
Mercia was one of the three notable Anglic kingdoms founded after Sub-Roman Britain was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred around the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England.

Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians ruled Mercia in the English Midlands from 911 until her death. She was the eldest daughter of Alfred the Great, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex, and his wife Ealhswith.

Staffordshire is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands County and Worcestershire to the south and Shropshire to the west.

Tamworth is a market town and borough in Staffordshire, England, 14 miles (23 km) north-east of Birmingham and on the West Coast Main Line. The town borders North Warwickshire to the east and north, Lichfield to the north, south-west and west. The M6 Toll runs to the south of the town. It takes its name from the River Tame, which flows through it. The population of Tamworth borough (mid-2019 est.) was 76,696. The wider urban area has a population of 81,964.

Lichfield is a cathedral city and civil parish in Staffordshire, England. Lichfield is situated roughly 18 miles (29 km) south-east of the county town of Stafford, 8.1 miles (13.0 km) south-east of Rugeley, 9 miles (14 km) north-east of Walsall, 7.9 miles (12.7 km) north-west of Tamworth and 13 miles (21 km) south-west of Burton Upon Trent. At the time of the 2011 Census, the population was estimated at 32,219 and the wider Lichfield District at 100,700.
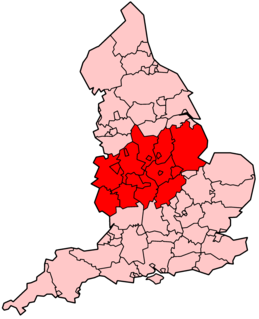
The Midlands are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries. They are split into the West Midlands and East Midlands. The region's biggest city, Birmingham – often considered the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands, – is the second-largest city and metropolitan area in the United Kingdom.

Chad of Mercia was a prominent 7th-century Anglo-Saxon Catholic monk who became abbot of several monasteries, Bishop of the Northumbrians and subsequently Bishop of the Mercians and Lindsey People. He was later canonised as a saint.

Lichfield is a local government district in Staffordshire, England. It is administered by Lichfield District Council, based in Lichfield.

Staffordshire is a landlocked county in the West Midlands of England. It adjoins Cheshire to the north west, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the south east, West Midlands and Worcestershire to the south, and Shropshire to the west. The historic county of Staffordshire includes Wolverhampton, Walsall, and West Bromwich, these three being removed for administrative purposes in 1974 to the new West Midlands authority. The resulting administrative area of Staffordshire has a narrow southwards protrusion that runs west of West Midlands to the border of Worcestershire. The city of Stoke-on-Trent was removed from the admin area in the 1990s to form a unitary authority, but is still part of Staffordshire for ceremonial and traditional purposes.

The Mercian Regiment is an infantry regiment of the British Army, which is recruited from five of the counties that formed the ancient kingdom of Mercia. Known as 'The Heart of England's Infantry', it was formed on 1 September 2007 by the amalgamation of three existing regiments. The Regiment has had fifteen operational deployments since its formation.
The Stafford knot, more commonly known as the Staffordshire knot, is a distinctive three-looped knot that is the traditional symbol of the English county of Staffordshire and of its county town, Stafford. It is a particular representation of the simple overhand knot, the most basic knot of all.

The Saint Alban's Cross is a yellow saltire on a blue field. It is found in several flags, notably that of the Cathedral and Abbey Church of St Alban, previously a Benedictine monastery, and the city of St Albans, Hertfordshire.

The Potteries Museum & Art Gallery is in Bethesda Street, Hanley, one of the six towns of Stoke-on-Trent in Staffordshire. Admission is free.

The Middle Angles were an important ethnic or cultural group within the larger kingdom of Mercia in England in the Anglo-Saxon period.

The Staffordshire Hoard is the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon gold and silver metalwork yet found. It consists of almost 4,600 items and metal fragments, amounting to a total of 5.1 kg (11 lb) of gold, 1.4 kg (3 lb) of silver and some 3,500 pieces of garnet cloisonné jewellery. It is described by the historian Cat Jarman as "possibly the finest collection of early medieval artefacts ever discovered".

Throughout its history the Kingdom of Mercia was a battleground between conflicting religious ideologies.
The Forsbrook Pendant is a piece of Anglo Saxon jewellery found in Forsbrook, Staffordshire, England and sold to the British Museum in 1879. It is a 7th-century setting of a 4th-century gold Roman coin in gold cellwork with garnet and blue glass inlays.

The Acting Witan of Mercia is a political concept based in the Midlands of England. It is the belief that the United Kingdom is in illegal occupation of the ancient English region of Mercia, as a result of the Norman Conquest and the perceived Norman Yoke, and the Acting Witan claims to be its de jure and acting government.

The Staffordshire helmet is an Anglo-Saxon helmet discovered in 2009 as part of the Staffordshire Hoard. It is part of the largest discovery of contemporary gold and silver metalwork in Britain, which contained more than 4,000 precious fragments, approximately a third of which came from a single high-status helmet. Following those found at Benty Grange (1848), Sutton Hoo (1939), Coppergate (1982), Wollaston (1997), and Shorwell (2004), it is only the sixth known Anglo-Saxon helmet.

The Lichfield Angel is an Anglo-Saxon stone carving discovered at Lichfield Cathedral in 2003. It depicts the archangel Gabriel, likely as the left hand portion of a larger plaque showing the annunciation; along with a right-hand panel of the Virgin Mary. The carving is though to be the end piece of a shrine containing the remains of Saint Chad to whom, with Mary, the cathedral is dedicated.



















