Related Research Articles
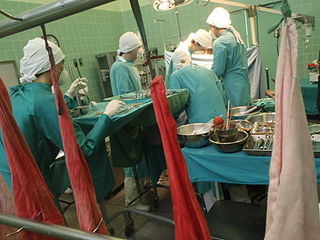
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source.

Joseph Edward Murray was an American plastic surgeon who performed the first successful human kidney transplant on identical twins Richard and Ronald Herrick on December 23, 1954.

The Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons is the medical school of Columbia University, located at the Columbia University Irving Medical Center in the Washington Heights neighborhood of Manhattan.
The School of Nursing is the graduate school of nursing at Columbia University in the Washington Heights neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 1892, it stands as one of the oldest nursing schools in the United States.

Sir Roy Yorke Calne was a British surgeon and pioneer in organ transplantation. He was part of the team that performed the first liver transplantation operation in Europe in 1968, the world's first liver, heart and lung transplantation in 1987, the first intestinal transplant in the UK in 1992 and the first successful combined stomach, intestine, pancreas, liver and kidney cluster transplantation in 1994.

Morgan Stanley Children's Hospital of NewYork-Presbyterian is a women's and children's hospital at 3959 Broadway, near West 165th Street, in the Washington Heights neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. It is a part of NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital and the Columbia University Irving Medical Center. The hospital treats patients aged 0–21 from New York City and around the world. The hospital features a dedicated regional ACS designated pediatric Level 1 Trauma Center and is named after financial firm Morgan Stanley, which largely funded its construction through philanthropy.
Henry M. Spotnitz is George H. Humphrey II Professor of Surgery, chairman of the Columbia University Medical Center Conflict of Interest Committee, co-chair of the NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Information Systems Clinical Advisory Committee, chair of the Information Technology Committee of the Faculty Practice Organization, and Vice-Chair for Research and Information Systems in the Department of Surgery.
Jean C. Emond is the current Thomas S. Zimmer Professor of Surgery at the Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons. He is also a Vice Chair in the Department of Surgery and the Chief of Transplantation at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center. Dr. Emond completed both his undergraduate ('75) and medical training ('79) at the University of Chicago.
Adrian Kantrowitz was an American cardiac surgeon whose team performed the world's second heart transplant attempt at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York on December 6, 1967. The infant lived for only six hours. At a press conference afterwards, Kantrowitz emphasized that he considered the operation to have been a failure.
The Rogosin Institute is an independent, not-for-profit treatment and research center with facilities throughout New York City that treat patients with kidney disease, including dialysis and kidney transplantation; lipid disorders; and hypertension. It is affiliated with NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medical College and is a leader in research programs for cancer and diabetes.
Tomoaki Kato is a pioneer in multiple-organ transplantation, pediatric and adult liver transplantation. Kato is Surgical Director of Adult and Pediatric Liver and Intestinal Transplantation at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center and is a professor of surgery at Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. Kato is also known for unique and innovative surgeries for adults and children, including a six-organ transplant; a procedure called APOLT that resuscitates a failing liver by attaching a partial donor liver, making immunosuppressant drugs unnecessary; and the first successful human partial bladder transplantation involving the transplant of two kidneys together with ureters connected to a patch of the donor bladder. In a highly publicized case, he led the first reported removal and re-implantation, or auto-transplantation, of six organs to excise a hard-to-reach abdominal tumor. Previously the director of pediatric liver and gastrointestinal transplant and professor of clinical surgery at the University of Miami School of Medicine, Kato received his medical degree from the Osaka University Medical School in Japan and received his residency training in surgery at Osaka University Hospital and Itami City Hospital in Hyogo, Japan. He completed a clinical fellowship in transplantation at the University of Miami/Jackson Memorial Hospital, in Miami, Florida, where he was subsequently appointed to the surgical faculty in 1997, and promoted to full professor in 2007. He served as a surgeon and senior leader of the liver and transplantation center at Miami's Jackson Memorial Hospital, beginning in 1997, and at University of Miami Hospital, beginning in 2004. Kato is a member of numerous professional and honorary organizations, and the author or co-author of more than 180 scientific papers in peer-reviewed journals.

