
A weather station is a facility, either on land or sea, with instruments and equipment for measuring atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasts and to study the weather and climate. The measurements taken include temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and precipitation amounts. Wind measurements are taken with as few other obstructions as possible, while temperature and humidity measurements are kept free from direct solar radiation, or insolation. Manual observations are taken at least once daily, while automated measurements are taken at least once an hour. Weather conditions out at sea are taken by ships and buoys, which measure slightly different meteorological quantities such as sea surface temperature (SST), wave height, and wave period. Drifting weather buoys outnumber their moored versions by a significant amount.

From May 2 to 8, 1999, a large tornado outbreak took place across much of the Central and parts of the Eastern United States, as well as southern Canada. During this week-long event, 152 tornadoes touched down in these areas. The most dramatic events unfolded during the afternoon of May 3 through the early morning hours of May 4 when more than half of these storms occurred. Oklahoma experienced its largest tornado outbreak on record, with 70 confirmed. The most notable of these was the F5 Bridge Creek–Moore tornado which devastated Oklahoma City and suburban communities. The tornado killed 36 people and injured 583 others; losses amounted to $1 billion, making it the first billion-dollar tornado in history. Overall, 50 people lost their lives during the outbreak and damage amounted to $1.4 billion. For these reasons, the outbreak is known in Oklahoma as the May 3rd outbreak or the Oklahoma tornado outbreak of 1999.

The Storm Prediction Center (SPC) is a US government agency that is part of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), operating under the control of the National Weather Service (NWS), which in turn is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the United States Department of Commerce (DoC).

A derecho is a widespread, long-lived, straight-line wind storm that is associated with a fast-moving group of severe thunderstorms known as a mesoscale convective system.
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs.

A tropical cyclone forecast model is a computer program that uses meteorological data to forecast aspects of the future state of tropical cyclones. There are three types of models: statistical, dynamical, or combined statistical-dynamic. Dynamical models utilize powerful supercomputers with sophisticated mathematical modeling software and meteorological data to calculate future weather conditions. Statistical models forecast the evolution of a tropical cyclone in a simpler manner, by extrapolating from historical datasets, and thus can be run quickly on platforms such as personal computers. Statistical-dynamical models use aspects of both types of forecasting. Four primary types of forecasts exist for tropical cyclones: track, intensity, storm surge, and rainfall. Dynamical models were not developed until the 1970s and the 1980s, with earlier efforts focused on the storm surge problem.

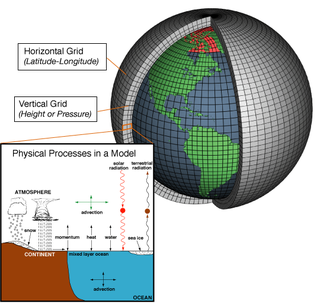
In atmospheric science, an atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive, dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes, heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. The different types of models run are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and nonhydrostatic. Some of the model types make assumptions about the atmosphere which lengthens the time steps used and increases computational speed.

The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Model is a numerical weather prediction (NWP) system designed to serve both atmospheric research and operational forecasting needs. NWP refers to the simulation and prediction of the atmosphere with a computer model, and WRF is a set of software for this. WRF features two dynamical (computational) cores, a data assimilation system, and a software architecture allowing for parallel computation and system extensibility. The model serves a wide range of meteorological applications across scales ranging from meters to thousands of kilometers.
In weather forecasting, model output statistics (MOS) is a multiple linear regression technique in which predictands, often near-surface quantities, are related statistically to one or more predictors. The predictors are typically forecasts from a numerical weather prediction (NWP) model, climatic data, and, if applicable, recent surface observations. Thus, output from NWP models can be transformed by the MOS technique into sensible weather parameters that are familiar to a layperson.
The Great Salt Lake effect is a small but detectable influence on the local climate and weather around the Great Salt Lake in Utah, United States. In particular, snowstorms are a common occurrence over the region and have major socio-economic impacts due to their significant precipitation amounts. The Great Salt Lake almost never freezes and can warm rapidly, which allows lake enhanced precipitation to occur from September through May. Lake-enhanced snowstorms are often attributed to creating what is locally known as "The Greatest Snow on Earth".

In meteorology and climatology, a mesonet, portmanteau of mesoscale network, is a network of automated weather and, often also including environmental monitoring stations, designed to observe mesoscale meteorological phenomena and/or microclimates.

