
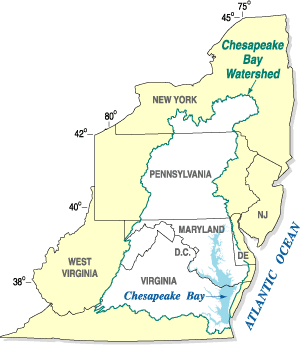
The Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland, the Eastern Shore of Virginia, and the state of Delaware. The mouth of the Bay at its southern point is located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's 64,299-square-mile (166,534 km2) drainage basin, which covers parts of six states, New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia, and all of Washington, D.C.

The National Estuarine Research Reserve System is a network of 30 protected areas established by partnerships between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and coastal states. The reserves represent different biogeographic regions of the United States. The National Estuarine Research Reserve System protects more than 1.3 million acres of coastal and estuarine habitats for long-term research, water-quality monitoring, education, and coastal stewardship.

The Monocacy River is a free-flowing left tributary to the Potomac River, which empties into the Atlantic Ocean via the Chesapeake Bay. The river is 58.5 miles (94.1 km) long, with a drainage area of about 970 square miles (2,500 km2). It is the largest Maryland tributary to the Potomac.
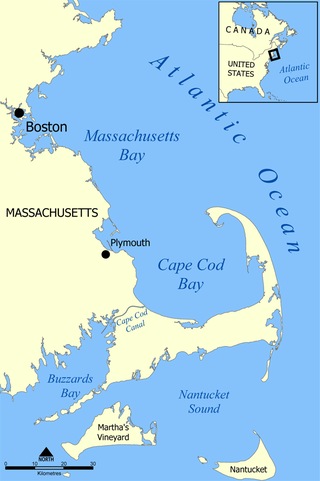
Cape Cod Bay is a large bay of the Atlantic Ocean adjacent to the U.S. state of Massachusetts. Measuring 604 square miles (1,560 km2) below a line drawn from Brant Rock in Marshfield to Race Point in Provincetown, Massachusetts, it is enclosed by Cape Cod to the south and east, and Plymouth County, Massachusetts, to the west. To the north of Cape Cod Bay lie Massachusetts Bay and the Atlantic Ocean. Cape Cod Bay is the southernmost extremity of the Gulf of Maine. Cape Cod Bay is one of the bays adjacent to Massachusetts that give it the name Bay State. The others are Narragansett Bay, Buzzards Bay, and Massachusetts Bay.

Assateague Island is a 37-mile (60 km) long barrier island located off the eastern coast of the Delmarva Peninsula facing the Atlantic Ocean. The northern two-thirds of the island is in Maryland while the southern third is in Virginia. The Maryland section contains the majority of Assateague Island National Seashore and Assateague State Park. The Virginia section contains Chincoteague National Wildlife Refuge and a one-mile stretch of land containing the lifeguarded recreational beach and interpretive facilities managed by the National Park Service. It is best known for its herds of feral horses, pristine beaches and the Assateague Lighthouse. The island also contains numerous marshes, bays, and coves, including Toms Cove. Bridge access for cars is possible from both Maryland and Virginia, though no road runs the full north/south length of the island.

The California State Coastal Conservancy is a non-regulatory state agency in California established in 1976 to enhance coastal resources and public access to the coast. The CSCC is a department of the California Natural Resources Agency. The agency's work is conducted along the entirety of the California coast, including the interior San Francisco Bay and is responsible for the planning and coordination of federal land sales to acquire into state land as well as award grant funding for improvement projects. The Board of Directors for the agency is made up of seven members who are appointed by the Governor of California and approved by the California Legislature, members of the California State Assembly and California State Senate engage and provide oversight within their legislative capacity.

Mattawoman Creek is a 30.0-mile-long (48.3 km) coastal-plain tributary to the tidal Potomac River with a mouth at Indian Head, Maryland, 20 miles (32 km) downstream of Washington, D.C. It comprises a 23-mile (37 km) river flowing through Prince George's and Charles counties and a 7-mile (11 km) tidal-freshwater estuary in Charles County. About three-fourths of its 94-square-mile (240 km2) watershed lies in Charles County, with the remainder in Prince George's County immediately to the north.
The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the Chesapeake Bay in the United States. As a partnership, the Chesapeake Bay Program brings together members of various state, federal, academic and local watershed organizations to build and adopt policies that support Chesapeake Bay restoration. By combining the resources and unique strengths of each individual organization, the Chesapeake Bay Program is able to follow a unified plan for restoration. The program office is located in Annapolis, Maryland.
The Maryland Department of Natural Resources (DNR) is a government agency in the state of Maryland charged with maintaining natural resources including state parks, public lands, state forests, state waterways, wildlife, and recreation areas. Its headquarters is in Annapolis.
The Alliance for the Chesapeake Bay (Alliance) is a regional nonprofit organization that builds and fosters partnerships and consensus to protect and to restore the Chesapeake Bay and its rivers and streams. Their motto is "Together, we can get the job done!".

