Related Research Articles

Thurston Island is a largely ice-covered, glacially dissected island, 135 nautical miles long and 55 nautical miles wide, lying between Amundsen Sea and Bellingshausen Sea a short way off the northwest end of Ellsworth Land, Antarctica. The island is separated from the mainland by Peacock Sound, which is occupied by the west portion of Abbot Ice Shelf.

Koettlitz Glacier is a large Antarctic glacier lying west of Mount Morning and Mount Discovery in the Royal Society Range, flowing from the vicinity of Mount Cocks northeastward between Brown Peninsula and the mainland into the ice shelf of McMurdo Sound.
Hobbs Coast is that portion of the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica extending from Cape Burks to a point on the coast opposite eastern Dean Island, at 74°42′S127°05′W, or between the Ruppert Coast in the west and the Bakutis Coast in the east. It stretches from 136°50′W to 127°35′. The coast was discovered by the US Antarctic Service (1939–1941) and named for Professor William H. Hobbs of the University of Michigan, a glaciologist specializing in polar geography and history. The United States Geological Survey completely mapped the coast from ground surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1959–1965.
Surveyors Range is a 30 miles (48 km) long mountain range in the Churchill Mountains of Antarctica.
The Porthos Range is the second range south in the Prince Charles Mountains of Antarctica, extending for about 30 miles in an east-to-west direction between Scylla Glacier and Charybdis Glacier. First visited in December 1956 by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party under W.G. Bewsher (1956-57) and named after Porthos, a character in Alexandre Dumas, père's novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.

Posadowsky Glacier is a glacier about 9 nautical miles long, flowing north to Posadowsky Bay immediately east of Gaussberg. Posadowsky Bay is an open embayment, located just east of the West Ice Shelf and fronting on the Davis Sea in Kaiser Wilhelm II Land. Kaiser Wilhelm II Land is the part of East Antarctica lying between Cape Penck, at 87°43'E, and Cape Filchner, at 91°54'E, and is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Other notable geographic features in this area include Drygalski Island, located 45 mi NNE of Cape Filchner in the Davis Sea, and Mirny Station, a Russian scientific research station.
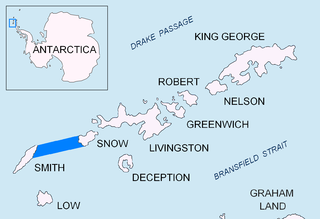
Boyd Strait is the 40-kilometre (25 mi) wide strait lying between Snow Island and Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, and linking Drake Passage and the Bransfield Strait.
Balch Glacier is a glacier 9 nautical miles (17 km) long, on the east coast of Graham Land, flowing southeast into Mill Inlet, to the south of Gould Glacier.

Belgica Glacier is a glacier 8 nautical miles (15 km) long, flowing into Trooz Glacier to the east of Lancaster Hill on Kyiv Peninsula, on the west coast of Graham Land. It was first charted by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill, 1934–37, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 after the RV Belgica, the ship of the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache which explored this area in 1897–99.
Johnston Passage is a channel in Antarctica, running north–south and separating the Amiot Islands from the southwestern part of Adelaide Island. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Captain William Johnston, from 1956 to 1962 Master of RRS John Biscoe, the ship which assisted the Royal Navy Hydrographic Survey Unit in charting this area in 1963.
Phelps Rock is an insular rock rising 10 m above sea level southwest of Hugo Island, in the west approaches to French Passage, Wilhelm Archipelago. The rock was charted by a Royal Navy Hydrographic Survey Unit from HMS Protector, 1966–67. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Captain Edmund M.S. Phelps, First Officer in John Biscoe, 1966-72, who assisted with the hydrographic survey of the area, 1965–67.
Forsters Passage is a body of water between Bristol Island and Southern Thule in the South Sandwich Islands. In 1775, a British expedition under James Cook gave the name "Forster's Bay", after John R. Forster, a naturalist with the expedition, to what appeared to be a bay in essentially this position. The "bay" was determined to be a strait by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen in 1820.

Mudge Passage is a marine passage running east–west from the vicinity of Prospect Point, Graham Coast, between Beer Island and Dodman Island to the north and Saffery Islands and Trump Islands to the south, to the vicinity of Extension Reef. The passage was navigated and charted by Captain C.R. Elliott in RRS John Biscoe in January 1979. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in association with Harrison Passage and Maskelyne Passage to the northeast, after Thomas Mudge (1715–94), English horologist who made substantial improvements to marine chronometers.
Hamblin Glacier is a glacier flowing to the southeast side of Widmark Ice Piedmont, in Graham Land, Antarctica. It was photographed by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd in 1955–57, and mapped from these photos by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for Theodore Hamblin (1873–1952), an English optician who in the 1930s helped in the evolution of the first satisfactory snow goggle design.
Lord Bank is a submarine bank in the Bellingshausen Sea with a least depth of 18 metres (60 ft) lying west-southwest of the entrance to Quest Channel, Adelaide Island, Antarctica. The bank was surveyed from HMS Endurance in January 1980 and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Captain James Trevor Lord, Royal Navy, the commanding officer of HMS Endurance, 1978–80.
Harrison Passage is a passage between Larrouy Island and Tadpole Island to the west, and the Llanquihue Islands and the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica, to the east. It was photographed by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd in 1956–57, and was mapped from these photos by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for John Harrison, an English horologist who first definitely solved the problem of determining longitude at sea.
Heap Island is an island off the southeast coast of Renaud Island in the Biscoe Islands of the Graham Coast of Antarctica, between Jurva Point and Bates Island. In association with the names of sea-ice specialists grouped in this area, it was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1985 after John A. Heap, a sea-ice specialist with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), 1955–62, who worked in the Antarctic with FIDS, 1955–56, with the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1956–57, and with the United States Antarctic Research Program, 1962–63. He was later head of the Polar Regions Section at the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, and a member of the UK-APC from 1976.
Starshot Glacier is a glacier 50 nautical miles (90 km) long that flows through the Churchill Mountains to enter the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica.
Snubbin Island is an island lying 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) west of Pickwick Island at the western end of the Pitt Islands, in the Biscoe Islands. Shown on an Argentine government chart of 1957. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1959 after Mr. Serjeant Snubbin, a barrister in Charles Dickens' Pickwick Papers.
Thunder Glacier is a through glacier, 4 nautical miles (7 km) long, which extends in an east–west direction across Wiencke Island between Sierra DuFief and the Wall Range, in the Palmer Archipelago. Probably known since the discovery of Wiencke Island by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition in 1898. Charted in 1944 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), and so named by them because a survey party was nearly overwhelmed there by an avalanche.
References
- ↑ "Maskelyne Passage". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 23 August 2013.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Maskelyne Passage". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Maskelyne Passage". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
