Sustainable development is an approach to growth and human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The aim is to have a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining planetary integrity. Sustainable development aims to balance the needs of the economy, environment, and society. The Brundtland Report in 1987 helped to make the concept of sustainable development better known.
Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes. The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.

In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization operates. Strategic management provides overall direction to an enterprise and involves specifying the organization's objectives, developing policies and plans to achieve those objectives, and then allocating resources to implement the plans. Academics and practicing managers have developed numerous models and frameworks to assist in strategic decision-making in the context of complex environments and competitive dynamics. Strategic management is not static in nature; the models can include a feedback loop to monitor execution and to inform the next round of planning.
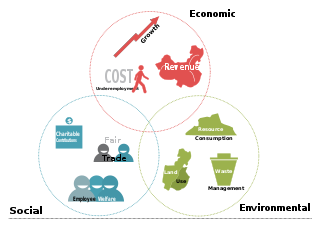
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and economic. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.

Forrester is one of the most influential research and advisory firms in the world, empowering leaders in technology, customer experience, digital, marketing, sales, and product functions to be bold at work and accelerate growth through customer obsession. Forrester's unique research and continuous guidance model helps executives and their teams achieve their initiatives and outcomes faster and with confidence.

Michael Eugene Porter is an American businessman and professor at Harvard Business School. He was one of the founders of the consulting firm The Monitor Group and FSG, a social impact consultancy. He is credited with creating Porter's five forces analysis, a widely-used management framework. He is generally regarded as the father of the modern strategy field. He is also regarded as one of the world's most influential thinkers on management and competitiveness as well as one of the most influential business strategists. His work has been recognized by governments, non-governmental organizations and universities.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."
Sitra, the Finnish Innovation Fund, is an independent public foundation which operates directly under the supervision of the Finnish Parliament. Its endowment was valued at 771 million euros in 2017. Its duties are stated in legislation: the objective of the foundation is "to promote stable and balanced development in Finland, qualitative and quantitative economic growth and international competitiveness and cooperation", by means of supporting "projects that increase the efficiency of the economy, improve the level of education or research, or study future development scenarios". Sitra functions both as a think tank and as an investment company. Sitra was founded in 1967 as a part of the Bank of Finland, on the country's 50th anniversary. However, most of the value of its current endowment comes from a donation of Nokia stock from the Finnish Parliament in 1992.
A sustainable business, or a green business, is an enterprise with a minimal negative impact or potentially a positive effect on the global or local environment, community, society, or economy. This business attempts to meet the triple bottom line. They cluster under different groupings, and the whole is sometimes referred to as "green capitalism." Often, sustainable businesses have progressive environmental and human rights policies. In general, a business is described as green if it matches the following four criteria:
- It incorporates principles of sustainability into each of its business decisions.
- It supplies environmentally friendly products or services that replace demand for nongreen products and/or services.
- It is greener than traditional competition.
- It has made an enduring commitment to environmental principles in its business operations.
Megatrends are trends that have an effect on a global scale. Some of the current megatrends relate to global threats.
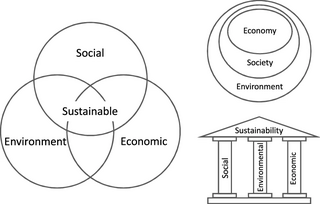
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions : environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "Sustainability is often thought of as a long-term goal, while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it."
Creating shared value (CSV) is a business concept first introduced in a 2006 Harvard Business Review article, Strategy & Society: The Link between Competitive Advantage and Corporate Social Responsibility. The concept was further expanded in the January 2011 follow-up piece entitled Creating Shared Value: Redefining Capitalism and the Role of the Corporation in Society. Written by Michael E. Porter, a leading authority on competitive strategy and head of the Institute for Strategy and Competitiveness at Harvard Business School, and Mark R. Kramer, of the Kennedy School at Harvard University and co-founder of FSG, the article provides insights and relevant examples of companies that have developed deep links between their business strategies and corporate social responsibility (CSR). Porter and Kramer define shared value as "the policies and practices that enhance the competitiveness of a company while simultaneously advancing social and economic conditions in the communities in which it operates", while a review published in 2021 defines the concept as "a strategic process through which corporations can turn social problems into business opportunities".
According to PIMS, an important lever of business success is growth. Among 37 variables, growth is mentioned as one of the most important variables for success: market share, market growth, marketing expense to sales ratio or a strong market position.

Green growth is a concept in economic theory and policymaking used to describe paths of economic growth that are environmentally sustainable. It is based on the understanding that as long as economic growth remains a predominant goal, a decoupling of economic growth from resource use and adverse environmental impacts is required. As such, green growth is closely related to the concepts of green economy and low-carbon or sustainable development. A main driver for green growth is the transition towards sustainable energy systems. Advocates of green growth policies argue that well-implemented green policies can create opportunities for employment in sectors such as renewable energy, green agriculture, or sustainable forestry.
The National Competitiveness Report of Armenia (ACR) is an annual publication of EV Consulting and the Economy and Values Research Center that aims to encourage and foster in-depth dialogue and analysis on improving Armenia's competitiveness.

François Adrianus "Frans" van Houten is a Dutch businessman. He served as the CEO of Royal Philips Electronics from 1 April 2011 to 15 October 2022.

A circular economy is a model of resource production and consumption in any economy that involves sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling existing materials and products for as long as possible. The concept aims to tackle global challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution by emphasizing the design-based implementation of the three base principles of the model. The main three principles required for the transformation to a circular economy are: designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. CE is defined in contradistinction to the traditional linear economy.

"Fourth Industrial Revolution", "4IR", or "Industry 4.0", is a neologism describing rapid technological advancement in the 21st century. It follows the Third Industrial Revolution. The term was popularised in 2016 by Klaus Schwab, the World Economic Forum founder and executive chairman, who asserts that these developments represent a significant shift in industrial capitalism.
Terence Chee Ming Tse [謝慈銘] is an educator, speaker, advisor and commentator. He is a co-founder of Nexus FrontierTech, an artificial intelligence studio. Tse is an Associate Professor of Finance at the ESCP business school, and Hult International Business School. In addition to working with the EU and UN, Tse regularly provides commentaries on the financial market in the Financial Times, The Guardian, The Economist, CNBC, the World Economic Forum and the Harvard Business Review blogs.
Olaf J. Groth is a German-American innovation futures and strategy scholar, author, advisor, and speaker. Groth is a full time Professional Faculty for Global Foresight, Strategy, Innovation and Policy at UC Berkeley Haas School of Business. At Berkeley, he is the Faculty Director for the Berkeley Executive Education program Future of Technology/Emerging Technologies Strategies, a Senior Adviser and Executive-in-Residence at the Institute for Business Innovation and a startup mentor at Berkeley Skydeck. He has been an Honorary Adjunct Professor at University of Technology Malaysia since May 2024. Groth started teaching as a full-time Professor of Practice at Hult International Business School in 2012 and transitioned to Adjunct Professor of Practice in 2023. He is the co-founder and CEO of Cambrian Futures and Cambrian Labs, and he sits on the advisory and ethics board at Hayden AI. Groth has been a member of the Global Expert Network for the 4th Industrial Revolution, the Global Alliance for AI Governance (AIGA) at the World Economic Forum.









