
Jesus College is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in England. It is in the centre of the city, on a site between Turl Street, Ship Street, Cornmarket Street and Market Street. The college was founded by Queen Elizabeth I of England on 27 June 1571. A major driving force behind the establishment of the college was Hugh Price, a churchman from Brecon in Wales. The oldest buildings, in the first quadrangle, date from the 16th and early 17th centuries; a second quadrangle was added between about 1640 and about 1713, and a third quadrangle was built in about 1906. Further accommodation was built on the main site to mark the 400th anniversary of the college, in 1971, and student flats have been constructed at sites in north and east Oxford. A fourth quadrangle was completed in 2021.
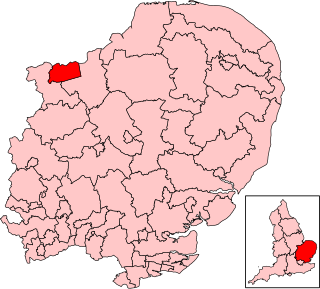
Peterborough is a borough constituency represented in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom since July 2024 by Andrew Pakes of the Labour Party. The constituency was previously represented by Conservative Party politician Paul Bristow who had been elected in 2019.

The Vice-Chamberlain of the Household is a member of the Royal Household of the Sovereign of the United Kingdom. The officeholder is usually a senior government whip in the British House of Commons ranking third or fourth after the Chief Whip and the Deputy Chief Whip. The Vice-Chamberlain is the Deputy to the Lord Chamberlain of the Household and, like the Lord Chamberlain, carries a white staff of office when on duty on state occasions.

Eaton Square is a rectangular, residential garden square in London's Belgravia district. It is the largest square in London. It is one of the three squares built by the landowning Grosvenor family when they developed the main part of Belgravia in the 19th century that are named after places in Cheshire — in this case Eaton Hall, the Grosvenor country house. It is larger but less grand than the central feature of the district, Belgrave Square, and both larger and grander than Chester Square. The first block was laid out by Thomas Cubitt from 1827. In 2016 it was named as the "Most Expensive Place to Buy Property in Britain", with a full terraced house costing on average £17 million — many of such town houses have been converted, within the same, protected structures, into upmarket apartments.

Pont Street is a fashionable street in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, London, traversing the areas of Knightsbridge and Belgravia. The street is not far from the Knightsbridge department store Harrods to its north-west. The street crosses Sloane Street in the middle, with Beauchamp Place to the west and Cadogan Place, and Chesham Place, to the east, eventually leading to Belgrave Square. On the west side, Hans Place leads off the street to the north and Cadogan Square to the south.

The Surrey Institution was an organisation devoted to scientific, literary and musical education and research, based in London. It was founded by private subscription in 1807, taking the Royal Institution, founded in 1799, as a model. The Institution lasted only until 1823, when it was dissolved.

Sir Thomas Shirley, of Wiston in Sussex, was an English Member of Parliament, government official and courtier who is said to have suggested the creation of the title of baronet.
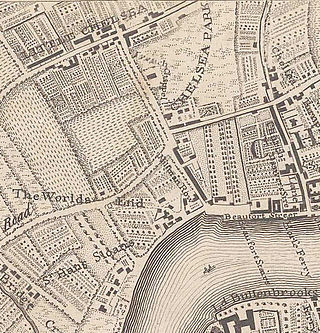
Little Chelsea was a hamlet, located on either side of Fulham Road, half a mile Southwest of Chelsea, London. The earliest references to the settlement date from the early 17th century, and the name continued to be used until the hamlet was surrounded by residential developments in the late 19th century.

The Lieutenant of the Tower of London serves directly under the Constable of the Tower. The office has been appointed at least since the 13th century. There were formerly many privileges, immunities and perquisites attached to the office. Like the Constable, the Lieutenant was usually appointed by letters patent, either for life or during the King's pleasure.

Justice of the Common Pleas was a puisne judicial position within the Court of Common Pleas of England and Wales, under the Chief Justice. The Common Pleas was the primary court of common law within England and Wales, dealing with "common" pleas. It was created out of the common law jurisdiction of the Exchequer of Pleas, with splits forming during the 1190s and the division becoming formal by the beginning of the 13th century. The court became a key part of the Westminster courts, along with the Exchequer of Pleas and the Court of King's Bench, but with the Writ of Quominus and the Statute of Westminster, both tried to extend their jurisdiction into the realm of common pleas. As a result, the courts jockeyed for power. In 1828 Henry Brougham, a Member of Parliament, complained in Parliament that as long as there were three courts unevenness was inevitable, saying that "It is not in the power of the courts, even if all were monopolies and other restrictions done away, to distribute business equally, as long as suitors are left free to choose their own tribunal", and that there would always be a favourite court, which would therefore attract the best lawyers and judges and entrench its position. The outcome was the Supreme Court of Judicature Act 1873, under which all the central courts were made part of a single Supreme Court of Judicature. Eventually the government created a High Court of Justice under Lord Coleridge by an Order in Council of 16 December 1880. At this point, the Common Pleas formally ceased to exist.

The position of Savilian Professor of Geometry was established at the University of Oxford in 1619. It was founded by Sir Henry Savile, a mathematician and classical scholar who was Warden of Merton College, Oxford, and Provost of Eton College, reacting to what has been described by one 20th-century mathematician as "the wretched state of mathematical studies in England" at that time. He appointed Henry Briggs as the first professor. Edward Titchmarsh said when applying that he was not prepared to lecture on geometry, and the requirement was removed from the duties of the post to enable his appointment, although the title of the chair was not changed. The two Savilian chairs have been linked with professorial fellowships at New College, Oxford, since the late 19th century. Before then, for over 175 years until the middle of the 19th century, the geometry professors had an official residence adjoining the college in New College Lane.

Essex Street Chapel, also known as Essex Church, is a Unitarian place of worship in London. It was the first church in England set up with this doctrine, and was established when Dissenters still faced legal threat. As the birthplace of British Unitarianism, Essex Street has particularly been associated with social reformers and theologians. The congregation moved west in the 19th century, allowing the building to be turned into the headquarters for the British and Foreign Unitarian Association and the Sunday School Association. These evolved into the General Assembly of Unitarian and Free Christian Churches, the umbrella organisation for British Unitarianism, which is still based on the same site, in an office building called Essex Hall. This article deals with the buildings, the history, and the current church, based in Kensington.

The Octagon Chapel, Liverpool, was a nonconformist church in Liverpool, England, opened in 1763. It was founded by local congregations, those of Benn's Garden and Kaye Street chapels. The aim was to use a non-sectarian liturgy; Thomas Bentley was a major figure in founding the chapel, and had a hand in the liturgy.
Professor Archibald Campbell SwintonFRSE DL LLD LLB, was a Scottish author, politician and professor of civil law at Edinburgh, 1842–62.

Sir Francis Taylor Piggott was a British jurist and author. He was the Chief Justice of Hong Kong from 1905 to 1912.
The Swiney Prize, a British award made every five years by the Royal Society of Arts with the Royal College of Physicians, was set up by the will of George Swiney, an English physician who died in 1844.

Twickenham Park was an estate in Twickenham in south-west London.

The Plumbers Arms is a Grade II listed public house at 14 Lower Belgrave Street, Belgravia, London SW1.

















