
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication.

Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as temporal frequency for clarity and to distinguish it from spatial frequency. Frequency is measured in hertz which is equal to the number of events per second. Ordinary frequency is related to angular frequency by a scaling factor of 2π. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency, f=1/T.

Tracy Lauren Marrow, better known by his stage name Ice-T, is an American rapper working in both the hip hop and heavy metal genres, as well as a songwriter, actor, and producer. He began his career as an underground rapper in the 1980s and was signed to Sire Records in 1987, when he released his debut album Rhyme Pays. The following year, he founded the record label Rhyme $yndicate Records and released another album, Power, which would go platinum. He also released several other albums that went gold.

Mr. T is an American actor. He is known for his roles as B. A. Baracus in the 1980s television series The A-Team and as boxer Clubber Lang in the 1982 film Rocky III. He is also known for his distinctive hairstyle inspired by Mandinka warriors in West Africa, his copious gold jewelry, his tough-guy persona and his catchphrase "I pity the fool!", first uttered as Clubber Lang in Rocky III, then turned into a trademark used in slogans or titles, like the reality show I Pity the Fool in 2006.

In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 treatment, the theory is presented as being based on just two postulates:
- The laws of physics are invariant (identical) in all inertial frames of reference.
- The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer.
T, or t, is the twentieth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is tee, plural tees. It is derived from the Semitic Taw 𐤕 of the Phoenician and Paleo-Hebrew script via the Greek letter τ (tau). In English, it is most commonly used to represent the voiceless alveolar plosive, a sound it also denotes in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second-most commonly used letter in English-language texts.

Thomas Stearns Eliot was a poet, essayist, publisher, playwright, literary critic and editor. He is considered to be one of the 20th century's greatest poets, as well as a central figure in English-language Modernist poetry. His trials in language, writing style, and verse structure reinvigorated English poetry. He is also noted for his critical essays, which often reevaluated long-held cultural beliefs.
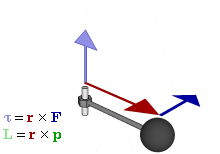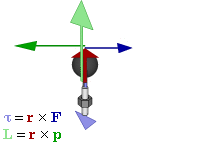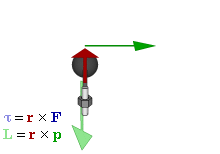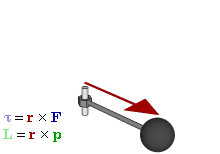
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force. It describes the rate of change of angular momentum that would be imparted to an isolated body.

Tyrannosaurus is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The species Tyrannosaurus rex, often called T. rex or colloquially T-Rex, is one of the best represented theropods. It lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. Tyrannosaurus had a much wider range than other tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of rock formations dating to the Maastrichtian age of the Upper Cretaceous period, 68 to 66 million years ago. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids and among the last non-avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.

Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, respectively, as when they modify current or voltage.

In physics and mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is a transform that converts a function into a form that describes the frequencies present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex-valued function of frequency. The term Fourier transform refers to both this complex-valued function and the mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made the Fourier transform is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical chord into terms of the intensity of its constituent pitches.

Newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws can be paraphrased as follows:
- A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless acted upon by a force.
- When a body is acted upon by a net force, the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass is equal to the net force.
- If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions.

The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by the Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first mass-affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. The relatively low price was partly the result of Ford's efficient fabrication, including assembly line production instead of individual handcrafting. It was mainly designed by three engineers, Joseph A. Galamb, Eugene Farkas, and Childe Harold Wills. The Model T was colloquially known as the "Tin Lizzie".
In linear algebra, an eigenvector or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a constant factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often represented by , is the multiplying factor.

A capacitor is an electronic device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communications networks. The Internet of things encompasses electronics, communication and computer science engineering. Internet of things has been considered a misnomer because devices do not need to be connected to the public internet, they only need to be connected to a network, and be individually addressable.

AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the world's third-largest telecommunications company by revenue and the largest wireless carrier in the United States. As of 2023, AT&T was ranked 13th on the Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations, with revenues of $120.7 billion.

The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per square metre, or pascal-seconds.

T-Mobile US, Inc. is an American wireless network operator headquartered in Overland Park, Kansas, and Bellevue, Washington, U.S. Its largest shareholder is multinational telecommunications company Deutsche Telekom AG, which as of April 2023, holds a 51.4% majority stake in the company. T-Mobile US is the third-largest wireless carrier in the United States, with 116.7 million subscribers at the end of Q2 2023.

Terminator 2: Judgment Day is a 1991 American science fiction action film directed by James Cameron, who co-wrote the script with William Wisher. Starring Arnold Schwarzenegger, Linda Hamilton, Robert Patrick, and Edward Furlong, it is the sequel to The Terminator (1984) and is the second installment in the Terminator franchise. In the film, the malevolent artificial intelligence Skynet sends a Terminator—a highly advanced killing machine—back in time to 1995 to kill the future leader of the human resistance John Connor, when he is a child. The resistance sends back a less advanced, reprogrammed Terminator to protect Connor and ensure the future of humanity.
















