
The BeBox is a dual CPU personal computer, briefly sold by Be Inc. to run the company's own operating system, BeOS. Notable aspects of the system include its CPU configuration, I/O board with "GeekPort", and "Blinkenlights" on the front bezel.
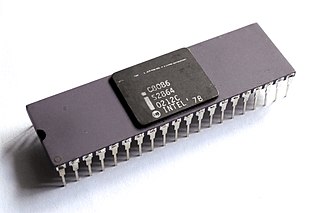
The 8086 is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit data bus, and is notable as the processor used in the original IBM PC design.

The Intel 8088 microprocessor is a variant of the Intel 8086. Introduced on June 1, 1979, the 8088 had an eight-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range were unchanged, however. In fact, according to the Intel documentation, the 8086 and 8088 have the same execution unit (EU)—only the bus interface unit (BIU) is different. The original IBM PC was based on the 8088, as were its clones.

The MOS Technology 6510 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by MOS Technology. It is a modified form of the very successful 6502. The 6510 was only widely used in the Commodore 64 (C64) home computer and its variants.

The 6800 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed and first manufactured by Motorola in 1974. The MC6800 microprocessor was part of the M6800 Microcomputer System that also included serial and parallel interface ICs, RAM, ROM and other support chips. A significant design feature was that the M6800 family of ICs required only a single five-volt power supply at a time when most other microprocessors required three voltages. The M6800 Microcomputer System was announced in March 1974 and was in full production by the end of that year.

MOS Technology, Inc., later known as CSG , was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Norristown, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is most famous for its 6502 microprocessor and various designs for Commodore International's range of home computers.

The Commodore PET is a line of home/personal computers produced starting in 1977 by Commodore International. The system combined a MOS 6502 microprocessor, Commodore BASIC in read only memory (ROM), a keyboard, a computer monitor and a cassette deck for data and program storage in a single all-in-one case.

The Intel 8085 ("eighty-eighty-five") is an 8-bit microprocessor produced by Intel and introduced in March 1976. It is a software-binary compatible with the more-famous Intel 8080 with only two minor instructions added to support its added interrupt and serial input/output features. However, it requires less support circuitry, allowing simpler and less expensive microcomputer systems to be built.

The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. It was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs.

The 6522 Versatile Interface Adapter (VIA) is an integrated circuit that was designed and manufactured by MOS Technology as an I/O port controller for the 6502 family of microprocessors. It provides two bidirectional 8-bit parallel I/O ports, two 16-bit timers, and an 8-bit shift register for serial communications or data conversion between serial and parallel forms. The direction of each bit of the two I/O ports can be individually programmed. In addition to being manufactured by MOS Technology, the 6522 was second sourced by other companies including Rockwell and Synertek.
National Semiconductor's Simple Cost-effective Micro Processor or SC/MP is an early microprocessor which became available in early 1974. It features a 16-bit address and an 8-bit data bus. The program counter is twelve bits wide, and there are separate instructions to set the upper four bits of the program counter, which are subsequently output on the address bus, along with status signals. This provides a memory map of sixteen four-kilobyte pages. Internally it provided five registers plus the program counter, but no stack pointer.

The Signetics 2650 was an 8-bit microprocessor introduced in mid-1975. According to Adam Osborne's book An Introduction to Microprocessors Vol 2: Some Real Products, it was "the most minicomputer-like" of the microprocessors available at the time. A combination of missing features and odd memory access limited its appeal, and the system saw little use in the market. Signetics became better known as a second-source supplier for the MOS 6502.

The 6532 RAM-I/O-Timer (RIOT) was an integrated circuit made by MOS Technology, as well as second sources such as Rockwell. It incorporated 128 bytes of static RAM, two bidirectional 8-bit digital input/output ports, and a Programmable interval timer. This high degree of integration made it quite popular in the late 1970s and early 1980s, as it could take the place of several different integrated circuits (ICs).

The 2N3055 is a silicon NPN power transistor intended for general purpose applications. It was introduced in the early 1960s by RCA using a hometaxial power transistor process, transitioned to an epitaxial base in the mid-1970s. Its numbering follows the JEDEC standard. It is a transistor type of enduring popularity.

The 6526/8520 Complex Interface Adapter (CIA) was an integrated circuit made by MOS Technology. It served as an I/O port controller for the 6502 family of microprocessors, providing for parallel and serial I/O capabilities as well as timers and a Time-of-Day (TOD) clock. The device's most prominent use was in the Commodore 64 and Commodore 128(D), each of which included two CIA chips. The Commodore 1570 and Commodore 1571 floppy disk drives contained one CIA each. Furthermore, the Amiga home computers and the Commodore 1581 floppy disk drive employed a modified variant of the CIA circuit called 8520. 8520 is functionally equivalent to the 6526 except for the simplified TOD circuitry.
The XNOR gate is a digital logic gate whose function is the logical complement of the exclusive OR (XOR) gate. The two-input version implements logical equality, behaving according to the truth table to the right, and hence the gate is sometimes called an "equivalence gate". A high output (1) results if both of the inputs to the gate are the same. If one but not both inputs are high (1), a low output (0) results.

The W65C21S is a very flexible Peripheral Interface Adapter (PIA) for use with WDC’s 65xx and other 8-bit microprocessor families. It is produced by Western Design Center (WDC).
I/O Controller Hub (ICH) is a family of Intel southbridge microchips used to manage data communications between a CPU and a motherboard, specifically Intel chipsets based on the Intel Hub Architecture. It is designed to be paired with a second support chip known as a northbridge. As with any other southbridge, the ICH is used to connect and control peripheral devices.
The IGEPv2 board is a low-power, fanless single-board computer based on the OMAP 3 series of ARM-compatible processors. It is developed and produced by Spanish corporation ISEE and is the second IGEP platform in the series. The IGEPv2 is open hardware, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-ShareAlike 3.0 unported license.
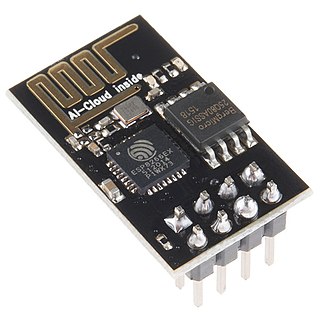
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with a full TCP/IP stack and microcontroller capability, produced by Espressif Systems in Shanghai, China.