
In meteorology, a cyclone is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above. Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale. Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within the smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone formation and intensification. Extratropical cyclones begin as waves in large regions of enhanced mid-latitude temperature contrasts called baroclinic zones. These zones contract and form weather fronts as the cyclonic circulation closes and intensifies. Later in their life cycle, extratropical cyclones occlude as cold air masses undercut the warmer air and become cold core systems. A cyclone's track is guided over the course of its 2 to 6 day life cycle by the steering flow of the subtropical jet stream.
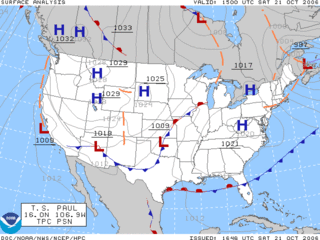
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations.

An Anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above. Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure.
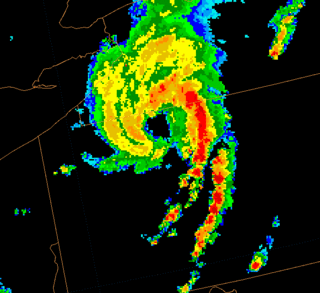
A squall line, or more accurately a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS), is a line of thunderstorms, often forming along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front. Linear thunderstorm structures often contain heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and occasionally tornadoes or waterspouts. Particularly strong straight-line winds can occur where the linear structure forms into the shape of a bow echo. Tornadoes can occur along waves within a line echo wave pattern (LEWP), where mesoscale low-pressure areas are present. Some bow echoes can grow to become derechos as they move swiftly across a large area. On the back edge of the rainband associated with mature squall lines, a wake low can be present, on very rare occasions associated with a heat burst.

In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather, while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places:

In meteorology, the synoptic scale is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1,000 km (620 mi) or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions. Most high- and low-pressure areas seen on weather maps are synoptic-scale systems, driven by the location of Rossby waves in their respective hemisphere. Low-pressure areas and their related frontal zones occur on the leading edge of a trough within the Rossby wave pattern, while high-pressure areas form on the back edge of the trough. Most precipitation areas occur near frontal zones. The word synoptic is derived from the Ancient Greek word συνοπτικός (sunoptikós), meaning "seen together".

The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere.

A derecho is a widespread, long-lived, straight-line wind storm that is associated with a fast-moving group of severe thunderstorms known as a mesoscale convective system.

A polar low is a mesoscale, short-lived atmospheric low pressure system (depression) that is found over the ocean areas poleward of the main polar front in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, as well as the Sea of Japan. The systems usually have a horizontal length scale of less than 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) and exist for no more than a couple of days. They are part of the larger class of mesoscale weather systems. Polar lows can be difficult to detect using conventional weather reports and are a hazard to high-latitude operations, such as shipping and gas and oil platforms. Polar lows have been referred to by many other terms, such as polar mesoscale vortex, Arctic hurricane, Arctic low, and cold air depression. Today the term is usually reserved for the more vigorous systems that have near-surface winds of at least 17 m/s (38 mph).

Cyclogenesis is the development or strengthening of cyclonic circulation in the atmosphere. Cyclogenesis is an umbrella term for at least three different processes, all of which result in the development of some sort of cyclone, and at any size from the microscale to the synoptic scale.

A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For instance, cold fronts can bring bands of thunderstorms and cumulonimbus precipitation or be preceded by squall lines, while warm fronts are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation and fog. In summer, subtler humidity gradients known as dry lines can trigger severe weather. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift.
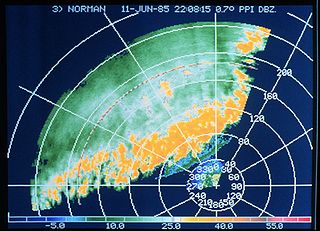
A rainband is a cloud and precipitation structure associated with an area of rainfall which is significantly elongated. Rainbands can be stratiform or convective, and are generated by differences in temperature. When noted on weather radar imagery, this precipitation elongation is referred to as banded structure. Rainbands within tropical cyclones are curved in orientation. Rainbands of tropical cyclones contain showers and thunderstorms that, together with the eyewall and the eye, constitute a hurricane or tropical storm. The extent of rainbands around a tropical cyclone can help determine the cyclone's intensity.

A mesoscale convective system (MCS) is a complex of thunderstorms that becomes organized on a scale larger than the individual thunderstorms but smaller than extratropical cyclones, and normally persists for several hours or more. A mesoscale convective system's overall cloud and precipitation pattern may be round or linear in shape, and include weather systems such as tropical cyclones, squall lines, lake-effect snow events, polar lows, and mesoscale convective complexes (MCCs), and generally forms near weather fronts. The type that forms during the warm season over land has been noted across North and South America, Europe, and Asia, with a maximum in activity noted during the late afternoon and evening hours.

A mesoscale convective complex (MCC) is a unique kind of mesoscale convective system which is defined by characteristics observed in infrared satellite imagery. They are long-lived, often form nocturnally, and commonly contain heavy rainfall, wind, hail, lightning, and possibly tornadoes.
The East Asian Monsoon is a monsoonal flow that carries moist air from the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean to East Asia. It affects approximately one-third of the global population, influencing the climate of Japan, the Korean Peninsula, Taiwan, China, the Philippines and Mainland Southeast Asia but most significantly Vietnam. It is driven by temperature differences between the East Asian continent and the Pacific Ocean. The East Asian monsoon is divided into a warm and wet summer monsoon and a cold and dry winter monsoon. This cold and dry winter monsoon is responsible for the aeolian dust deposition and pedogenesis that resulted in the creation of the Loess Plateau. The monsoon influences weather patterns as far north as Siberia, causing wet summers that contrast with the cold and dry winters caused by the Siberian High, which counterbalances the monsoon's effect on northerly latitudes.

Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone.

A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone, at the leading edge of its cold air advection pattern—known as the cyclone's dry "conveyor belt" flow. Temperature differences across the boundary can exceed 30 °C (54 °F) from one side to the other. When enough moisture is present, rain can occur along the boundary. If there is significant instability along the boundary, a narrow line of thunderstorms can form along the frontal zone. If instability is weak, a broad shield of rain can move in behind the front, and evaporative cooling of the rain can increase the temperature difference across the front. Cold fronts are stronger in the fall and spring transition seasons and are weakest during the summer.

Inflow is the flow of a fluid into a large collection of that fluid. Within meteorology, inflow normally refers to the influx of warmth and moisture from air within the Earth's atmosphere into storm systems. Extratropical cyclones are fed by inflow focused along their cold front and warm fronts. Tropical cyclones require a large inflow of warmth and moisture from warm oceans in order to develop significantly, mainly within the lowest 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) of the atmosphere. Once the flow of warm and moist air is cut off from thunderstorms and their associated tornadoes, normally by the thunderstorm's own rain-cooled outflow boundary, the storms begin to dissipate. Rear inflow jets behind squall lines act to erode the broad rain shield behind the squall line, and accelerate its forward motion.
The following is a glossary of tornado terms. It includes scientific as well as selected informal terminology.

Conditional symmetric instability, or CSI, is a form of convective instability in a fluid subject to temperature differences in a uniform rotation frame of reference while it is thermally stable in the vertical and dynamically in the horizontal. The instability in this case develop only in an inclined plane with respect to the two axes mentioned and that is why it can give rise to a so-called "slantwise convection" if the air parcel is almost saturated and moved laterally and vertically in a CSI area. This concept is mainly used in meteorology to explain the mesoscale formation of intense precipitation bands in an otherwise stable region, such as in front of a warm front. The same phenomenon is also applicable to oceanography.

















