
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethnolinguistic group of Northern European origin identified by Roman-era authors as distinct from neighbouring Celtic peoples, and identified in modern scholarship as speakers, at least for the most part, of early Germanic languages.

Native Americans, also known as American Indians, Indigenous Americans and other terms, are the indigenous peoples of the United States, except Hawaii. There are over 500 federally recognized tribes within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. The term "American Indian" excludes Native Hawaiians and some Alaska Natives, while Native Americans are American Indians, plus Alaska Natives of all ethnicities. Native Hawaiians are not counted as Native Americans by the US Census, instead being included in the Census grouping of "Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander".

As general terms, Indian Territory, the Indian Territories, or Indian country describe an evolving land area set aside by the United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land. In general, the tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian Territory was an outcome of the 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the government was one of assimilation.

The Bedouin or Bedu are a grouping of nomadic Arab people who have historically inhabited the desert regions in North Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq and the Levant. The English word bedouin comes from the Arabic badawī, which means "desert dweller", and is traditionally contrasted with ḥāḍir, the term for sedentary people. Bedouin territory stretches from the vast deserts of North Africa to the rocky sands of the Middle East. They are traditionally divided into tribes, or clans, and share a common culture of herding camels and goats. The vast majority of Bedouin adhere to Islam.

According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Judah was one of the twelve Tribes of Israel.

Survivor is a reality competition television franchise produced in many countries throughout the world.

A Tribe Called Quest was an American hip hop collective formed in 1985 and originally composed of MC and main producer Q-Tip, MC Phife Dawg, DJ and co-producer Ali Shaheed Muhammad, and MC Jarobi White, who left the group amicably in 1991. Later that year, the group released its jazz-influenced second album, The Low End Theory, regarded for helping shape alternative hip hop in the 1990s. Along with De La Soul, the group was a central part of the Native Tongues, enjoying the most commercial success out of all the groups to emerge from that collective. In 1998, the band broke up shortly before releasing its fifth album, The Love Movement, but in 2006, the group's original members reunited and toured the United States. In 2016, the group released its sixth and final album, We Got It from Here... Thank You 4 Your Service, which was still incomplete when Phife Dawg died suddenly in March 2016, and was completed by the other members after his death.
The Seminole are a Native American people originally from Florida. Today, they principally live in Oklahoma with a minority in Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Tribe of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, and Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida, as well as independent groups. The Seminole nation emerged in a process of ethnogenesis from various Native American groups who settled in Florida in the 18th century, most significantly northern Muscogee (Creeks) from what is now Georgia and Alabama. The word "Seminole" is derived from the Creek word simanó-li, which may itself be derived from the Spanish word cimarrón, meaning "runaway" or "wild one".

Myrtaceae or the myrtle family is a family of dicotyledonous plants placed within the order Myrtales. Myrtle, pohutukawa, bay rum tree, clove, guava, acca (feijoa), allspice, and eucalyptus are some notable members of this group. All species are woody, contain essential oils, and have flower parts in multiples of four or five. The leaves are evergreen, alternate to mostly opposite, simple, and usually entire. The flowers have a base number of five petals, though in several genera the petals are minute or absent. The stamens are usually very conspicuous, brightly coloured and numerous.

Cicadidae is the largest family of cicadas, with more than 3,000 species worldwide.

An Indian reservation is a legal designation for an area of land managed by a federally recognized Native American tribe under the U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs rather than the state governments of the United States in which they are physically located. Each of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States is associated with a particular Native American nation. Not all of the country's 567 recognized tribes have a reservation—some tribes have more than one reservation, while some share reservations. In addition, because of past land allotments, leading to some sales to non–Native Americans, some reservations are severely fragmented, with each piece of tribal, individual, and privately held land being a separate enclave. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political, and legal difficulties.

Adivasi is the collective term for the indigenous peoples of mainland South Asia. Adivasi make up 8.6% of India's population, or 104 million people, according to the 2011 census, and a large percentage of the Nepalese population. They comprise a substantial indigenous minority of the population of India and Nepal and a minority group of the Sri Lankan society called Vedda. The same term Adivasi is used for the ethnic minorities of Bangladesh and the native Tharu people of Nepal. The word is also used in the same sense in Nepal, as is another word, janajati, although the political context differed historically under the Shah and Rana dynasties.
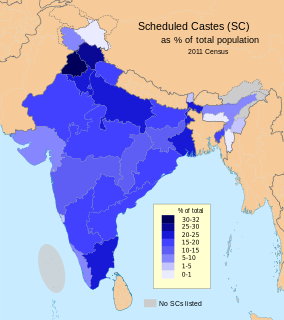
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of historically disadvantaged people in India. The terms are recognised in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes. The people in scheduled castes are essentially the lowest part of Hindu society.

Blister beetles are beetles of the family Meloidae, so called for their defensive secretion of a blistering agent, cantharidin. About 7,500 species are known worldwide. Many are conspicuous and some are aposematically colored, announcing their toxicity to would-be predators.

In the Hebrew Bible, the Twelve Tribes of Israel or Tribes of Israel descended from the 12 sons of the patriarch Jacob and his two wives, Leah and Rachel, and two concubines, Zilpah and Bilhah.
A tribal chief is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom.
The ten lost tribes were the ten of the Twelve Tribes of Israel that were said to have been deported from the Kingdom of Israel after its conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire circa 722 BCE. These are the tribes of Reuben, Simeon, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Issachar, Zebulun, Manasseh, and Ephraim. Claims of descent from the "lost" tribes have been proposed in relation to many groups, and some religions espouse a messianic view that the tribes will return.














