 | |
Luxembourg | Vietnam |
|---|---|
Luxembourg and Vietnam established diplomatic relations in 1973. [1] Luxembourg's representation in Vietnam is through its embassy in Beijing, China. [2] Vietnam is represented through its embassy in Brussels, Belgium. [3]
 | |
Luxembourg | Vietnam |
|---|---|
Luxembourg and Vietnam established diplomatic relations in 1973. [1] Luxembourg's representation in Vietnam is through its embassy in Beijing, China. [2] Vietnam is represented through its embassy in Brussels, Belgium. [3]
In December 2008, Vietnam called on Luxembourg to support its ties with European Union. For its part, Vietnam is backing Luxembourg's candidacy for the post of non-permanent member at the UN Security Council. [4]
Vietnam is one of the ten key countries in Luxembourg's development cooperation program. [5] The countries have agreed to build a legal framework to facilitate business ties. [6] At a meeting between Vietnamese Prime Minister Nguyễn Tấn Dũng and his Luxembourg counterpart, Jean-Claude Juncker, in September 2006, the two Prime Ministers agreed the need to boost bilateral trade ties based on the combination of Luxembourg's advanced technology and Vietnam's intensive labour force. [7] Nguyễn Tấn Dũng, in October 2007, praised the cooperation by Luxembourg companies in finance and education and expressed the wish to boost bilateral ties with Luxembourg in these areas. [8] In December 2008, according to Vietnam National Assembly Chairman Nguyễn Phú Trọng, there was still much potential for further economic and commercial co-operation. [9]
Luxembourg pledged EUR35 million in aid for the 2002-05 period. [1]

As of June 2024, Vietnam maintains diplomatic relationships with 190 UN member states, State of Palestine and Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. In 2011 the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam, at the 11th National Congress of the Communist Party of Vietnam, released an official statement about Vietnam's foreign policy and a section of the statement stated: "Vietnam is a friend and reliable partner of all countries in the international community, actively taking part in international and regional cooperation processes. Deepen, stabilize and sustain established international relations. Develop relations with countries and territories in the world, as well as international organizations, while showing: respect for each other's independence; sovereignty and territorial integrity; non-interference in each other's international affairs; non-use or threat of force; settlement of disagreements and disputes by means of peaceful negotiations; mutual respect, equality and mutual benefit."
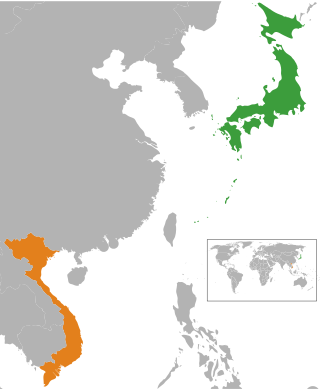
Japanese–Vietnamese relations are over a millennium old, and the establishment of friendly trade relations can be traced to at least the 16th century. Modern relations between the two countries are based on Vietnam's developing economy and Japan's role as an investor and foreign aid donor, as well as migrant Vietnamese workers supplying much needed labour in Japan.

Relations between Vietnam and China had been extensive for a couple of millennia, with Northern Vietnam especially under heavy Sinosphere influence during historical times. Despite their Sinospheric and socialist background, centuries of conquest by modern China's imperial predecessor as well as modern-day tensions have made relations wary. The People's Republic of China (PRC) ruled by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) assisted North Vietnam and the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) during the Vietnam War whilst the Taiwan-based Republic of China (ROC) was allied with South Vietnam.

India–Vietnam relations, also known as Indian-Vietnamese relations, are the bilateral relations of India and Vietnam.

Republic of Greece and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam have bilateral relations. Greece hosts the Vietnamese embassy in Athens, and Vietnam hosts its Greek counterpart in Hanoi.

Denmark–Vietnam relations relates to foreign relations between Denmark and Vietnam. Both countries established diplomatic relations on November 25, 1971. On April 1, 1994, Denmark established an embassy in Hanoi, and since August 12, 2000, Vietnam has had an embassy in Copenhagen.

