Related Research Articles
Education reform is the name given to the goal of changing public education. The meaning and education methods have changed through debates over what content or experiences result in an educated individual or an educated society. Historically, the motivations for reform have not reflected the current needs of society. A consistent theme of reform includes the idea that large systematic changes to educational standards will produce social returns in citizens' health, wealth, and well-being.

Diane Silvers Ravitch is a historian of education, an educational policy analyst, and a research professor at New York University's Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development. Previously, she was a U.S. Assistant Secretary of Education. In 2010, she became "an activist on behalf of public schools". Her blog at DianeRavitch.net has received more than 36 million page views since she began blogging in 2012. Ravitch writes for the New York Review of Books.
The Doctor of Education is a research or professional doctoral degree that focuses on the field of education. It prepares the holder for academic, research, administrative, clinical, or professional positions in educational, civil, private organizations, or public institutions.

Robert Ellsworth Wise Jr. is an American politician who served as the 33rd Governor of West Virginia from 2001 to 2005. A member of the Democratic Party, Wise also served in the United States House of Representatives from 1983 until 2001. In 2005 Wise became the president of the Alliance for Excellent Education, a nonprofit organization that focuses on reforming the nation's high schools. In 2015, North Carolina State University honored Wise with the William and Ida Friday Institute for Educational Innovation's Friday Medal which recognizes significant, distinguished and enduring contributions to education through advocating innovation, advancing education and imparting inspiration.
Educational assessment or educational evaluation is the systematic process of documenting and using empirical data on the knowledge, skill, attitudes, aptitude and beliefs to refine programs and improve student learning. Assessment data can be obtained from directly examining student work to assess the achievement of learning outcomes or can be based on data from which one can make inferences about learning. Assessment is often used interchangeably with test, but not limited to tests. Assessment can focus on the individual learner, the learning community, a course, an academic program, the institution, or the educational system as a whole. The word 'assessment' came into use in an educational context after the Second World War.

The No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 (NCLB) was a U.S. Act of Congress that reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act; it included Title I provisions applying to disadvantaged students. It supported standards-based education reform based on the premise that setting high standards and establishing measurable goals could improve individual outcomes in education. The Act required states to develop assessments in basic skills. To receive federal school funding, states had to give these assessments to all students at select grade levels.
Education policy consists of the principles and policy decisions that influence the field of education, as well as the collection of laws and rules that govern the operation of education systems. Education governance may be shared between the local, state, and federal government at varying levels. Some analysts see education policy in terms of social engineering.

The Carnegie Corporation of New York is a philanthropic fund established by Andrew Carnegie in 1911 to support education programs across the United States, and later the world. Carnegie Corporation has endowed or otherwise helped to establish institutions that include the United States National Research Council, what was then the Russian Research Center at Harvard University, the Carnegie libraries and the Children's Television Workshop. It also for many years generously funded Carnegie's other philanthropic organizations, the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (CEIP), the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching (CFAT), and the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS). According to the OECD, Carnegie Corporation of New York's financing for 2019 development increased by 27% to US$24 million.

Agricultural education is the teaching of agriculture, natural resources, and land management. At higher levels, agricultural education is primarily undertaken to prepare students for employment in the agricultural sector. Classes taught in an agricultural education curriculum may include horticulture, land management, turf grass management, agricultural science, small animal care, machine and shop classes, health and nutrition, livestock management, and biology.
The Certificate of Mastery (CIM) was created by report "America's Choice: High Skills or Low Wages". The CIM has been called an outcome-based education diploma as it would be necessary to either receive or replace the high school diploma, and was characteristic of education reform legislation in many states such as Washington and Oregon.
The National Center on Education and the Economy (NCEE) is an American not-for-profit education research, advocacy, and educator professional learning organization based in Washington, DC, that first formed in 1988 as the Carnegie Forum on Education and the Economy.
The National Educational Goals, also known as the Goals 2000Act were set by the U.S. Congress in the 1990s to set goals for standards-based education reform. The intent was for certain criteria to be met by the millennium (2000). Many of these goals were based on the principles of outcomes-based education, and not all of the goals were attained by the year 2000 as intended. Many see this as the predecessor to the No Child Left Behind program, which mandated measurable improvement in student achievement across all groups. Goals 2000 established a framework in which to identify world-class academic standards, to measure student progress, and to provide the support that students may need to help meet the standards.
Education reform in the United States since the 1980s has been largely driven by the setting of academic standards for what students should know and be able to do. These standards can then be used to guide all other system components. The SBE reform movement calls for clear, measurable standards for all school students. Rather than norm-referenced rankings, a standards-based system measures each student against the concrete standard. Curriculum, assessments, and professional development are aligned to the standards.
Linda Darling-Hammond is an American academic who is the Charles E. Ducommun Professor of Education Emeritus at the Stanford Graduate School of Education. She was also the President and CEO of the Learning Policy Institute. She is author or editor of more than 25 books and more than 500 articles on education policy and practice. Her work focuses on school restructuring, teacher education, and educational equity. She was education advisor to Barack Obama's 2008 presidential campaign and was reportedly among candidates for United States Secretary of Education in the Obama administration.
Patricia Wasley, EdD, is the Chief Executive Officer at Teaching Channel and is responsible for setting the educational direction of the website. Prior to joining Teaching Channel, Dr. Wasley was dean of the College of Education at the University of Washington from 2000 to 2012. Wasley has conducted a variety of research on student voice, teacher education and whole-school reform. She is the author of several books on school reform, including Teachers Who Lead and Stirring the Chalkdust, and is the co-author of Kids and School Reform.
The National Board for Professional Teaching Standards (NBPTS) is a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization in the United States. Founded in 1987, NBPTS develops and maintains advanced standards for educators and offers a national, voluntary assessment, National Board Certification, based on the NBPTS Standards. As of December 2017, more than 118,000 educators have become National Board Certified Teachers in the United States. Its headquarters is located in Arlington, Va.

