
Mold health issues are potentially harmful effects of molds and their mycotoxins. However, recent research has shown these adverse health effects stem not just from molds, but also other microbial agents and biotoxins associated with dampness, mold, and water-damaged buildings, such as gram-negative bacteria that produce endotoxins, and actinomycetes and their associated exotoxins.

A mould or mold is a fungus that grows in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. In contrast, fungi that can adopt a single-celled growth habit are called yeasts.

Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly Aspergillus species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn, wheat, millet, sorghum, cassava, rice, chili peppers, cottonseed, peanuts, tree nuts, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, and various spices. In short, the relevant fungi grow on almost any crop or food. When such contaminated food is processed or consumed, the aflatoxins enter the general food supply. They have been found in both pet and human foods, as well as in feedstocks for agricultural animals. Animals fed contaminated food can pass aflatoxin transformation products into eggs, milk products, and meat. For example, contaminated poultry feed is the suspected source of aflatoxin-contaminated chicken meat and eggs in Pakistan.
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom and is capable of causing disease and death in both humans and other animals. The term 'mycotoxin' is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops.
Abraham Z. Joffe (1909–2000) was Professor of Mycology and Mycotoxicology at the Hebrew University, Jerusalem. Joffe's professional interests were centered primarily in toxigenic fungi associated with production of mycotoxins ; ecology and environmental factors favoring formation and distribution of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereal grains, feeds and foods; and phytotoxic action of Fusarium strains, and their toxicity in animals and humans.

T-2 Mycotoxin is a trichothecene mycotoxin. It is a naturally occurring mold byproduct of Fusarium spp. fungus which is toxic to humans and animals. The clinical condition it causes is alimentary toxic aleukia and a host of symptoms related to organs as diverse as the skin, airway, and stomach. Ingestion may come from consumption of moldy whole grains. T-2 can be absorbed through human skin. Although no significant systemic effects are expected after dermal contact in normal agricultural or residential environments, local skin effects can not be excluded. Hence, skin contact with T-2 should be limited.

Fumonisin B1 is the most prevalent member of a family of toxins, known as fumonisins, produced by several species of Fusarium molds, such as Fusarium verticillioides, which occur mainly in maize (corn), wheat and other cereals. Fumonisin B1 contamination of maize has been reported worldwide at mg/kg levels. Human exposure occurs at levels of micrograms to milligrams per day and is greatest in regions where maize products are the dietary staple.
Yellow rain was the subject of a 1981 political incident in which the United States Secretary of State Alexander Haig accused the Soviet Union of supplying T-2 mycotoxin to the Communist states in Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia for use in counterinsurgency warfare. Refugees described many different forms of "attacks", including a sticky yellow liquid falling from planes or helicopters, which was dubbed "yellow rain". The U.S. government alleged that over ten thousand people had been killed in attacks using these supposed chemical weapons. The Soviets denied these claims and an initial United Nations investigation was inconclusive.

Trichothecenes are a very large family of chemically related mycotoxins produced by various species of Fusarium, Myrothecium, Trichoderma, Trichothecium, Cephalosporium, Verticimonosporium, and Stachybotrys. Trichothecenes are a class of sesquiterpenes. The most important structural features causing the biological activities of trichothecenes are the 12,13-epoxy ring, the presence of hydroxyl or acetyl groups at appropriate positions on the trichothecene nucleus, and the structure and position of the side-chain. They are produced on many different grains like wheat, oats or maize by various Fusarium species such as F. graminearum, F. sporotrichioides, F. poae and F. equiseti.

Zearalenone (ZEN), also known as RAL and F-2 mycotoxin, is a potent estrogenic metabolite produced by some Fusarium and Gibberella species. Particularly, is produced by Fusarium graminearum, Fusarium culmorum, Fusarium cerealis, Fusarium equiseti, Fusarium verticillioides, and Fusarium incarnatum.
Mycotoxicology is the branch of mycology that focuses on analyzing and studying the toxins produced by fungi, known as mycotoxins. In the food industry it is important to adopt measures that keep mycotoxin levels as low as practicable, especially those that are heat-stable. These chemical compounds are the result of secondary metabolism initiated in response to specific developmental or environmental signals. This includes biological stress from the environment, such as lower nutrients or competition for those available. Under this secondary path the fungus produces a wide array of compounds in order to gain some level of advantage, such as incrementing the efficiency of metabolic processes to gain more energy from less food, or attacking other microorganisms and being able to use their remains as a food source.

