
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society c. 1190 in Acre,Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights,having historically served as a crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages,as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe.

The Hospitallers of St Thomas of Canterbury at Acre,usually called the Knights of St Thomas was a Christian military order of the Catholic Church. Membership was restricted to Englishmen.
A military order is a Christian religious society of knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar,the Knights Hospitaller,the Order of the Holy Sepulchre,the Order of Saint James,the Order of Calatrava,and the Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades,in the Holy Land,the Baltics,and the Iberian peninsula;their members being dedicated to the protection of pilgrims and Christians,as well as the defence of the Crusader states. They are the predecessors of chivalric orders.

Raymond du Puy (1083–1160) was a knight from Dauphinéin France and the second Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller,also known as the Order of St. John of Jerusalem,from around 1121 until 1160. Officially,he succeeded Blessed Gerard,the founder of the Order,as Grand Master. While traditionally cited as the direct successor upon Gerard's death in 1118 or 1120,his assumption of the magisterium was in 1121 or 1123 after one or two interim superiors,Pierre de Barcelona and Boyant Roger. Raymond divided the membership of the Order into clerical,military,and serving brothers and established the first significant Hospitaller infirmary near the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem.

Robert IV de Sablé was Lord of Sablé,the eleventh Grand Master of the Knights Templar from 1191 to 1192 and Lord of Cyprus from 1191 to 1192. He was known as the Grand Master of the Knights Templars and the Grand Master of the Holy and Valiant Order of Knights Templars.

Assassin's Creed is a 2007 action-adventure game developed by Ubisoft Montreal and published by Ubisoft. It is the first installment in the Assassin's Creed series. The video game was released for PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360 in November 2007. A Microsoft Windows version titled Assassin's Creed:Director's Cut Edition containing additional content was released in April 2008.

Montfort is a ruined Crusader castle in the Upper Galilee region in northern Israel,about 22 miles (35 km) northeast of the city of Haifa and 10 miles (16 km) south of the border with Lebanon.

Rashid al-Din Sinan also known as the Old Man of the Mountain,was an Arab Muslim missionary who served as the leader of the Nizari Ismaili state and the Order of Assassins from 1162 until his death in 1193. An adherent of Nizari Ismailism,a branch of Shia Islam,he was a prominent figure during the Crusades.

Jean de Villiers was the twenty-second grand master of the Knights Hospitaller,serving from 1285 until 1293. He was elected Grand Master after the death of Nicolas Lorgne. De Villiers was Prior of France beginning in 1282 and he remained in France to deal with existing problems of the Order. Jacques de Taxi became Grand Master ad interim,perhaps through 27 June 1286,while awaiting the arrival of the newly elected Grand Master in the Holy Land. De Villiers was present at the Siege of Acre in 1291,but escaped just before the city fell to the Mamluks. He was succeeded by Odon de Pins.

Assassin's Creed:Altaïr's Chronicles is a 2008 action-adventure video game developed by Gameloft and published by Ubisoft. It is the first spin-off installment in the Assassin's Creed franchise,and a prequel to 2007's Assassin's Creed. Taking place in the year 1190 AD,one year prior to the events of Assassin's Creed,the game revolves around Altaïr Ibn-LaʼAhad's search for an artifact called the Chalice,which brings him into conflict with the Templar Order. Altaïr travels to several cities in the Middle East during the game,including Jerusalem,Acre,and Damascus,as well as Tyre and Aleppo,which are new to the series.

Garnier de Nablus,also known as Garnier of Syria,was the tenth Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller from 1190 to 1192,succeeding Armengol de Aspa. He fought at the Battle of Arsuf in 1191 during the Third Crusade. It was under his magistracy that the headquarters of the Order were transferred from Tyre to Acre. He was succeeded by Geoffroy de Donjon.

Teutonic Knights,a crusading military order for the forced conversion to Catholicism in the Holy Land and the Baltics during the Middle Ages,are often depicted in popular culture.

Assassin's Creed:Bloodlines is a 2009 action-adventure video game developed by Griptonite Games and published by Ubisoft. It is the second spin-off installment in the Assassin's Creed franchise,and acts as a direct sequel to Assassin's Creed (2007). Beginning shortly after that game's events,Bloodlines follows Altaïr Ibn-LaʼAhad as he travels to Cyprus to eliminate the last remnants of the Templar Order and learn more about their plans. The game also explores Altaïr's relationship with Maria Thorpe,a Templar agent whose life he spared in the first game and who would eventually become his wife.
Armand Bouchart was a Knight Templar who commanded a small garrison during the Templar rule of Cyprus in 1192.

Geoffroy de Donjon,also known as or Geoffroy de Duisson, was the eleventhth Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller serving from 1193 through his death in 1202. He succeeded Garnier de Nablus who died in August 1192.

Bertrand de Thessy,also known as Bertrand of Thercy,was the fifteenth Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller,serving between 1228 and 1230 or 1231. He succeeded Guérin de Montaigu upon his death on 1 March 1228. Thessy was either from France or Italy,most likely the former. He was succeeded by Guérin Lebrun.
Jean de Ronay was knight of the Order of Saint John of Jerusalem who was appointed Grand Commander of the Knights Hospitaller by the Grand Master Guillaume de Chateauneuf in 1243 or 1244. He served as interim Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller from 1244 to 1250 during the captivity of de Chateauneuf. He died in battle during the Seventh Crusade.

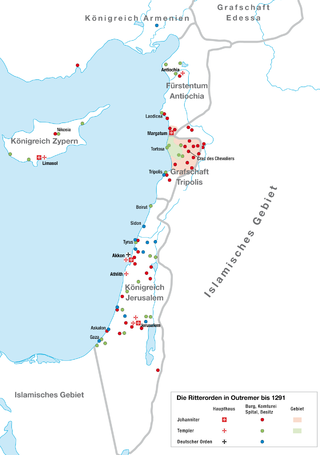
The fall of Outremer describes the history of the Kingdom of Jerusalem from the end of the last European Crusade to the Holy Land in 1272 until the final loss in 1302. The kingdom was the center of Outremer—the four Crusader states—formed after the First Crusade in 1099 and reached its peak in 1187. The loss of Jerusalem in that year began the century-long decline. The years 1272–1302 are fraught with many conflicts throughout the Levant as well as the Mediterranean and Western European regions,and many Crusades were proposed to free the Holy Land from Mamluk control. The major players fighting the Muslims included the kings of England and France,the kingdoms of Cyprus and Sicily,the three Military Orders and Mongol Ilkhanate. Traditionally,the end of Western European presence in the Holy Land is identified as their defeat at the Siege of Acre in 1291,but the Christian forces managed to hold on to the small island fortress of Ruad until 1302.
The history of the Knights Hospitaller in the Levant is concerned with the early years of the Order of the Hospital of St. John of Jerusalem,the Knights Hospitaller,through 1309. The Order was formed in the later part of the eleventh century and played a major role in the Kingdom of Jerusalem,in particular,the Crusades. This lasted until the West was expelled from the Holy Land,with the Order conquering Rhodes in the early fourteenth century. Among the most important internal events of the early years of the kingdom were the foundation of the Military Orders,which included the Hospitallers,the Knights Templar and the Teutonic Order. Unlike the Hospitallers' beginnings as a benevolent organization,the Templars and Teutonic knights began with a military mission. These three major Orders would play a major role in the military activities of the kingdom,sometimes cooperatively,sometimes not. On the battlefield they frequently shared among them the most important tactical roles,the vanguard and rear-guard.
