Pakistan-Vietnam relations, or Pakistani-Vietnamese relations, refers to the bilateral relationship between the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and Islamic Republic of Pakistan. The relationship is largely based on mutual trade and international political cooperation between the two countries. Pakistan is represented in Vietnam by its embassy in Hanoi, and Vietnam also maintains an embassy in Islamabad. During the Cold War, Pakistan maintained close ties with the United States-led Western Bloc to counter rival India's allegiance with the Soviet Union and Eastern Bloc. Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, the United States was involved in the Vietnam War against Soviet-backed North Vietnam while in the same time period, Pakistan had engaged in two major wars with neighbouring India in 1965 and 1971, the latter of which resulted in a devastating defeat for Pakistan and saw the emergence of an independent Bangladesh. Due to the fact that Pakistan was an ally with the United States and had begun to indirectly wage war against the Soviets in Afghanistan with heavy U.S.−backing, relations became strained between the two, with Pakistan closing its diplomatic mission in Vietnam in 1980 and Vietnam doing the same in 1984. However, relations greatly improved in the 2000s, and Pakistan reopened its embassy in Hanoi in October 2000. Vietnam also reopened its embassy in Islamabad and trade office in Karachi in December and November 2005, respectively. Relations between the two countries have continued to remain friendly, with Vietnam expressing an interest in increased economic and military cooperation with Pakistan. The heads of both nations have in recent times paid official visits to each other, with Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf visiting Vietnam in May 2001 and Vietnamese President Trần Đức Lương also paying an official visit to Pakistan in March 2004. Throughout the following decade, several visits were made by various Vietnamese and Pakistani ministries to each other. A major part of Pakistan's pursuit to enhance its relationship with Vietnam is outlined in Pakistan's "Vision East Asia" strategy. The emergence of such a strategy came as a result of Pakistan's desire to balance its relations with Vietnam and other East Asian / Southeast Asian states by making an effort to circumvent Pakistan's close relationship with China and Vietnam's growing relationship with India—the former being a cause of concern for Vietnam due to its tense relationship with China and the latter being a cause of concern for Pakistan due to its rivalry and history of armed conflict with India.

Israel–Vietnam relations refers to the bilateral relations between the State of Israel and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Vietnam and Israel established diplomatic relations on July 12, 1993, followed by Israel opening its resident embassy in Hanoi in December 1993. The current Vietnamese Ambassador to Israel is Lý Đức Trung, who has been assigned since April 2022. Ambassador Lý Đức Trung operates out of the Vietnamese embassy in Tel Aviv. The current Israeli Ambassador to Vietnam is Yaron Mayer, who has been assigned since August 2022. Ambassador Mayer operates out of the Israeli embassy in Hanoi.

Malaysia–Vietnam relations date to at least the 15th century. Malaysia forged diplomatic ties with the modern-day Vietnamese state on 30 March 1973; as of 2015, these ties are still in existence. During the late 1970s and 1980s, the countries' relationship became strained as a result of the Cambodian–Vietnamese War and the influx of Vietnamese boat people into Malaysia. The subsequent resolution of these issues saw the cultivation of strong trade and economic ties, and bilateral trade between the countries grew strongly, with an expansion into areas including information technology, education and defence. Both countries are members of APEC and ASEAN.

Holy See–Vietnam relations are foreign relations between the Holy See and Vietnam.

Mongolia–Vietnam relations are bilateral relations between Mongolia and Vietnam. Vietnam has an embassy in Ulaanbaatar. Mongolia has an embassy in Hanoi.

Venezuela and Vietnam established diplomatic links on December 8, 1989. Vietnam has an embassy in Caracas and Venezuela has an embassy in Hanoi. Though bilateral trade was US$11.7 million in 2007, relations show "great potential". Since 2008, the two countries have witnessed new developments in various fields, including politics, economics, culture and society, particularly in the oil and gas industry.

Trương Tấn Sang is a Vietnamese politician, who served as the eighth President of Vietnam from 2011 to 2016. He was one of Vietnam's top leaders, alongside prime minister Nguyễn Tấn Dũng and Party general secretary Nguyễn Phú Trọng. In July 2011, Trương Tấn Sang was elected state president of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam by the National Assembly of Vietnam and nominated by his predecessor Nguyễn Minh Triết who retired from office.
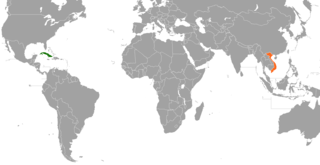
Cuban–Vietnam relations are the interstate and special relations between the Republic of Cuba and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The relations are based on trade, credits, and investments which have increased significantly since the 1990s and on shared ideological beliefs – they are both socialist states. Diplomatic relations between the post-revolutionary Cuba and the Democratic Republic of Vietnam were established on December 12, 1960. Since then, Vietnam has become Cuba's second-largest trading partner in Asia, with Vietnam trailing behind China.

Indonesia and Vietnam established diplomatic relations in 1955. Indonesia has an embassy in Hanoi and a consulate general in Ho Chi Minh City while Vietnam has an embassy in Jakarta. Both are neighboring nations that have a maritime border which lies on the South China Sea and are members of ASEAN and APEC.

The nations of Mexico and Vietnam established diplomatic relations in 1975. Both nations are members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, Forum of East Asia-Latin America Cooperation and the United Nations.

Bangladesh–Vietnam relations refer to the bilateral relations between Bangladesh and Vietnam.

Iran–Vietnam relations refer to the bilateral relations between Iran and Vietnam, which were formally established in 1973. Iran has an embassy in Hanoi while Vietnam maintains an embassy in Tehran.

Jorge Trindade Neves de Camões is an East Timorese diplomat who currently serves as ambassador to Brussels with concurrent accreditations to the European Union and other countries. He was a student activist and member of the Conselho Nacional de Resistência Timorese (CNRT) who campaigned to resist Indonesian invasion of East Timor.