Nutrient pollution, a form of water pollution, refers to contamination by excessive inputs of nutrients. It is a primary cause of eutrophication of surface waters, in which excess nutrients, usually nitrogen or phosphorus, stimulate algal growth. Sources of nutrient pollution include surface runoff from farm fields and pastures, discharges from septic tanks and feedlots, and emissions from combustion. Raw sewage is a large contributor to cultural eutrophication since sewage is high in nutrients. Releasing raw sewage into a large water body is referred to as sewage dumping, and still occurs all over the world. Excess reactive nitrogen compounds in the environment are associated with many large-scale environmental concerns. These include eutrophication of surface waters, harmful algal blooms, hypoxia, acid rain, nitrogen saturation in forests, and climate change.

In the United States, the National Estuary Program (NEP) provides grants to states where governors have identified nationally significant estuaries that are threatened by pollution, land development, or overuse. Governors have identified a total of 28 estuaries, and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) awards grants to these states to develop comprehensive management plans to restore and protect the estuaries. Congress created the NEP in the 1987 amendments to the Clean Water Act.
Back River is a tidal estuary in Baltimore County, Maryland, located about 2 miles (3 km) east of the city of Baltimore. The estuary extends from Essex, Maryland, southeast for about 8.8 miles (14.2 km) to the Chesapeake Bay. The watershed area is 39,075 acres (15,813 ha) and includes Essex Skypark Airport and the Back River Wastewater Treatment Plant. The river is shared between Essex, MD, Dundalk, MD, and Edgemere, MD
Restore America's Estuaries (RAE) is a national 501(c)(3) non-profit conservation organization dedicated to preserving the nation's network of estuaries through coastal protection and restoration projects which promote the richness and diversity of coastal life. Based in Arlington, VA with staff in Seattle, Colorado, and Florida, Restore America's Estuaries is an alliance of eleven community-based coastal conservation organizations that includes the American Littoral Society (ALS), Chesapeake Bay Foundation (CBF), Coalition to Restore Coastal Louisiana (CRCL), Conservation Law Foundation (CLF), Galveston Bay Foundation (GBF), North Carolina Coastal Federation (NCCF), Save The Bay – San Francisco (STB-SF), EarthCorps, Save The Bay – Narragansett Bay (STB-NB), Save the Sound (STS)-a program of Connecticut Fund for the Environment, and Tampa Bay Watch (TBW).
The North Carolina Coastal Federation is a nonprofit organization that works with coastal residents and visitors to protect and restore the beautiful and productive N.C. coast. The four main areas in which the federation operates include: coastal advocacy; environmental education; habitat and water quality restoration and preservation; and support in the improvement and enforcement of environmental laws. The federation headquarters are located in Newport (Ocean), North Carolina, with regional offices in Wanchese and Wrightsville Beach, North Carolina. The federation is currently a member of Restore America's Estuaries (RAE).

The San Francisco Estuary Partnership (Partnership) is one of the 28 National Estuary Programs created in the 1987 Amendments to the Clean Water Act. The Partnership is a non-regulatory federal-state-local collaboration working to restore water quality and manage the natural resources of the San Francisco Bay-Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta estuary. The Partnership works with over 100 municipalities, non-profits, governmental agencies, and businesses and helps develop, find funding for, and implement over 40 projects and programs aimed at improving the health of the estuary. The partnership either directly implements these projects, or administers and manages grants, holds educational workshops and highlights project results. The Partnership is also the official representative for the San Francisco Bay region to the Most Beautiful Bays in the World.

The Cheetham Wetlands are 420 hectares of artificial and natural lagoons, created on old salt works land on the western shores of Port Phillip Bay, Australia. The wetlands are approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of Melbourne, and sit within the Municipal Councils of Hobsons Bay and Wyndham City.
Chesapeake Conservancy is a non-profit organisation, whose aim is to use technology and advocacy to support conservation of the Chesapeake Bay estuary on the east coast of the United States. The group is based in Annapolis, Maryland.

The Chesapeake Bay Commission is an advisory body that consults with the legislatures of Maryland, Virginia and Pennsylvania about environmental, economic and social issues related to the Chesapeake Bay. The commission is a signatory to all agreements on matters regarding the bay, and advises Congress on bay-related issues. The commission was established under state law in 1980 by the states of Maryland and Virginia. Pennsylvania joined the commission in 1985.
Ilia Fehrer was an environmentalist and member of the Maryland Women's Hall of Fame most widely known for fighting to preserve Assateague Island, Chincoteague Bay, and other Chesapeake Bay coastal regions from destructive urban development.













