point between the watersheds of the Colorado, Columbia, and Mississippi Rivers.
Shale Mountain is located in the northern Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Shale Mountain straddles the Continental Divide and is in both Bridger-Teton and Shoshone National Forests. Shale Mountain is 5 mi (8.0 km) north of Downs Mountain.

Whiskey Mountain is located in the northern Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Located 5 mi (8.0 km) south of Dubois, Wyoming, Whiskey Mountain is within the Whiskey Mountain Wilderness Study Area, which has the largest wintering concentration of Rocky Mountain Bighorn sheep in the coterminous United States.
Knife Point Mountain is located in the northern Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Situated 2.7 mi (4.3 km) southeast of Fremont Peak, Knife Point Mountain is on the Continental Divide. North of Knife Point Mountain is the origination point of Knife Point Glacier, while Harrower Glacier lies just to the west. Knife Point Mountain is the 32nd tallest peak in Wyoming.
Bow Mountain is located in the northern Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Situated 1 mi (1.6 km) west of American Legion Peak, Bow Mountain is in the Bridger Wilderness of Bridger-Teton National Forest. Stroud Glacier lies just to the north of the peak. Bow Mountain is the 29th tallest peak in Wyoming.
Harrower Peak is located in the northern Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming, and it is the 28th tallest mountain in the state. Harrower Peak is in the Bridger Wilderness of Bridger-Teton National Forest and the Harrower Glacier is less than .50 mi (0.80 km) northeast of the peak.
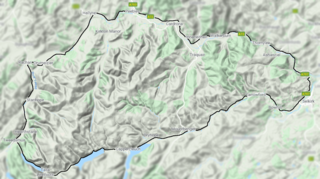
The Manor Hills, also known as the Tweedsmuir Hills, are a range of hills south of Peebles in the Scottish Borders, one of the ranges which collectively form the Southern Uplands. They are separated from the Moffat Hills by the Talla Reservoir, Megget Reservoir and St. Mary's Loch, the Moorfoot Hills by the A72 and the Culter Hills in South Lanarkshire by the A701. The western portion of the hills are designated as the 'Tweedsmuir Hills' Site of Special Scientific Interest and the 'Upper Tweeddale' National Scenic Area, with the major tributary rivers designated as Special Areas of Conservation.

Dun Law is a hill in the Lowther Hills range, part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland. It is the next Donald after Green Lowther, the highest point of the ridge, when walking northeast and is usually ascended from this direction.

Comb Law is a hill in the Lowther Hills range, part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland. The second lowest Donald in the area south of the A702 road, it is surrounded on most sides by tracks or roads and there are various routes to the summit, but the easiest ascent is from the Daer Reservoir.

East Mount Lowther is a hill in the Lowther Hills range, part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland. The hill is most often climbed as a detour before or after ascending Lowther Hill, however much longer approaches from the south utilising ancient pathways such as the medieval Enterkin Pass are also possible - a viewpoint indicator is located at the summit.

Earncraig Hill is a hill in the Lowther Hills range, part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland. The lowest and craggiest Donald hill in the range, it lies on the border between Dumfries and Galloway and South Lanarkshire, helping form the source of the River Clyde. It is most quickly ascended from the Daer Reservoir to the north or from Mitchellslacks to the south, passing by Burleywhag bothy.