Francis L. Delmonico, MD, FACS is an American surgeon, clinical professor and health expert in the field of transplantation. He serves on numerous committees and is affiliated with various leading organizations and institutions. He is the chief medical officer of the New England Organ Bank (NEOB) and Professor of Surgery, Part-Time at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts, where he is emeritus director of renal transplantation. He served as president of The Transplantation Society (TTS) from 2012 to 2014, an international non-profit organization based in Montreal, Canada that works with international transplantation physicians and researchers. He also served as the president of the United Network of Organ Sharing (UNOS) in 2005, which overseas the practice of organ donation and transplantation in the United States. He was appointed and still serves as an advisor to the World Health Organization in matters of organ donation and transplantation. He was appointed by Pope Francis to the Pontifical Academy of Science in 2016. In 2020, he became the recipient of the Medawar Prize of The Transplantation Society.

A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. As of 2018, the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart, with or without both lungs, from a recently deceased organ donor and implant it into the patient. The patient's own heart is either removed and replaced with the donor heart or, much less commonly, the recipient's diseased heart is left in place to support the donor heart.
Sarbeswar Sahariah is an Indian nephrologist and organ transplant specialist, known for his expertise in renal and pancreatic transplantation. He was honoured by the Government of India, in 2014, by bestowing on him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, for his contributions to the field of medicine. Sahariah is credited with more than 3000 renal transplantations, which many consider, has made him the most prolific kidney transplant surgeon in the country.
Christopher S. Ahmad is the head team physician for the New York Yankees and a member of the Major League Baseball Team Physicians Association. He is a professor of clinical orthopaedic surgery at the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons and an attending orthopaedic surgeon at the New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center. In 2013, New York Yankee Alex Rodriguez filed a medical malpractice lawsuit against Ahmad, which he subsequently dropped.
Rainer W.G. Gruessner is a German-born American general surgeon and transplant surgeon, most noted as a surgical pioneer for his clinical and research innovations. Gruessner was the first transplant surgeon to perform all types of abdominal transplants from living donors.

René Küss was a French urologist and transplant surgeon who made pioneering contributions in renal tract surgery and kidney transplantation with the establishment of transplant programs. At a time of unavoidable transplant rejection, he was involved in two particularly historic transplant operations. The first was a human-to-human extraperitoneal kidney transplant procedure in 1951 and later a pig-to-human kidney transplant in 1966, both of which ended in abrupt rejection. He later introduced kidney transplantation schedules involving at first irradiation, later immunosuppressants, living-related and unrelated donors and later organs from deceased donors.
Eric A. Rose is an American cardiothoracic surgeon, scientist, entrepreneur and professor and Chairman of the Department of Population Health Science & Policy, and Associate Director for Clinical Outcomes at Mount Sinai Heart. He is best known for performing the first successful paediatric heart transplant, in 1984 while at NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital (NYP).

Keith Reemtsma was an American transplant surgeon, best known for the cross-species kidney transplantation operation from chimpanzee to human in 1964. With only the early immunosuppressants and no long-term dialysis, the female recipient survived nine months, long enough to return to work.

Priyadarshi Ranjan is an Indian urologist, robotic surgery specialist, kidney transplant surgeon, and researcher. He is commonly perceived as the "Kidney Man of India". He is among the top 10 transplant surgeons across the globe who is certified of performing a Robotic Kidney Transplant. Currently, regarded as one of the pioneering leads for kidney transplantation across the globe.
References
- ↑ "Retirement of Transplant Pioneer Dr. Mark Hardy Shows How Far We've Come". columbiasurgery.org. Columbia University’s Department of Surgery. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
- 1 2 3 "Mark Hardy, MD". asts.org. American Society of Transplant Surgeons. Retrieved February 14, 2024.