
Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.

Manitoba is a province of Canada at the longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's fifth-most populous province, with a population of 1,342,153 as of 2021. Manitoba has a widely varied landscape, from arctic tundra and the Hudson Bay coastline in the north to dense boreal forest, large freshwater lakes, and prairie grassland in the central and southern regions.

Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of 1,230,000 km2 (470,000 sq mi). It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. It is an inland marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. The Hudson Strait provides a connection between the Labrador Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the northeast, while the Foxe Channel connects Hudson Bay with the Arctic Ocean in the north. The Hudson Bay drainage basin drains a very large area, about 3,861,400 km2 (1,490,900 sq mi), that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay.

The Nelson River is a river of north-central North America, in the Canadian province of Manitoba. The river drains Lake Winnipeg and runs 644 kilometres (400 mi) before it ends in Hudson Bay. Its full length is 2,575 kilometres (1,600 mi), it has mean discharge of 2,370 cubic metres per second (84,000 cu ft/s), and has a drainage basin of 1,072,300 square kilometres (414,000 sq mi), of which 180,000 square kilometres (69,000 sq mi) is in the United States.

The Saskatchewan River is a major river in Canada. It stretches about 550 kilometres (340 mi) from where it is formed by the joining of the North Saskatchewan River and South Saskatchewan River just east of Prince Albert, Saskatchewan. It flows roughly eastward across Saskatchewan and Manitoba to empty into Lake Winnipeg. Through its tributaries the North Saskatchewan and South Saskatchewan, its watershed encompasses much of the prairie regions of Canada, stretching westward to the Rocky Mountains in Alberta and north-western Montana in the United States.
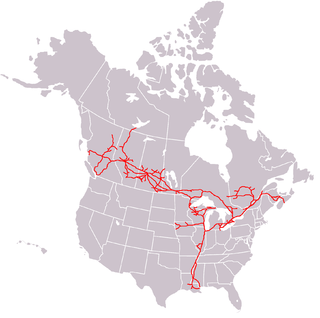
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.

Via Rail Canada Inc., operating as Via Rail or Via, is a Canadian Crown corporation that operates intercity passenger rail service in Canada.

Churchill is a subarctic port town in northern Manitoba, Canada, on the west shore of Hudson Bay, roughly 140 km (87 mi) from the Manitoba–Nunavut border. It is most famous for the many polar bears that move toward the shore from inland in the autumn, leading to the nickname "Polar Bear Capital of the World" and to the benefit of its burgeoning tourism industry.

Northern Manitoba is a geographic and cultural region of the Canadian province of Manitoba. Originally encompassing a small square around the Red River Colony, the province was extended north to the 60th parallel in 1912. The region's specific boundaries vary, as "northern" communities are considered to share certain social and geographic characteristics, regardless of latitude.

The Cape Breton and Central Nova Scotia Railway is a short line railway that operates in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. CBNS operates of main line and associated spurs between Truro in the central part of the province to Point Tupper on Cape Breton Island.

Hudson Bay Railway is a Canadian short line railway operating over 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) of track in northeastern Saskatchewan and northern Manitoba.

Petroleum production in Canada is a major industry which is important to the overall economy of North America. Canada has the third largest oil reserves in the world and is the world's fourth largest oil producer and fourth largest oil exporter. In 2019 it produced an average of 750,000 cubic metres per day (4.7 Mbbl/d) of crude oil and equivalent. Of that amount, 64% was upgraded from unconventional oil sands, and the remainder light crude oil, heavy crude oil and natural-gas condensate. Most of the Canadian petroleum production is exported, approximately 600,000 cubic metres per day (3.8 Mbbl/d) in 2019, with 98% of the exports going to the United States. Canada is by far the largest single source of oil imports to the United States, providing 43% of US crude oil imports in 2015.

The Huron Central Railway is a railway operating in northern Ontario, Canada. It is operated by Genesee & Wyoming Canada, the Canadian subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming.

The Port of Churchill is a privately-owned port on Hudson Bay in Churchill, Manitoba, Canada. Routes from the port connect to the North Atlantic through the Hudson Strait. As of 2008, the port had four deep-sea berths capable of handling Panamax-size vessels for the loading and unloading of grain, bulk commodities, general cargo, and tanker vessels. The port is connected to the Hudson Bay Railway, which shares the same parent company, and cargo connections are made with the Canadian National Railway system at HBR's southern terminus in The Pas. It is the only port of its size and scope in Canada that does not connect directly to the country's road system; all goods shipped overland to and from the port must travel by rail.

Highway 9 is a paved, undivided provincial highway in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It runs from North Dakota Highway 8 at the US border near Port of Northgate until it transitions into Provincial Road 283 at the Manitoba provincial boundary.
The Saskota Flyway is known as the International Road to Adventure, because it takes you from Hudson Bay, Saskatchewan, all the way south to Bismarck, North Dakota.

Petroleum transport is the transportation of petroleum and derivatives such as gasoline (petrol). Petroleum products are transported via rail cars, trucks, tanker vessels, and pipeline networks. The method used to move the petroleum products depends on the volume that is being moved and its destination. Even the modes of transportation on land such as pipeline or rail have their own strengths and weaknesses. One of the key differences are the costs associated with transporting petroleum though pipeline or rail. The biggest problems with moving petroleum products are pollution related and the chance of spillage. Petroleum oil is very hard to clean up and is very toxic to living animals and their surroundings.

In rail transport, the U.S. DOT-111 tank car, also known as the TC-111 in Canada, is a type of unpressurized general service tank car in common use in North America. Tank cars built to this specification must be circular in cross section, with elliptical, formed heads set convex outward. They have a minimum plate thickness of 7⁄16 inch (11.1 mm) and a maximum capacity of 34,500 US gallons. Tanks may be constructed from carbon steel, aluminum alloy, high alloy steel, or nickel plate steel by fusion welding.

Lake Athapapuskow is a glacial lake in Manitoba and Saskatchewan, Canada, located 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) southeast of Flin Flon, Manitoba. The lake is in the Hudson Bay drainage basin and is the source of the Goose River.
Arctic Gateway Group LP is a limited partnership that owns and operates the Port of Churchill and the Hudson Bay Railway, which connects The Pas to Churchill, Manitoba. It was originally formed as a public-private partnership; with a fifty percent share held by Missinippi Rail, a consortium of northern Manitoba First Nations and local governments, and the private share split between Toronto-based Fairfax Financial Holdings and Regina-based grains company AGT Food and Ingredients. Fairfax and AGT transferred their shares of Arctic Gateway to OneNorth in March 2021, meaning that Arctic Gateway is completely owned by the local governments and Indigenous partners.
The Ponton train derailment, near Ponton, Manitoba on September 15, 2018, fatally injured train conductor Kevin Anderson, injured the train's engineer, and triggered a spill of diesel fuel.

















