The history of Grenada in the Caribbean, part of the Lesser Antilles group of islands, covers a period from the earliest human settlements to the establishment of the contemporary nationstate of Grenada. First settled by indigenous peoples, Grenada by the time of European contact was inhabited by the Caribs. British colonists killed most of the Caribs on the island and established plantations on the island, eventually importing African slaves to work on the sugar plantations.

The demography of the people of Grenada, Grenadians, includes population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Whit Monday or Pentecost Monday, also known as Monday of the Holy Spirit, is the holiday celebrated the day after Pentecost, a moveable feast in the Christian liturgical calendar. It is moveable because it is determined by the date of Easter. In the Catholic Church, it is the Memorial of the Blessed Virgin Mary, Mother of the Church, marking the resumption of Ordinary Time.

Catherine-Dominique de Pérignon, 1st Marquis de Pérignon was a French general during the French Revolutionary Wars, and was appointed Marshal of the Empire in 1804 by Napoleon Bonaparte.

Saint Andrew's is the largest parish in Grenada. The main town is Grenville, which is also Grenada's second largest town after St George's. Grenville is also known as La Baye.
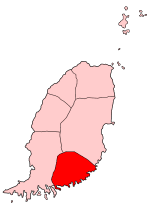
Saint David's Parish is the fourth largest of the parishes of Grenada in the island's southeast. The parish's main town is St. David's, located between La Tante and Westerhall. Because St David's is so small, the parish is sometimes referred to as "The Virgin Parish".

Admiral Sir William Cornwallis, was a Royal Navy officer. He was the brother of Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, British commander at the siege of Yorktown. Cornwallis took part in a number of decisive battles including the siege of Louisbourg in 1758, when he was 14, and the Battle of the Saintes but is best known as a friend of Lord Nelson and as the commander-in-chief of the Channel Fleet during the Napoleonic Wars. He is depicted in the Horatio Hornblower novel, Hornblower and the Hotspur.
Grenville is the third largest town in Grenada, after St. George's and Gouyave and it is the capital of the largest parish, Saint Andrew. It is one of four coastal villages located about halfway up the eastern coast of the Caribbean island of Grenada that make up the Grenville Bay Area.

Sauteurs is a fishing town in the Saint Patrick Parish, Grenada and is the sixth-largest town on the island of Grenada, with a population of about 1,300. It is located in the far north of Grenada. Sauteurs overlooks the Sauteurs Bay. It is the largest town in the northern part of Grenada, and it is the capital city of the Saint Patrick Parish.

Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about 100 miles (160 km) north of Trinidad and the South American mainland.

Afro-Grenadians or Black Grenadians are Grenadian people of largely African descent. This term is not generally recognised by Grenadians or indeed Caribbeans. They usually refer to themselves simply as 'Grenadians' or 'Caribbean'. The term was first coined by an African Americans history professor, John Henrik Clarke (1915–1998), in his piece entitled A Note on Racism in History. The term may also refer to a Grenadian of African ancestry. Social interpretations of race are mutable rather than deterministic and neither physical appearance nor ancestry are used straightforwardly to determine whether a person is considered a Black Grenadian. According to the 2012 Census, 82% of Grenada's population is Black, 13% is mixed European and black and 2% is of Indian origin.

The Capture of Grenada was an amphibious expedition in July 1779 during the American Revolutionary War. Charles Hector, comte D'Estaing led French forces against the British-held West Indies island of Grenada. The French forces landed on 2 July and the assault occurred on the night of 3–4 July. The French forces assaulted the British fortifications on Hospital Hill, overlooking the island's capital, Saint George's. The British cannons were captured and turned against Fort George. British Governor Lord Macartney opened negotiations to surrender.

Jean Gaspard de Vence was a French privateer, admiral and Maritime Prefect of Toulon.

Church of Pentecost in Markušica is Serbian Orthodox church in eastern Croatia. The church is one of two in the Eparchy of Osječko polje and Baranja that is dedicated to Pentecost. The church was built in the period between 1795 and 1810 at the site of an earlier wooden church dedicated in 1698.

Marquis Cornwallis was a merchantman built in Calcutta in 1789 or 1791. She made one voyage transporting convicts in 1796 from Ireland to Australia. The voyage was marred by mutiny that resulted in the death of 11 convicts. Marquis Cornwallis then made a voyage for the British East India Company (EIC) as an "extra ship", sailing from India back to Britain.
Fédon's rebellion was an uprising against British rule in Grenada. Although a significant number of slaves were involved, they fought on both sides. Predominantly led by free mixed-race French-speakers, the stated purpose was to create a black republic as had already occurred in neighbouring Haiti rather than to free slaves, so it is not properly called a slave rebellion, although freedom of the slaves would have been a consequence of its success. Under the leadership of Julien Fédon, owner of a plantation in the mountainous interior of the island, and encouraged by French Revolutionary leaders on Guadeloupe, the rebels seized control of most of the island, but were eventually defeated by a military expedition led by General Ralph Abercromby.
Julien Fédon, also called Julien Fedon, Foedonn, Feydn, and Fidon, was the leader of the Fédon Rebellion, a revolt against British rule led primarily by free mixed-race French-speakers that took place in Grenada between 2 March 1795 and 19 June 1796.
The French corvette Républicaine was a merchant ship launched in 1793 that the French Navy requisitioned in 1795 at Grenada. On 14 October 1795 Mermaid captured her in the Leeward Islands. The Royal Navy took Republicaine into service as HMS Republican, a lugger of 18 guns. It is not clear that Republican was ever commissioned. The Navy sold her at Grenada in 1803.
Old Dick was launched at Bermuda in 1789. She sailed to England and was lengthened in 1792. From 1792 on she made two full voyages as a Liverpool-based slave ship in the triangular trade in enslaved people. On her second she recaptured two British merchant ships. She was lost in 1796 at Jamaica after having landed her third cargo of captives.