Joseph G. Galway, was an American meteorologist pioneering in the fields of severe convective storm forecasting and research. He was one of the first forecasters for the Severe Local Storms Unit and the National Severe Storms Forecast Center, and developed widely used synoptic predictors associated with severe thunderstorms and tornadoes, such as the jet streak and lifted index.

Ronald William Przybylinski was an American meteorologist who made important contributions to understanding of bow echoes, mesovortices, related quasi-linear convective system (QLCS) structures and processes, as well as QLCS related tornadoes. He also was an expert on technical aspects of weather radar and applications to both operational meteorology and research.

An upper tropospheric cyclonic vortex is a vortex, or a circulation with a definable center, that usually moves slowly from east-northeast to west-southwest and is prevalent across Northern Hemisphere's warm season. Its circulations generally do not extend below 6,080 metres (19,950 ft) in altitude, as it is an example of a cold-core low. A weak inverted wave in the easterlies is generally found beneath it, and it may also be associated with broad areas of high-level clouds. Downward development results in an increase of cumulus clouds and the appearance of circulation at ground level. In rare cases, a warm-core cyclone can develop in its associated convective activity, resulting in a tropical cyclone and a weakening and southwest movement of the nearby upper tropospheric cyclonic vortex. Symbiotic relationships can exist between tropical cyclones and the upper level lows in their wake, with the two systems occasionally leading to their mutual strengthening. When they move over land during the warm season, an increase in monsoon rains occurs.

A wake low, or wake depression, is a mesoscale low-pressure area which trails the mesoscale high following a squall line. Due to the subsiding warm air associated with the system's formation, clearing skies are associated with the wake low. Once difficult to detect in surface weather observations due to their broad spacing, the formation of mesoscale weather station networks, or mesonets, has increased their detection. Severe weather, in the form of high winds, can be generated by the wake low when the pressure difference between the mesohigh preceding it and the wake low is intense enough. When the squall line is in the process of decay, heat bursts can be generated near the wake low. Once new thunderstorm activity along the squall line concludes, the wake low associated with it weakens in tandem.
The Oklahoma Mesonet is a network of environmental monitoring stations designed to measure the environment at the size and duration of mesoscale weather events. The phrase "mesonet" is a portmanteau of the words mesoscale and network.

The history of numerical weather prediction considers how current weather conditions as input into mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather and future sea state has changed over the years. Though first attempted manually in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of the computer and computer simulation that computation time was reduced to less than the forecast period itself. ENIAC was used to create the first forecasts via computer in 1950, and over the years more powerful computers have been used to increase the size of initial datasets and use more complicated versions of the equations of motion. The development of global forecasting models led to the first climate models. The development of limited area (regional) models facilitated advances in forecasting the tracks of tropical cyclone as well as air quality in the 1970s and 1980s.
The Jule G. Charney Award is the American Meteorological Society's award granted to "individuals in recognition of highly significant research or development achievement in the atmospheric or hydrologic sciences". The prize was originally known as the Second Half Century Award, and first awarded to mark to fiftieth anniversary of the society.

Project NIMROD was a meteorological field study of severe thunderstorms and their damaging winds conducted by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It took place in the Greater Chicago area from May 15 to June 30, 1978. Data collected was from single cell thunderstorms as well as mesoscale convective systems, such as bow echoes. Using Doppler weather radars and damage clues on the ground, the team studied mesocyclones, downbursts and gust fronts. NIMROD was the first time that microbursts, very localized strong downdrafts under thunderstorms, were detected; this helped improve airport and public safety by the development of systems like the Terminal Doppler Weather Radar and the Low-level windshear alert system.
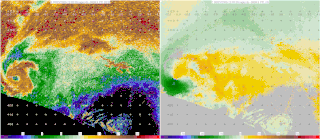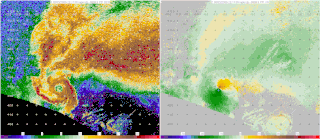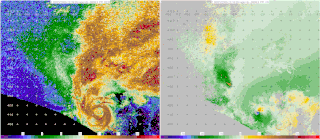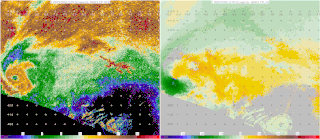
Starting in the mid-1900s, mobile radar vehicles were being used for academic and military research. In the late 1900s, mobile doppler weather radars were designed and created with the goal to study atmospheric phenomena.















