The Cenozoic is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66 million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants. It is the latest of three geological eras, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Cenozoic started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor.

The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch 3,000 miles in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in the southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the U.S., its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande rift and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the tectonically younger Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada, which both lie farther to its west.

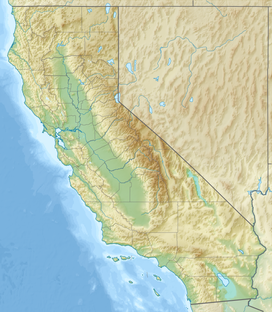
Death Valley National Park is an American national park that straddles the California–Nevada border, east of the Sierra Nevada. The park boundaries include Death Valley, the northern section of Panamint Valley, the southern section of Eureka Valley and most of Saline Valley.

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. Here, the term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain. The general definition used is one followed by the US Geological Survey and the Geologic Survey of Canada to describe the respective countries' physiographic regions. The US uses the term Appalachian Highlands and Canada uses the term Appalachian Uplands..

The Pacific Coast Ranges are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Although they are commonly thought to be the westernmost mountain range of the continental United States and Canada, the geologically distinct Insular Mountains of Vancouver Island lie farther west.

The Front Range is a mountain range of the Southern Rocky Mountains of North America located in the central portion of the U.S. State of Colorado, and southeastern portion of the U.S. State of Wyoming. It is the first mountain range encountered as one goes westbound along the 40th parallel north across the Great Plains of North America.

Mount Mazama is a complex volcano in the western U.S. state of Oregon, in a segment of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and Cascade Range. Most of the mountain collapsed following a major eruption approximately 7,700 years ago. The volcano is in Klamath County, in the southern Cascades, 60 miles (97 km) north of the Oregon–California border. Its collapse, due to the eruption of magma emptying the underlying magma chamber, formed a caldera that holds Crater Lake. The mountain is in Crater Lake National Park. Mount Mazama originally had an elevation of 12,000 feet (3,700 m), but following its climactic eruption this was reduced to 8,157 feet (2,486 m). Crater Lake is 1,943 feet (592 m) deep, the deepest freshwater body in the U.S. and the second deepest in North America after Great Slave Lake in Canada.

The richly textured landscape of the United States is a product of the dueling forces of plate tectonics, weathering and erosion. Over the 4.5 billion-year history of the Earth, tectonic upheavals and colliding plates have raised great mountain ranges while the forces of erosion and weathering worked to tear them down. Even after many millions of years, records of Earth's great upheavals remain imprinted as textural variations and surface patterns that define distinctive landscapes or provinces.

The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries.

The Uinta Mountains are an east-west trending chain of mountains in northeastern Utah extending a short distance into northwest Colorado and slightly into southwestern Wyoming in the United States. As a subrange of the Rocky Mountains, they are unusual for being the highest range in the contiguous United States running east to west, and lie approximately 100 miles (160 km) east of Salt Lake City. The range has peaks ranging from 11,000 to 13,528 feet, with the highest point being Kings Peak, also the highest point in Utah. The Mirror Lake Highway crosses the western half of the Uintas on its way to Wyoming. Utah state highway 44 crosses the east end of the Uintas between Vernal UT and Manila UT.

The Medicine Bow Mountains are a mountain range in the Rocky Mountains that extend 100 miles (160 km) from northern Colorado into southern Wyoming. The northern extent of this range is the sub-range the Snowy Range. From the northern end of Colorado's Never Summer Mountains, the Medicine Bow mountains extend north from Cameron Pass along the border between Larimer and Jackson counties in Colorado and northward into south central Wyoming. In Wyoming, the range sits west of Laramie, in Albany and Carbon counties to the route of the Union Pacific Railroad and U.S. Interstate 80. The mountains often serve as a symbol for the city of Laramie. The range is home to Snowy Range Ski Area.

Nokhu Crags is a rock formation and mountain summit in the Never Summer Mountains range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The name is derived from the Arapaho language, Neaha-no-xhu, meaning "Eagles Nest." The 12,490-foot (3,807 m) peak is located in State Forest State Park, 2.5 miles (4.0 km) south of Cameron Pass in Jackson County, Colorado, United States. The summit lies just northwest of the Continental Divide and Rocky Mountain National Park, near the headwaters of the Michigan River. The peak is prominently visible from State Highway 14 and can be seen throughout the southern North Park basin where it is known also known as "the Crags" or "Sleeping Indian" for its resemblance to the form of a supine chief. To the east lie the shallow basins of Snow Lake and the Michigan or American Lakes; to the north lies a snow filled couloir; to the west the mountain descends directly into the deep waters of Lake Agnes; and to the south lie Static Peak, Mount Richthofen, and the remainder of the Never Summer Mountain Range.
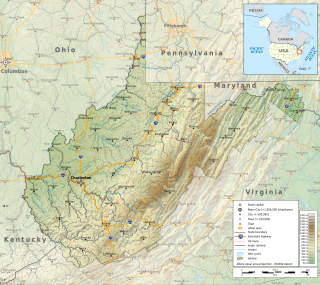
The Environment of West Virginia encompasses terrain and ecosystems ranging from plateaus to mountains. Most of West Virginia lies within the Appalachian mixed mesophytic forests ecoregion, while the higher elevations along the eastern border and in the panhandle lie within the Appalachian-Blue Ridge forests.

Golden Gate Highlands National Park is located in Free State, South Africa, near the Lesotho border. It covers an area of 340 km2 (130 sq mi). The park's most notable features are its golden, ochre, and orange-hued, deeply eroded sandstone cliffs and outcrops, especially the Brandwag rock. Another feature of the area is the numerous caves and shelters displaying San rock paintings. Wildlife featured at the park includes mongooses, eland, zebras, and over 100 bird species. It is the Free State's only national park and is more famous for the beauty of its landscape than for its wildlife. Numerous palaeontology finds have been made in the park, including dinosaur eggs and skeletons.

The geology of the Rocky Mountains is that of a discontinuous series of mountain ranges with distinct geological origins. Collectively these make up the Rocky Mountains, a mountain system that stretches from Northern British Columbia through central New Mexico and which is part of the great mountain system known as the North American Cordillera.

The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition, structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as well as some of its hazards, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and landslides.

The Oregon Coast Range, often called simply the Coast Range and sometimes the Pacific Coast Range, is a mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region, in the U.S. state of Oregon along the Pacific Ocean. This north-south running range extends over 200 miles (320 km) from the Columbia River in the north on the border of Oregon and Washington, south to the middle fork of the Coquille River. It is 30 to 60 miles wide and averages around 1,500 feet (460 m) in elevation above sea level. The coast range has three main sections, a Northern, Central, and Southern.
The South Warner Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area 12 miles (19 km) east of Alturas, California, United States. It encompasses more than 70,000 acres (283 km2) of the Warner Mountains. It is within the Modoc National Forest and managed by the US Forest Service. Elevations range from 5,000 feet (1,500 m) to 9,895 feet at Eagle Peak.

Eucyon is an extinct genus of medium omnivorous coyote-like canid that first appeared in the Western United States during the late Middle Miocene 10 million years ago. It was the size of a jackal and weighed around 15kg. Its species E. zhoui was one of a number of North American mammals which invaded East Asia around 5–6 million years ago, followed by the genus going extinct 3 million years ago. This genus is proposed to have given rise to genus Canis 6 million years ago.

West Beckwith Mountain is a prominent mountain summit in the West Elk Mountains range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The 12,185-foot (3,714 m) peak is located in the West Elk Wilderness of Gunnison National Forest, about 16.5 miles (26.5 km) southwest of Crested Butte in Gunnison County, Colorado, United States.