Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that causes genes to be expressed or not, depending on whether they are inherited from the mother or the father. Genes can also be partially imprinted. Partial imprinting occurs when alleles from both parents are differently expressed rather than complete expression and complete suppression of one parent's allele. Forms of genomic imprinting have been demonstrated in fungi, plants and animals. In 2014, there were about 150 imprinted genes known in mice and about half that in humans. As of 2019, 260 imprinted genes have been reported in mice and 228 in humans.

Nature is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, Nature features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. Nature was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 Journal Citation Reports, making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. As of 2012, it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month.
Olfactory receptors (ORs), also known as odorant receptors, are chemoreceptors expressed in the cell membranes of olfactory receptor neurons and are responsible for the detection of odorants which give rise to the sense of smell. Activated olfactory receptors trigger nerve impulses which transmit information about odor to the brain. These receptors are members of the class A rhodopsin-like family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The olfactory receptors form a multigene family consisting of around 800 genes in humans and 1400 genes in mice.

The laboratory mouse or lab mouse is a small mammal of the order Rodentia which is bred and used for scientific research or feeders for certain pets. Laboratory mice are usually of the species Mus musculus. They are the most commonly used mammalian research model and are used for research in genetics, physiology, psychology, medicine and other scientific disciplines. Mice belong to the Euarchontoglires clade, which includes humans. This close relationship, the associated high homology with humans, their ease of maintenance and handling, and their high reproduction rate, make mice particularly suitable models for human-oriented research. The laboratory mouse genome has been sequenced and many mouse genes have human homologues.

Comparative genomics is a field of biological research in which the genomic features of different organisms are compared. The genomic features may include the DNA sequence, genes, gene order, regulatory sequences, and other genomic structural landmarks. In this branch of genomics, whole or large parts of genomes resulting from genome projects are compared to study basic biological similarities and differences as well as evolutionary relationships between organisms. The major principle of comparative genomics is that common features of two organisms will often be encoded within the DNA that is evolutionarily conserved between them. Therefore, comparative genomic approaches start with making some form of alignment of genome sequences and looking for orthologous sequences in the aligned genomes and checking to what extent those sequences are conserved. Based on these, genome and molecular evolution are inferred and this may in turn be put in the context of, for example, phenotypic evolution or population genetics.

Peromyscus is a genus of rodents. They are commonly referred to as deer mice or deermice, not to be confused with the chevrotain or "mouse deer". They are New World mice only distantly related to the common house and laboratory mouse, Mus musculus. From this relative, Peromyscus species are distinguished by relatively larger eyes, and also often two-tone coloring, with darker colors over the dorsum (back), and white abdominal and limb hair-coloring. In reference to the coloring, the word Peromyscus comes from Greek words meaning "booted mouse". They are also accomplished jumpers and runners by comparison to house mice, and their common name of "deer mouse" is in reference to this agility.
Nature Portfolio is a division of the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature that publishes academic journals, magazines, online databases, and services in science and medicine.

Boreoeutheria is a magnorder of placental mammals that groups together superorders Euarchontoglires and Laurasiatheria. With a few exceptions male animals in the clade have a scrotum, an ancestral feature of the clade. The sub-clade Scrotifera was named after this feature.
Mouse Genome Informatics (MGI) is a free, online database and bioinformatics resource hosted by The Jackson Laboratory, with funding by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the National Cancer Institute (NCI), and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). MGI provides access to data on the genetics, genomics and biology of the laboratory mouse to facilitate the study of human health and disease. The database integrates multiple projects, with the two largest contributions coming from the Mouse Genome Database and Mouse Gene Expression Database (GXD). As of 2018, MGI contains data curated from over 230,000 publications.

Karen B. Avraham is an Israeli-American human geneticist. Born in Canada in 1962, Avraham moved to the US at a young age. She holds the Drs Sarah and Felix Dumont Chair for Research of Hearing Disorders.

Kerstin Lindblad-Toh is a scientist in comparative genomics, specializing in mammalian genetics. She is the Scientific Director of vertebrate genomics at the Broad Institute and a professor in comparative genomics at Uppsala University. In 2010 she co-founded Science for Life Laboratory (SciLifeLab) together with Mathias Uhlén and acted as Co-Director until 2015. As the leader of the Broad Institute's Mammalian Genome Initiative she has led the effort to sequence and analyze the genomes of various mammals, including mouse, dog, chimpanzee, horse, rabbit and opossum. She has researched extensively on the genetics of dogs, identifying genes and genetic variants important in disease susceptibility, morphology and behavior.

60S ribosomal protein L38 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL38 gene.
Rudi Balling is a German geneticist. He is the founding director of the Luxembourg Centre for Systems Biomedicine at the University of Luxembourg (2009-2021) He has served as President of the International Mammalian Genome Society and as co-editor of the Annual Review of Nutrition since 2018. In 2016 Balling received Luxembourg's Ordre de Mérite (Commandeur) from Prime Minister Xavier Bettel.

A genetically modified mouse or genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) is a mouse that has had its genome altered through the use of genetic engineering techniques. Genetically modified mice are commonly used for research or as animal models of human diseases, and are also used for research on genes. Together with patient-derived xenografts (PDXs), GEMMs are the most common in vivo models in cancer research. Both approaches are considered complementary and may be used to recapitulate different aspects of disease. GEMMs are also of great interest for drug development, as they facilitate target validation and the study of response, resistance, toxicity and pharmacodynamics.

A knockout rat is a genetically engineered rat with a single gene turned off through a targeted mutation used for academic and pharmaceutical research. Knockout rats can mimic human diseases and are important tools for studying gene function and for drug discovery and development. The production of knockout rats was not economically or technically feasible until 2008.

Stephen J. O'Brien is an American geneticist. He is known for his research contributions in comparative genomics, virology, genetic epidemiology, mammalian systematics and species conservation. Member of the National Academy of Sciences and a Foreign Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Author or co-author of over 850 scientific articles and the editor of fourteen volumes.

The International Mammalian Genome Society (IMGS) is a professional scientific organization that promotes and coordinates the genetic and genomic study of mammals. It has a scientific journal, Mammalian Genome, and organizes an annual international meeting, the International Mammalian Genome Conference (IMGC).
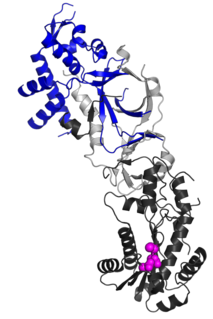
Ribonuclease H2, subunit B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2B gene. RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit (A) and two non-catalytic subunits, and degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. The non-catalytic B subunit of RNase H2 is thought to play a role in DNA replication.

Steve David Macleod Brown is director of the Medical Research Council (MRC) Mammalian Genetics Unit, MRC Harwell at Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Oxfordshire, a research centre on mouse genetics. In addition, he leads the Genetics and Pathobiology of Deafness research group.
Mouse News Letter (MNL) was a bulletin of mouse genetics information published from 1949 to 1998. In 1990 Mouse News Letter changed its name to Mouse Genome which merged with the journal Mammalian Genome in 1998. Mouse News Letter now exists as a company, Mouse News Letter Ltd, which promotes the science of Genetics and provides funds to enable younger scientists to attend Genetics Conferences. “To survey the history of the Mouse News Letter is to see the history of mouse genetics unfold.” So wrote Mary F Lyon in 1997.













