
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR).
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e. in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft.
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as aerospace, which is the general term for Earth's atmosphere and the outer space in its vicinity.

In aviation, visual meteorological conditions (VMC) is an aviation flight category in which visual flight rules (VFR) flight is permitted—that is, conditions in which pilots have sufficient visibility to fly the aircraft maintaining visual separation from terrain and other aircraft. They are the opposite of instrument meteorological conditions (IMC). The boundary criteria between IMC and VMC are known as the VMC minima and are defined by: visibility, cloud ceilings, and cloud clearances.
In aviation, lowest safe altitude (LSALT) is an altitude that is at least 500 feet above any obstacle or terrain within a defined safety buffer region around a particular route that a pilot might fly. The safety buffer allows for errors in the air by including an additional area that a pilot might stray into by flying off track. By flying at or above this altitude a pilot complies with terrain clearance requirements on that particular flight leg.

Flight plans are documents filed by a pilot or flight dispatcher with the local Air Navigation Service Provider prior to departure which indicate the plane's planned route or flight path. Flight plan format is specified in ICAO Doc 4444. They generally include basic information such as departure and arrival points, estimated time en route, alternate airports in case of bad weather, type of flight, the pilot's information, number of people on board, and information about the aircraft itself. In most countries, flight plans are required for flights under IFR, but may be optional for flying VFR unless crossing international borders. Flight plans are highly recommended, especially when flying over inhospitable areas such as water, as they provide a way of alerting rescuers if the flight is overdue. In the United States and Canada, when an aircraft is crossing the Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ), either an IFR or a special type of VFR flight plan called a DVFR flight plan must be filed. For IFR flights, flight plans are used by air traffic control to initiate tracking and routing services. For VFR flights, their only purpose is to provide needed information should search and rescue operations be required, or for use by air traffic control when flying in a "Special Flight Rules Area."
In general aviation, scud running is a practice in which pilots lower their altitude to avoid clouds or instrument meteorological conditions (IMC). The goal of scud running is to stay clear of weather to continue flying with visual, rather than instrument, references. This practice is widely accepted to be dangerous, and has led to death in many cases from pilots flying into terrain or obstacles, such as masts and towers, normally referred to as controlled flight into terrain, or CFIT; however, even instrument-rated pilots sometimes elect to take the risk to avoid icing or embedded thunderstorms in cloud, or in situations where the minimum instrument altitudes are too high for their aircraft.

In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing, or to a point from which a landing may be made visually. These approaches are approved in the European Union by EASA and the respective country authorities and in the United States by the FAA or the United States Department of Defense for the military. The ICAO defines an instrument approach as, "a series of predetermined maneuvers by reference to flight instruments with specific protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if landing is not completed, to a position at which holding or enroute obstacle clearance criteria apply."
In aviation, atmospheric sciences and broadcasting, a height above ground level is a height measured with respect to the underlying ground surface. This is as opposed to height above mean sea level, height above ellipsoid, or height above average terrain. In other words, these expressions indicate where the "zero level" or "reference altitude" - the vertical datum - is located.
Special visual flight rules are a set of aviation regulations under which a pilot may operate an aircraft. It is a special case of operating under visual flight rules (VFR).
The World Geographic Reference System (GEOREF) is a geocode, a grid-based method of specifying locations on the surface of the Earth. GEOREF is essentially based on the geographic system of latitude and longitude, but using a simpler and more flexible notation. GEOREF was used primarily in aeronautical charts for air navigation, particularly in military or inter-service applications, but it is rarely seen today. However, GEOREF can be used with any map or chart that has latitude and longitude printed on it.
An aeronautical chart is a map designed to assist in the navigation of aircraft, much as nautical charts do for watercraft, or a roadmap does for drivers. Using these charts and other tools, pilots are able to determine their position, safe altitude, best route to a destination, navigation aids along the way, alternative landing areas in case of an in-flight emergency, and other useful information such as radio frequencies and airspace boundaries. There are charts for all land masses on Earth, and long-distance charts for trans-oceanic travel.

In United States aviation, a sectional chart, often called sectional for short, is a type of aeronautical chart designed for air navigation under visual flight rules (VFR).
Standard instrument departure (SID) routes, also known as departure procedures (DP), are published flight procedures followed by aircraft on an IFR flight plan immediately after takeoff from an airport.

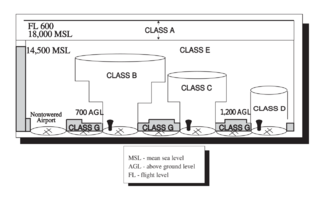
The United States airspace system's classification scheme is intended to maximize pilot flexibility within acceptable levels of risk appropriate to the type of operation and traffic density within that class of airspace – in particular to provide separation and active control in areas of dense or high-speed flight operations.
This article describes the graphic conventions used in Sectional charts and Terminal area charts published for aeronautical navigation under Visual Flight Rules in the United States of America. The charts are published "in accordance with Interagency Air Cartographic Committee specifications and agreements, approved by the Department of Defense and the Federal Aviation Administration".

In air traffic control, separation is the name for the concept of keeping an aircraft outside a minimum distance from another aircraft to reduce the risk of those aircraft colliding, as well as prevent accidents due to secondary factors, such as wake turbulence. Separation can also apply to terrain, obstacles, and controlled airspace, wherein an aircraft must stay at a minimum distance from a block of airspace; as an example, all aircraft must be approved by the controller who "owns" the airspace before the aircraft is approved to enter that sector.
In aviation, an en-route chart is an aeronautical chart that guides pilots flying under instrument flight rules (IFR) during the en-route phase of flight.
There are two types of minimum off-route altitudes (MORAs): the route MORA and the grid MORA. MORAs give at least 1,000 feet altitude clearance above terrain, and 2,000 feet in mountainous terrain.

In the United States and Canada, Victor airways are low-altitude airways. They are defined in straight-line segments, each of which is based on a straight line between either two VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) stations, or a VOR and a VOR intersection, hence the beginning letter V.








