
Calvinism, also called Reformed Christianity, is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Calvin and various other Reformation-era theologians. It emphasizes the sovereignty of God and the authority of the Bible.
The Reformation was a major movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in part posed a challenge to papal authority. The Reformation marked the start of Protestantism and in the Western Church, the Latin Church, remained the Catholic Church.

The priesthood of all believers or universal priesthood is a biblical principle in Protestant branches of Christianity which is distinct from the institution of the ministerial priesthood found in some other branches, including the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox. Derived from the Bible and elaborated in the theology of Martin Luther and John Calvin, the principle became prominent as a tenet of Protestant Christian doctrine, though the exact meaning of the belief and its implications vary widely among denominations.

The Schmalkaldic League was a military alliance of Lutheran princes within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century.

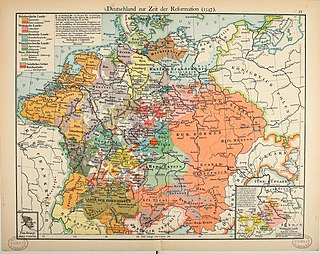
The Peace of Augsburg, also called the Augsburg Settlement, was a treaty between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, and the Schmalkaldic League, signed in September 1555 at the imperial city of Augsburg. It officially ended the religious struggle between the two groups and made the legal division of Christianity permanent within the Holy Roman Empire, allowing rulers to choose either Lutheranism or Roman Catholicism as the official confession of their state. Calvinism was not allowed until the Peace of Westphalia.

Cuius regio, eius religio is a Latin phrase which literally means "whose realm, their religion" – meaning that the religion of the ruler was to dictate the religion of those ruled. This legal principle marked a major development in the collective freedom of religion within Western civilization. Before tolerance of individual religious divergences became accepted, most statesmen and political theorists took it for granted that religious diversity weakened a state – and particularly weakened ecclesiastically-transmitted control and monitoring in a state. The principle of "cuius regio" was a compromise in the conflict between this paradigm of statecraft and the emerging trend toward religious pluralism developing throughout the German-speaking lands of the Holy Roman Empire. It permitted assortative migration of adherents to just two theocracies, Roman Catholic and Lutheran, eliding other confessions.

Jan Łaski or Johannes à Lasco was a Polish Calvinist reformer. Owing to his influential work in England (1548–1553) during the English Reformation, he is known to the English-speaking world by the Anglicised form John à Lasco.
Prosperity theology is a religious belief among some Charismatic Christians that financial blessing and physical well-being are always the will of God for them, and that faith, positive speech, and donations to religious causes will increase one's material wealth. Material and especially financial success is seen as a sign of divine favor.

Anti-Protestantism is bias, hatred or distrust against some or all branches of Protestantism and/or its followers.
The Augsburg Interim was an imperial decree ordered on 15 May 1548 at the 1548 Diet of Augsburg by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, who had just defeated the forces of the Protestant Schmalkaldic League in the Schmalkaldic War of 1546/47. Although it ordered Protestants to readopt traditional Catholic beliefs and practices, including the seven Sacraments, it allowed for Protestant clergymen the right to marry and for the laity to receive communion in both kinds. It is considered the first significant step in the process leading to the political and religious legitimization of Protestantism as a valid alternative Christian creed to Roman Catholicism finally realized in the 1552 Peace of Passau and the 1555 Peace of Augsburg. The Interim became Imperial law on 30 June 1548. The Pope advised all bishops to abide by the concessions made to the Protestants in the Interim in August 1549.

A Beerwolf is a German folk-tale monster commonly known as a werewolf.

John Witte Jr. is a Canadian-American academic. He is a Robert W. Woodruff University Professor and a McDonald Distinguished Professor at Emory University School of Law in Atlanta, Georgia, and is director of the Center for the Study of Law and Religion there.
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Protestant Reformation.

Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began in the 16th century with the goal of reforming the Catholic Church from perceived errors, abuses, and discrepancies.
The religion of Protestantism, a form of Christianity, was founded within Germany in the 16th-century Reformation. It was formed as a new direction from some Roman Catholic principles. It was led initially by Martin Luther and later by John Calvin.
Resistance theory is an aspect of political thought, discussing the basis on which constituted authority may be resisted, by individuals or groups. In the European context it came to prominence as a consequence of the religious divisions in the early modern period that followed the Protestant Reformation. Resistance theories could justify disobedience on religious grounds to monarchs, and were significant in European national politics and international relations in the century leading up to the Peace of Westphalia of 1648. They can also underpin and justify the concept of revolution as now understood. The resistance theory of the early modern period can be considered to predate the formulations of natural and legal rights of citizens, and to co-exist with considerations of natural law.
Law and religion is the interdisciplinary study of relationships between law, especially public law, and religion. Over a dozen scholarly organizations and committees focussing on law and religion were in place by 1983, and a scholarly quarterly, the Journal of Law and Religion, was first published that year. The Ecclesiastical Law Journal began publication in 1987. The Rutgers Journal of Law and Religion was founded in 1999. The Oxford Journal of Law and Religion was founded in England in 2012.
Historicism is a method of interpretation in Christian eschatology which associates biblical prophecies with actual historical events and identifies symbolic beings with historical persons or societies; it has been applied to the Book of Revelation by many writers. The Historicist view follows a straight line of continuous fulfillment of prophecy which starts in Daniel's time and goes through John of Patmos' writing of the Book of Revelation all the way to the Second Coming of Jesus Christ.

The doctrine of the lesser magistrate is a concept in Protestant thought. A lesser magistrate is a ruler such as a prince who is under a greater ruler such as an emperor. The doctrine of the lesser magistrate is a legal system explaining the exact circumstances in which a lesser magistrate has both the right and the responsibility to resist the greater ruler.

The right to resist is a human right, although its scope and content are controversial. The right to resist, depending on how it is defined, can take the form of civil disobedience or armed resistance against a tyrannical government or foreign occupation; whether it also extends to non-tyrannical governments is disputed. Although Hersch Lauterpacht, one of the most distinguished jurists, called the right to resist the supreme human right, this right's position in international human rights law is tenuous and rarely discussed. Forty-two countries explicitly recognize a constitutional right to resist, as does the African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights.