Vomitoxin, also known as deoxynivalenol (DON), is a type B trichothecene, an epoxy-sesquiterpenoid. This mycotoxin occurs predominantly in grains such as wheat, barley, oats, rye, and corn, and less often in rice, sorghum, and triticale. The occurrence of deoxynivalenol is associated primarily with Fusarium graminearum and F. culmorum, both of which are important plant pathogens which cause fusarium head blight in wheat and gibberella or fusarium ear blight in corn. The incidence of fusarium head blight is strongly associated with moisture at the time of flowering (anthesis), and the timing of rainfall, rather than the amount, is the most critical factor. However, increased amount of moisture towards harvest time has been associated with lower amount of vomitoxin in wheat grain due to leaching of toxins. Furthermore, deoxynivalenol contents are significantly affected by the susceptibility of cultivars towards Fusarium species, previous crop, tillage practices, and fungicide use. It occurs abundantly in grains in Norway due to heavy rainfall.

Alternariol is a toxic metabolite of Alternaria fungi. It is an important contaminant in cereals and fruits. Alternariol exhibits antifungal and phytotoxic activity. It is reported to inhibit cholinesterase enzymes. It is also a mycoestrogen.
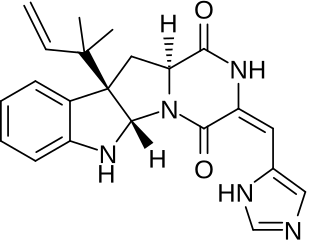
Roquefortine C is a mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced by various fungi, particularly species from the genus Penicillium. It was first isolated from a strain of Penicillium roqueforti, a species commercially used as a source of proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes during maturation of the blue-veined cheeses, Roquefort, Danish Blue, Stilton and Gorgonzola.

Aspergillus versicolor is a slow-growing filamentous fungus commonly found in damp indoor environments and on food products. It has a characteristic musty odor associated with moldy homes and is a major producer of the hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin sterigmatocystin. Like other Aspergillus species, A. versicolor is an eye, nose, and throat irritant.

5-Chloro-α-methyltryptamine (5-Chloro-αMT), also known as PAL-542, is a tryptamine derivative related to α-methyltryptamine (αMT) and one of only a few known specific serotonin-dopamine releasing agents (SDRAs). It has been investigated in animals as a potential treatment for cocaine dependence. The EC50 values of 5-chloro-αMT in evoking the in vitro release of serotonin (5-HT), dopamine (DA), and norepinephrine (NE) in rat synaptosomes were reported as 16 nM, 54 nM, and 3434 nM, with an NE/DA ratio of 63.6 and a DA/5-HT ratio of 3.38, indicating that it is a highly specific and well-balanced SDRA. However, 5-chloro-αMT has also been found to act as a potent full agonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, with an EC50 value of 6.27 nM and an efficacy of 105%, and almost assuredly acts as a potent agonist of other serotonin receptors as well.

β-Zearalenol is a nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in Fusarium spp. It is the β epimer of α-zearalenol and along with α-zearalenol is a major metabolite of zearalenone formed mainly in the liver but also to a lesser extent in the intestines during first-pass metabolism. A relatively high proportion of α-zearalenol is formed from zearalenone compared to β-zearalenol in humans. β-Zearalenol is about the same or slightly less potent as an estrogen relative to zearalenone.
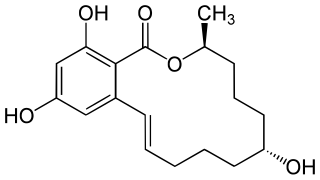
α-Zearalenol is a nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in Fusarium spp. It is the α epimer of β-zearalenol and along with β-zearalenol is a major metabolite of zearalenone formed mainly in the liver but also to a lesser extent in the intestines during first-pass metabolism. A relatively low proportion of β-zearalenol is formed from zearalenone compared to α-zearalenol in humans. α-Zearalenol is about 3- to 4-fold more potent as an estrogen relative to zearalenone.

Chaetochromin, also known as 4548-G05, is an orally active, small-molecule, selective agonist of the insulin receptor. It has potent and long-lasting antidiabetic activity in vivo in mice. The drug may represent a novel potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetes which is more convenient and tolerable to administer than injected insulin. It was discovered in 1981 in Chaetomium gracile fungi, and its interaction with the insulin receptor was identified in 2014.
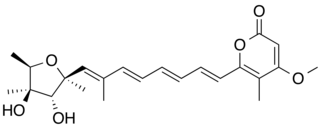
Citreoviridin is a mycotoxin which is produced by Penicillium and Aspergillus species. If rice, corn, cereals or meat products are contaminated with Penicillin citreoviridin, citreoviridin can be produced if the food is stored in a damp place. Consuming food which is contaminated with citreoviridin can cause the disease cardiac beri beri. Furthermore it damages liver and kidneys.
















