
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.

Ergoline is a chemical compound whose structural skeleton is contained in a variety of alkaloids, referred to as ergoline derivatives or ergoline alkaloids. Ergoline alkaloids, one being ergine, were initially characterized in ergot. Some of these are implicated in the condition ergotism, which can take a convulsive form or a gangrenous form. Even so, many ergoline alkaloids have been found to be clinically useful. Annual world production of ergot alkaloids has been estimated at 5,000–8,000 kg of all ergopeptines and 10,000–15,000 kg of lysergic acid, used primarily in the manufacture of semi-synthetic derivatives.

Harmaline is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and beta-carbolines. It is the partially hydrogenated form of harmine.
Tropane is a nitrogenous bicyclic organic compound. It is mainly known for a group of alkaloids derived from it, which include atropine and cocaine, among others. Tropane alkaloids occur in plants of the families Erythroxylaceae and Solanaceae.

Ibogaine is a naturally occurring psychoactive substance found in plants in the family Apocynaceae such as Tabernanthe iboga, Voacanga africana, and Tabernaemontana undulata. It is a psychedelic with dissociative properties.

D-Lysergic acid α-hydroxyethylamide, also known as D-lysergic acid methyl carbinolamide, is an alkaloid of the ergoline family, believed to be present in small amounts in various species in the Convolvulaceae (LSA), as well as some species of fungi.

Sceletium tortuosum is a succulent plant commonly found in South Africa, which is also known as Kanna, Channa, Kougoed —which literally means, 'chew(able) things' or 'something to chew'.

Voacangine is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the Voacanga africana tree, as well as in other plants such as Tabernanthe iboga, Tabernaemontana africana, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Tabernaemontana divaricata and Ervatamia yunnanensis. It is an iboga alkaloid which commonly serves as a precursor for the semi-synthesis of ibogaine. It has been demonstrated in animals to have similar anti-addictive properties to ibogaine itself. It also potentiates the effects of barbiturates. Under UV-A and UV-B light its crystals fluoresce blue-green, and it is soluble in ethanol.

Aporphine is an alkaloid with the chemical formula C
17H
17N. It is the core chemical substructure of the aporphine alkaloids, a subclass of quinoline alkaloids. It can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms, (R)-aporphine and (S)-aporphine.
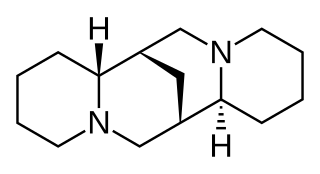
Sparteine is a class 1a antiarrhythmic agent; a sodium channel blocker. It is an alkaloid and can be extracted from scotch broom. It is the predominant alkaloid in Lupinus mutabilis, and is thought to chelate the bivalent cations calcium and magnesium. It is not FDA approved for human use as an antiarrhythmic agent, and it is not included in the Vaughan Williams classification of antiarrhythmic drugs.

Mesembrine is an alkaloid present in Sceletium tortuosum (kanna). It has been shown to act as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (Ki = 1.4 nM), and more recently, has also been found to behave as a weak inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) (Ki = 7,800 nM). Still more recently, in an in vitro study published in 2015, scientist concluded that "a high-mesembrine Sceletium extract exerts its anti-depressant effect by acting primarily as monoamine releasing agent, rather than as selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor." As such, mesembrine likely plays a dominant role in the antidepressant effects of kanna. The levorotatory isomer, (−)-mesembrine, is the natural form.

A serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the neurotransmitter serotonin by blocking the action of the serotonin transporter (SERT). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and, therefore, an increase in serotonergic neurotransmission. It is a type of monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI); other types of MRIs include dopamine reuptake inhibitors and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.

Akuammine (vincamajoridine) is an indole alkaloid. It is the most abundant alkaloid found in the seeds from the tree Picralima nitida, commonly known as akuamma, comprising 0.56% of the dried powder. It has also been isolated from Vinca major. Akuammine is structurally related to both yohimbine, mitragynine and more distantly Voacangine, all of which are alkaloid plant products with pharmacological properties.
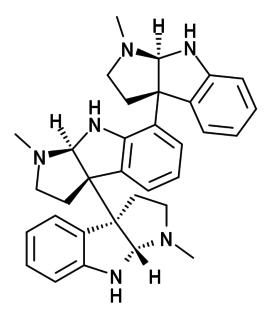
Hodgkinsine is an alkaloid found in plants of the genus Psychotria, particularly Psychotria colorata, although it is also found in Psychotria lyciiflora and probably other species in this family,

Pericine is one of a number of indole alkaloids found in the tree Picralima nitida, commonly known as akuamma. As with some other alkaloids from this plant such as akuammine, pericine has been shown to bind to mu opioid receptors in vitro, and has an IC50 of 0.6 μmol, within the range of a weak analgesic. It may also have convulsant effects.

Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga and Crepe Jasmine. Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Gigactonine is a naturally occurring diterpene alkaloid first isolated from Aconitum gigas. It occurs widely in the Ranunculaceae plant family. The polycyclic ring system of this chemical compound contains nineteen carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom, which is the same as in aconitine and this is reflected in its preferred IUPAC name.

Tortuosamine is an alkaloid found in Sceletium tortuosum.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.



