Literacy in the United States was categorized by the National Center for Education Statistics into different literacy levels, with 92% of American adults having at least "Level 1" literacy in 2019. According to the U.S. Department of Education, 54% of adults in the United States have prose literacy below the 6th-grade level.
Barnett Berry is a research professor at the University of South Carolina, where he is the founding director of Accelerating for Learning and Leadership for South Carolina (ALL4SC) — an initiative launched in 2019, to marshal the resources of an entire R1 institution of higher education in service of high need school communities. Barnett’s career includes serving as a high school teacher, a social scientist at the RAND Corporation, a professor at UofSC, a senior state education agency leader, and senior consultant with the National Commission on Teaching and America's Future, leading its state partnership network. From 1999 to 2018, Barnett led Center for Teaching Quality website, a non-profit he founded to conduct research and ignite teacher leadership to transform the teaching profession and public education for more equitable outcomes for students. Barnett has authored a wide array of over 120 policy and research reports, journal articles, and commissioned papers. His two books, TEACHING 2030 and Teacherpreneurs: Innovative Teachers Who Lead But Don't Leave, frame a bold vision for the profession's future. He is the 2021 recipient of the James A. Kelly Award for Advancing Accomplished Teaching from the National Board for Professional Teaching Standards and is a policy advisor for the Learning Policy Institute.
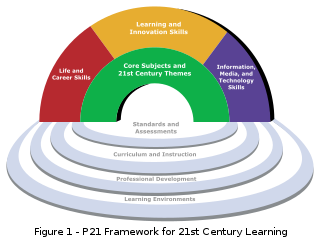
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. This is part of a growing international movement focusing on the skills required for students to master in preparation for success in a rapidly changing, digital society. Many of these skills are also associated with deeper learning, which is based on mastering skills such as analytic reasoning, complex problem solving, and teamwork. These skills differ from traditional academic skills in that they are not primarily content knowledge-based.
Martin Carnoy is an American labour economist and Vida Jacks Professor of Education at the Stanford Graduate School of Education. He is an elected member of the National Academy of Education as well as of the International Academy of Education. Professor Carnoy has graduated nearly 100 PhD students, a record at Stanford University.
References
- ↑ National Research Council (2002). "Appendix C: Biographical Sketches". Investigating the Influence of Standards: A Framework for Research in Mathematics, Science, and Technology Education. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. pp. 115–124. doi:10.17226/10023. ISBN 978-0-309-07276-2.
- ↑ "Marc Tucker".
- ↑ "Marc Tucker". 25 September 2011.
- ↑ Reviews of A Nation Prepared: Robert Laurent, Recherche & formation (in French),
- ↑ Rigden, John S. (1986). "Editorial: The Carnegie report, A Nation Prepared: Teachers for the 21st Century". American Journal of Physics. American Association of Physics Teachers (AAPT). 54 (8): 683. Bibcode:1986AmJPh..54..683R. doi:10.1119/1.14502. ISSN 0002-9505.
- ↑ Review of America's Choice: Horst Brand, "Setting new standards for skills in the workplace", Monthly Labor Review, JSTOR 41843396
- ↑ Kirst, Michael; Marshall, Ray; Tucker, Marc (1993). "Thinking for a Living: Education and the Wealth of Nations". Political Science Quarterly. Wiley. 108 (2): 345. doi:10.2307/2152024. ISSN 0032-3195. JSTOR 2152024.
- ↑ Barry Bluestone, Journal of Economic Literature, JSTOR 2728451;
- ↑ Review of Standards for Our Schools: Publishers Weekly
- ↑ Review of The Principal Challenge: Harold Wenglinsky, "From Practice to Praxis: Books about the New Principal Preparation", Educational Researcher, JSTOR 3699822
- ↑ Reviews of Surpassing Shanghai: Susan D. Patrick, "Can American Schools Challenge the World's Leading K-12 Educational Systems?", Educational Technology, JSTOR 44430046